www.free-education.in is a platform where you can get pdf notes from 6th to 12th class notes, General Knowledge post, Engineering post, Career Guidelines, English Speaking Trick, How to crack an interview and lots more. ( Classification of Elements Notes and NCERT Solution )
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 3 | Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties |
| 3.1 | Why do we Need to Classify Elements ? |
| 3.2 | Genesis of Periodic Classification |
| 3.3 | Modern Periodic Law and the present form of the Periodic Table |
| 3.4 | Nomenclature of Elements with Atomic Numbers > 100 |
| 3.5 | Electronic Configurations of Elements and the Periodic Table |
| 3.6 | Electronic Configurations and Types of Elements: s-, p-, d-, f – Blocks |
| 3.7 | Periodic Trends in Properties of Elements |
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Notes
Introduction
It is always easy to distinguish the items from one another by sorting them on some basis. In malls or in shops we always get the things sorted at their respective places. In shops kids wear can be bought from kid section which cannot be found in any other section. Grocery shops also align the items in a systematic way.
There are all total 92 well known naturally occurring elements of which 70 are metals and remaining 20 are the non-metals. There are certain elements possessing the characteristics of both metals as well as non-metals. They are termed as metalloids. For instance, boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, tellurium, and polonium.


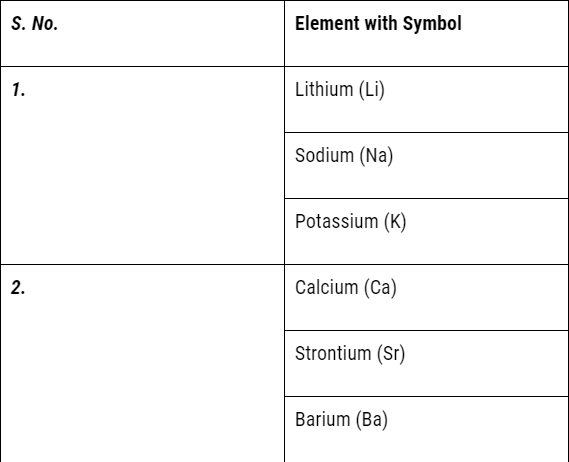
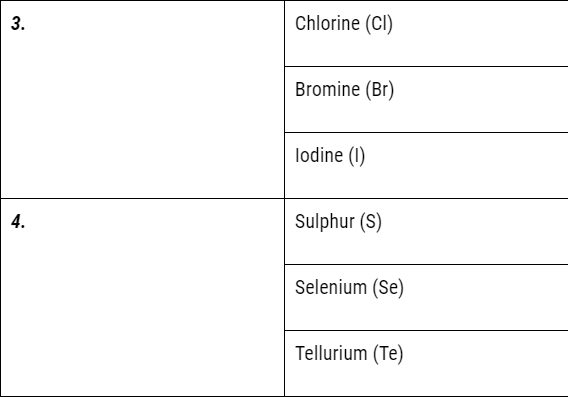
But it could not exist for long because of the following limitations:
- Döbereiner’s triads could find only three triads; .i.e total of 9 elements only but actually there were many more elements known at that time.
- Therefore Dobereiner’s could not classify most of the elements known at that time.

Limitations of Newlands’ law of octaves
- Newlands assumed that only 56 elements existed in nature and no more elements would be further discovered in the nearer future. But later on several new elements were discovered, whose properties couldn’t be defined as per the Law of Octaves.
- In order to fit elements into law of octaves Newlands not only adjusted two elements
in the same slot but also adjusted some unlike elements under the same note. - Cobalt and nickel are in the same slot and are positioned in the same column with fluorine, chlorine and bromine possessing different properties than these elements.
- Iron possessing similar properties as cobalt and nickel, is placed far away from these elements.
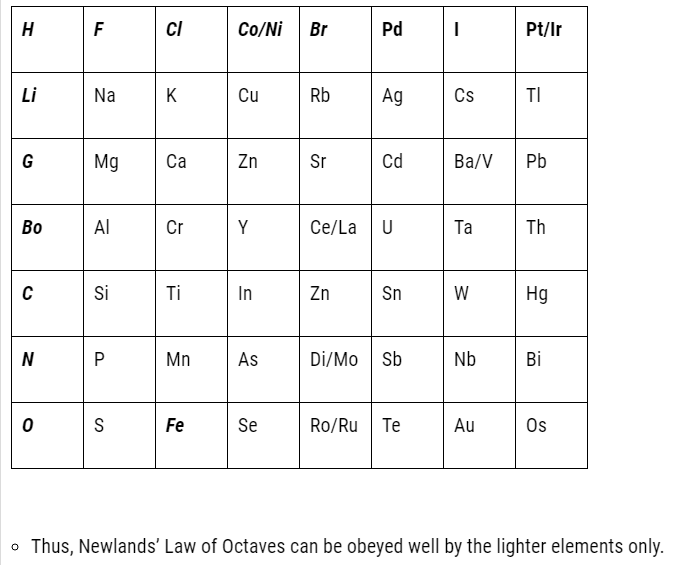
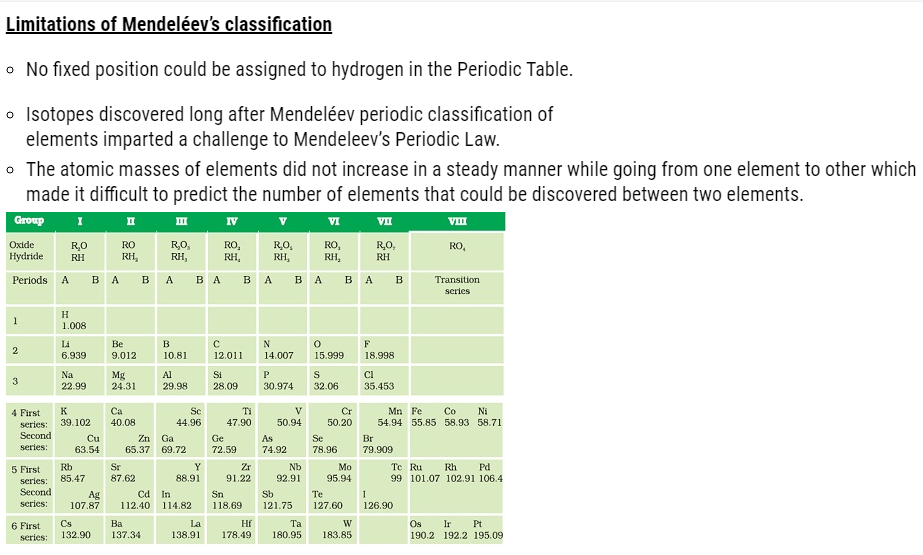
Mendeléev’s periodic table ( Classification of Elements )
- In Mendeléev’s periodic table only 63 elements were arranged that were examined on the basis of the relationship between the atomic masses of elements
and their physical and chemical properties. - Hydrogen and oxygen were selected due to their high reactivity and formation of compounds with most elements giving rise to hydrides and oxides that were treated as one of the basic properties of an element.
- Properties of 63 elements were written on 63 cards and then the elements with similar properties were sorted.
- Most of the elements were arranged in the order of their increasing atomic masses in the Periodic Table with the occurrence of periodic recurrence of elements with similar physical and chemical properties.
- As per the arrangement of elements Mendeléev formulated a Periodic Law stated as ‘the properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic masses’.
- The Periodic Table consists of vertical columns termed as ‘groups’ and horizontal rows termed as ‘periods’.
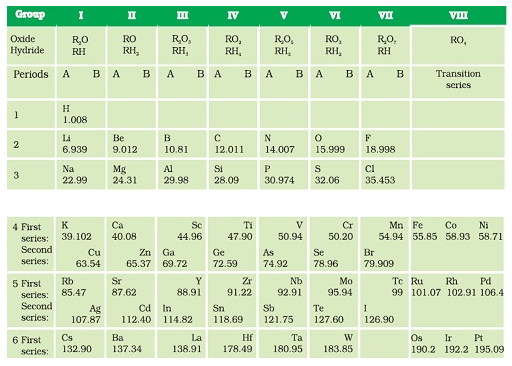
Achievements of Mendeléev’s periodic table ( Classification of Elements )
- element with a slightly greater atomic mass were placed
before an element with a slightly lower atomic mass with an inverted sequence so as to group the elements with similar properties. For example, cobalt with atomic mass 58.9 was placed before nickel with atomic mass 58.7. - He left some gaps in the Periodic Table with the prediction of
existence of some elements that were not discovered at that time. - He named the future elements by prefixing a Sanskrit numeral, Eka (one) to the name of preceding element in the same group.
- For instance, scandium, gallium and germanium, discovered later, have properties
similar to Eka–boron, Eka–aluminium and Eka–silicon, respectively. - Noble gases like helium (He), neon (Ne) and argon (Ar) were discovered
later as they are present in exceptionally low concentrations in the atmosphere due to their inertness.

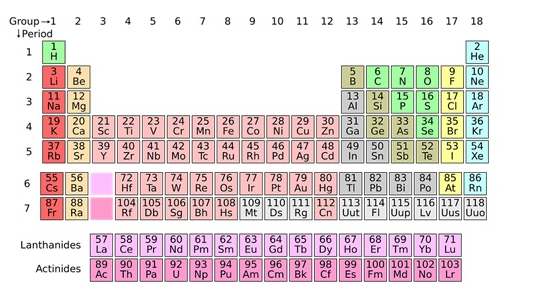
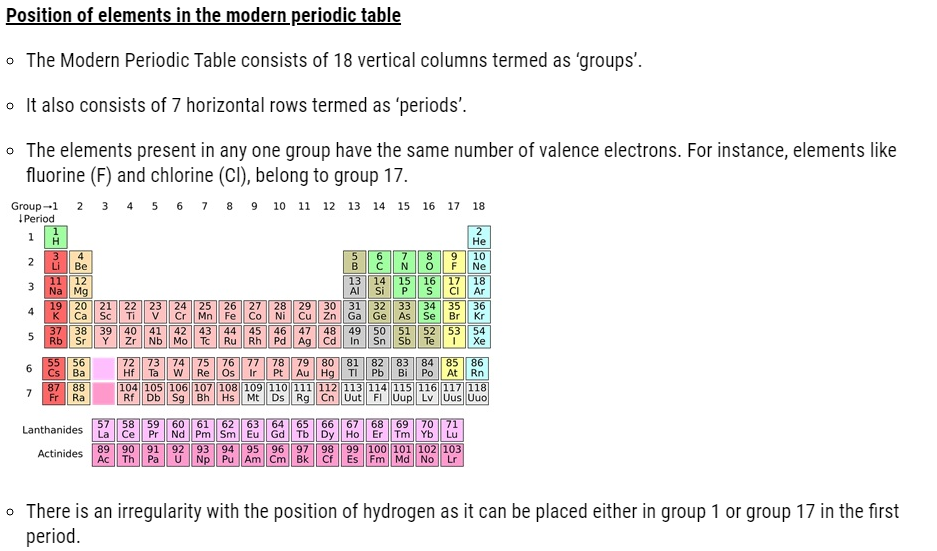

Trends in the modern periodic table ( Classification of Elements )
- The number of shells increases on going down the group.
- The number of valence shell electrons increases with the increase in atomic number on moving from left to right in a period with each period marking the filling of a new electronic shell.
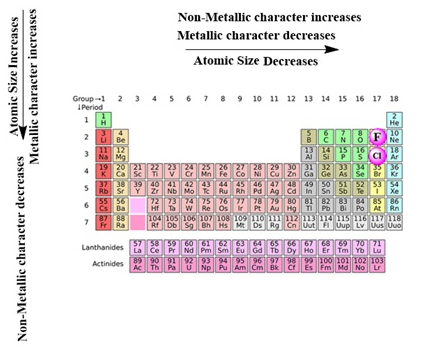
- Atomic size decreases in moving from left to right along a period due to an increase in nuclear charge pulling the electrons closer to the nucleus.
- Addition of new shells down the group increases the distance between the outermost electrons and the nucleus thereby increasing the atomic size down the group.
- Across a period effective nuclear charge acting on the valence shell electrons increases which decreases the tendency to lose electrons. Hence metallic character decreases and non-metallic character increases across a period.
- Down the group, the effective nuclear charge decreases which increases the tendency to lose electrons. Hence metallic character increases and non-metallic character decreases down a group.
Related link you must like:-
Study material for Competition Exam
Mohd. Sharif Qualification: B.Tech (Mechanical Engineering) [Founder of Wisdom Academy] [Aim Foundation & Free-Education.In] [Engineer By Profession | Teacher By Choice] [Blogger, YouTube Creator]






