Introduction
The potential energy of a body is the energy possessed by a body by virtue of its position relative to others, stresses within it, electric charge, and other factors. Examples of mechanical potential energy are throwing a ball in air, a tightened spring etc. Work done in throwing ball and keeping spring tightened gets stored in the form of potential energy which gets converted into kinetic energy once the ball lands on the ground or the spring is released.
Conservative Forces
When one form of energy gets converted to another completely on application or removal of external force, the forces are said to be conservative. Examples of conservative forces are sum of kinetic and potential energies working on a body, spring and gravitational force, coulomb force between two stationary charges, etc.
Electrostatic Potential
Electrostatic potential at a point is the work done by the external force in bringing a charge from infinity to that point.


- The quantity of potential difference is more physically significant than actual value of potential energy.
WRP = ΔU = UP – UR
(UP +α)-(UR +α) = UP– UR , the arbitrary α has no effect on potential energy difference
If the initial point is at infinity, W∞P = ΔU = UP– U∞
U∞is usually considered as 0, so W∞P = ΔU = UP
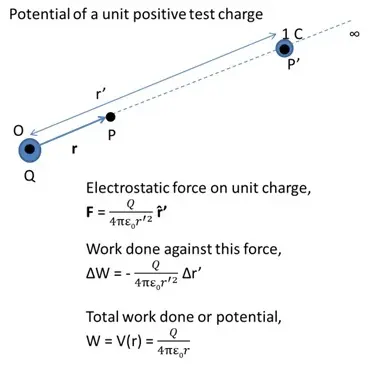
Electrostatic Potential due to a Point Charge
The electrostatic potential in bringing a unit positive test charge from infinity to a point P against repulsive force of another positive charge is always positive.
- If the charge Q is negative, the potential is also negative as the test charge will have a force of attraction.
- Electrostatic potential is inversely proportional to r and electrostatic field is inversely proportional to square of r.

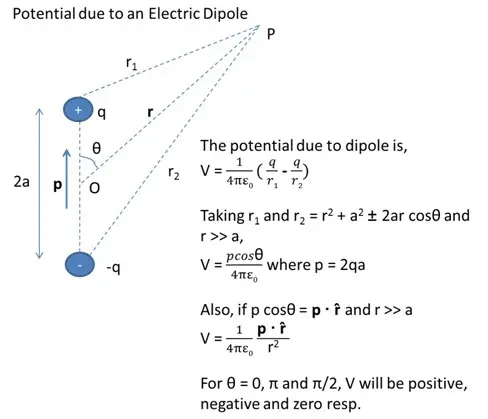
Electrostatic Potential due to an Electric Dipole
An electric dipole is an arrangement of two equal and opposite charges separated by a distance 2a. The dipole moment is represented by p which is a vector quantity.
- The potential due to a dipole depends on r (distance between the point where potential is calculated and the mid-point of the dipole) and angle between position vector r and dipole moment p.
- Dipole potential is inversely proportional to square of r.
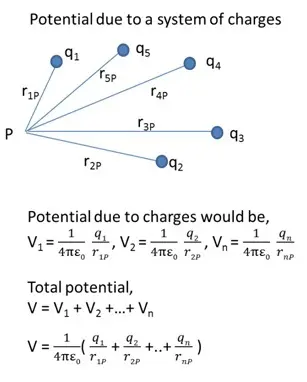
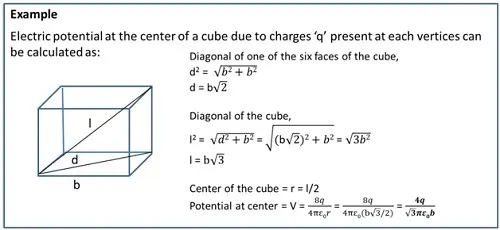
Electrostatic Potential due to a system of charges
For a number of charges present in space, the total potential at a point due to all those charges will be equal to the sum of individual potential of each charge at that point.

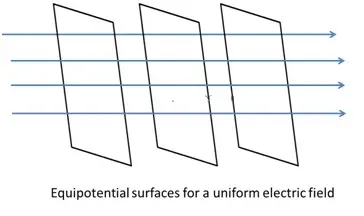
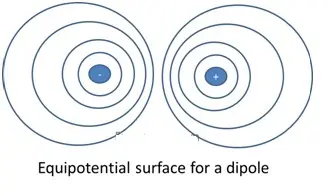
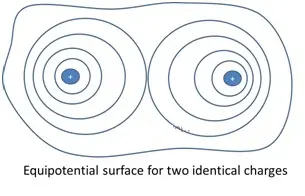
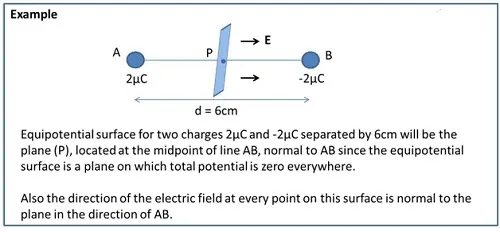
Equipotential Surfaces
An equipotential surface is one where the potential is same at every point on the surface. For a single charge,
- Since r is constant, the equipotential surfaces are concentric spherical surfaces centered at the charge.
- Electric field lines are radial starting from or ending at the charge for positive and negative charges respectively.

Relation between electric field and potential
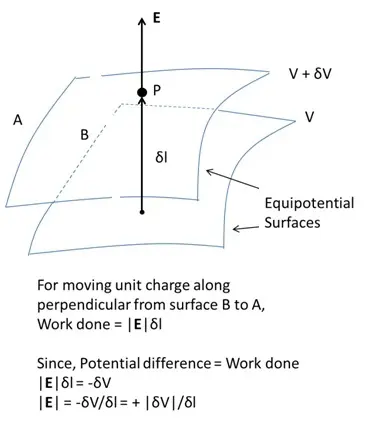
According to the relation between electric field and potential,
- Electric field is in the direction in which the potential decreases steepest.
- Its magnitude is given by the change in the magnitude of potential per unit displacement normal to the equipotential surface at the point.
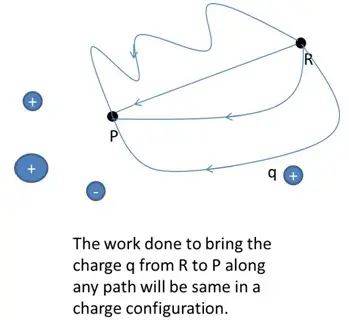
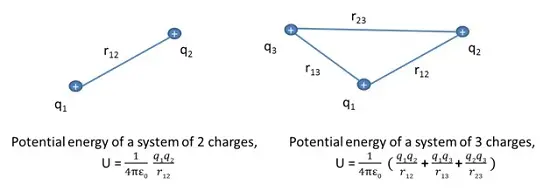
Potential Energy of a system of charges
The potential energy is characteristic of the current state of configuration and not the way how this configuration was achieved.
The potential for a system of charges is calculated as below:
- Potential energy for the first charge is considered as zero which is brought from infinity to a point having no external repulsive forces (no other charges present in the space).
- Bringing another charge will face attractive or repulsive force from the first charge and the work done to bring it from infinity to the point is stored in the form of potential energy.
- Similarly, all further charges being brought from infinity will face attractive or repulsive force from all other charges present in the space.
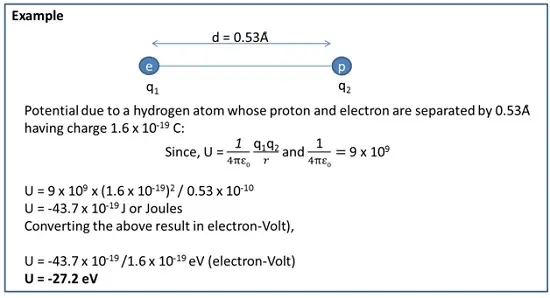
Potential Energy of point charge in an external field
When the potential energy of charge(s) is calculated in an external field, following things are understood:
- The electric field, E, is produced by external sources which are fixed and may be unknown.
- The charge q does not affect these external sources.
- Potential energy of the external sources is ignored.
| Potential Energy of a single charge | Potential energy of a system of two charges |
| qV(r) r– position vectorV(r) – external potential at point r | q1V(r1) + q2V(r2) + q1q2/(4πε0r12)r1&r2– position vectorsV(r1) & V(r2) – external potential at point r1&r2 |
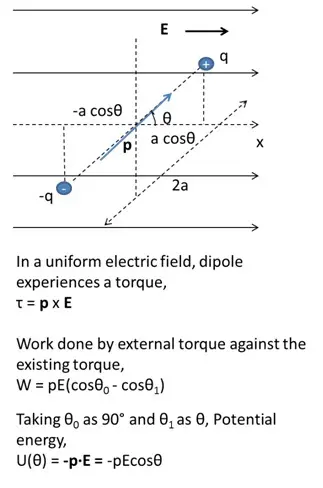
Potential Energy of a dipole in an external field
Dipole in an external field experiences a torque which tries to align it in the direction of the electric field. The work done to oppose this force gets stored in the form of potential energy.