Introduction to Conductors
A conductor is an object or type of material that allow the flow of electrical current in one or more directions. A metal wire is a common electrical conductor.
- Conductors contain mobile charge carriers in the form of electrons.
- The valence electrons facilitate the flow of current in a conductor.
- Examples of conducting materials are Human body, Metallic objects, water etc.
Electrostatics of Conductors
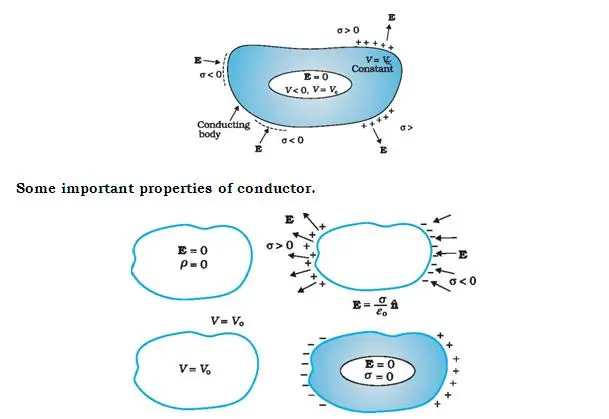
Conductors have loosely bound electrons to allow current to flow. In an external electric field, they drift against the direction of the field. The electrostatic field at different points in a conductor is given below.
- Inside Conductor
- The electrostatic field inside the conductor is zero.
- Under no external electric field or static condition, the charge carriers are distributed evenly and there is no electric field inside.

At the surface of a charged conductor
- The electrostatic field at the surface of a charged conductor is normal to the surface at every point.
- For a non-normal Electric field, there is a non-zero component along the normal. Therefore, Electric field should have no tangential component in static.
- Interior of a conductor
- There is no electrostatic field in the interior of the conductor. All the excess charge resides at the surface.
- Under static conditions, the excess charge resides at the surface of the conductor. On a closed surface, the electrostatic field is zero. So from gauss’s law, there is no net charge enclosed by the surface.
- Throughout the Volume of the conductor
- The Electrostatic potential is constant throughout the volume of the conductor and is equal to its value on surface.
- Since, conductor has no tangential component; no work is done in moving charge within conductor and on its surface. Hence the potential is constant.
Electrostatic Shielding
Electric field inside a cavity in a conductor is always zero. Even if the conductor is charged or charges are induced on a neutral conductor by an external field, all charges reside only on the outer surface of the conductor. Hence, the any cavity of any shape and size is always shielded from outer electric influence. This is called electrostatic shielding.
Dielectrics
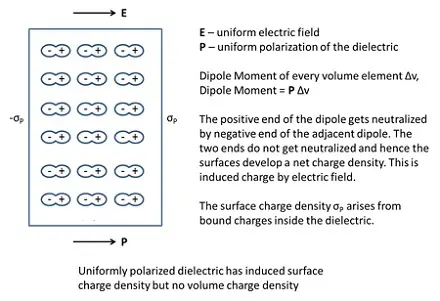
Dielectrics are non-conducting substances having negligible number of charge carriers. In presence of an external electric field, dipole moments are induced in dielectrics by stretching and re-orienting the molecules of the dielectric. The collective dipole moment is the net charge on the surface of dielectric which opposes and reduces (does not cancel) the external field.
Some of the dielectric materials are:
- Porcelain (ceramic), mica, glass, plastics, and the oxides of various metals.
- Some liquids and gases
- Dry air
- Distilled water
- Vacuum
Polar and Non-Polar Molecules
When multiple atoms are bonded to each other, a molecule is formed. These bonds or electron sharing arrangement can be polar (when electrons are shared unequally) and non-polar (when electrons are shared equally).
- Various substances may have polar and non-polar molecules depending upon the charge configuration inside them.
- A substance can be polarized from an external electric field which leads to development of induced dipole moment inside them.
| Criteria | Polar | Non-Polar |
| Centers of positive and negative charges | The centers are separated even in the absence of external electric field | The centers coincide |
| Dipole Moment | Permanent dipole moment | No permanent dipole moment |
| Examples | Hydro Chloric Acid (HCl) and Water (H2O) | Oxygen(O2) and Hydrogen(H2) |
| Dielectrics in External Electric Field | The individual dipole moments tend to align with the field. They develop a net dipole moment in the direction of the field. | Positive and negative charges get displaced. They develop an induced dipole moment as a restoring force against the direction of electric field. |
Polarization of dielectrics
A dielectric develops a net dipole moment in the presence of an external field.The dipole moment per unit volume is called polarization and is denoted by P. For linear isotropic dielectrics (substances where induced dipole moment is in the direction of the field and is proportional to the field strength),
P = χe E
χe – electric susceptibility of the dielectric medium
Capacitors and Capacitance
A capacitor is a system of two conductors separated by an insulator.
- The total charge of a capacitor is zero while the conductors have charge Q and –Q.
- A single conductor can be considered as capacitor with other conductor at infinity.
- Electric field in the region between the conductors is proportional to the charge Q.
- Capacitanceis denoted by, C = Q/V. It depends on:
- Geometrical configuration (shape, size, separation) of the system of two conductors.
- Nature of insulator/dielectric separating
- Charge on the capacitor leaks away due to reduction in the insulating power of the intervening medium. This happens due to higher potential difference causing strong electric fields.
- Maximum electric field which a dielectric medium can withstand without breakdown and prevent leaking of charge is called dielectric strength. Air dielectric strength is 3 x 106 Vm-1.
- SI unit of capacitance is F (Farad).

Parallel Plate Capacitor
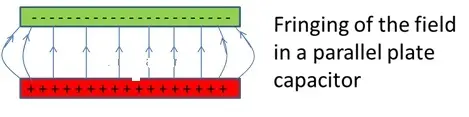
A parallel plate capacitor is a capacitor with 2 large plane parallel conducting plates separated by a small distance.
- Electric field inside the capacitor has a direction from positive to negative plate.
- For very small‘d’, the electric field is considered as uniform. For large‘d’, the electric field is non-uniform and it bends around the corners of the plate which is called fringing of the field.


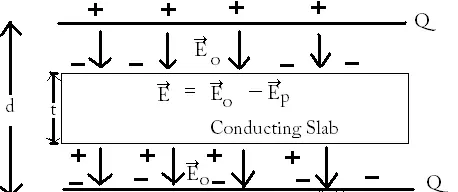
Effect of dielectric on Capacitance
When a dielectric is present between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor fully occupying the region, the dielectric is polarized by the electric field. The surface charge densities are considered as σp and -σp.
Dielectric constant of a substance is the factor by which the capacitance increases from its vacuum value, when the dielectric is fully inserted in between the plates of the capacitor

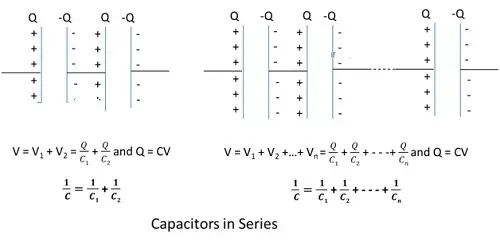
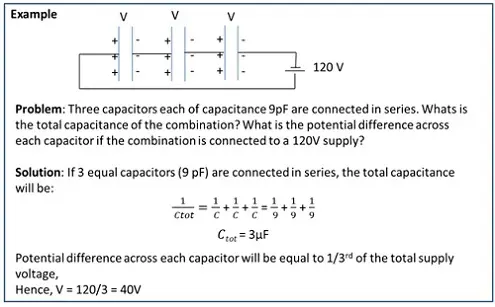
Combination of Capacitors – Series
Capacitors are said to be connected in serieswhen the second plate of a capacitor is connected to the first plate of the next capacitor and so on.
- Capacitors are connected in series as per the below diagram.
- The charge across the arrangement will remain the same.
- The total potential drop is the sum of individual potential drops across each capacitor.
- The inverse of total capacitance is the sum of inverse of individual capacitances.
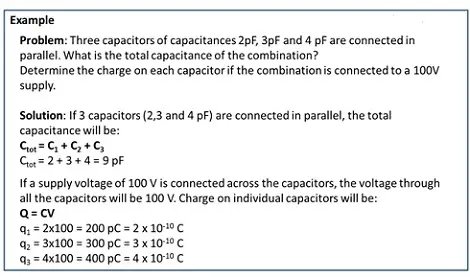
Combination of Capacitors – Parallel
Capacitors are said to be connected in parallel when the firstand second plate of a capacitor is connected to the first and second plate of the next capacitor respectively.
- Capacitors are connected in parallel as per the below diagram.
- The potential across the arrangement will remain the same.
- The total charge is the sum of individual charges across each capacitor.
- The total capacitance is sum of individual capacitances.

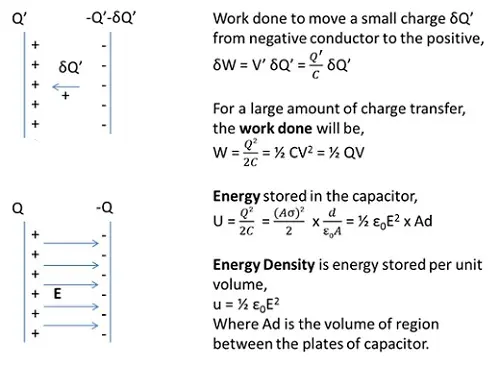
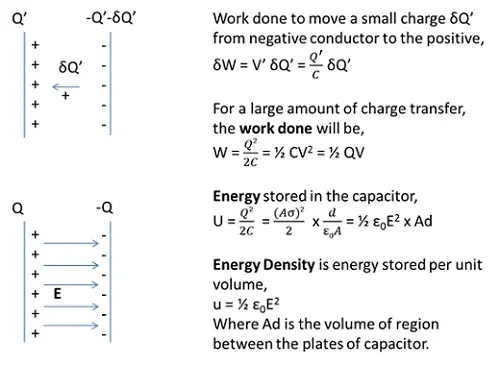
Energy stored in a Capacitor
Energy is stored in the capacitor when work is done to move a positive charge from negative conductor towards the positive conductor against the repulsive force.




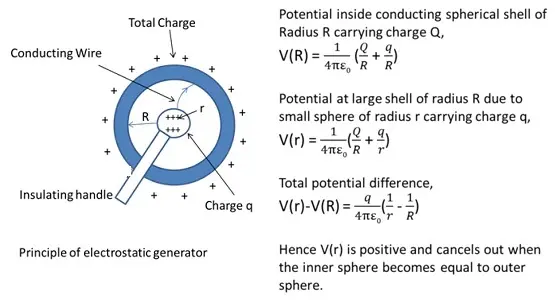
VAN DE GRAAFF Generator
Van de graaff generator is used to generate high voltages of the order of a few million volts. This results in generation of large electric fields for experimental purposes.
Principle