Automobile Interview Question : Preparing for an interview in the field of automobile engineering can be a daunting task. It’s important to have a good understanding of the industry and be familiar with common interview questions that may be asked. In this blog post, we will discuss the top 100 automobile engineering interview questions and provide detailed answers to help you prepare for your next interview.
Technical Interview Question for Automobile Engineering : Automobile Interview Questions
1. What is the difference between diesel and petrol engines?
Diesel and petrol engines have several differences. The main difference lies in the ignition process. Diesel engines use compression ignition, where fuel is compressed and ignited by the heat generated by compression. Petrol engines, on the other hand, use spark ignition, where fuel is ignited by a spark plug.
2. What is the function of a catalytic converter?
A catalytic converter is an important component of a vehicle’s exhaust system. Its main function is to reduce the harmful emissions produced by the engine. It converts harmful gases, such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, into less harmful substances, like carbon dioxide and nitrogen.
3. What is the role of a suspension system in an automobile?
The suspension system in an automobile plays a crucial role in providing a comfortable and safe ride. It helps to absorb shocks and vibrations from the road surface, ensuring that the tires maintain contact with the road at all times. It also helps to maintain vehicle stability and control.
Automobile Interview Questions
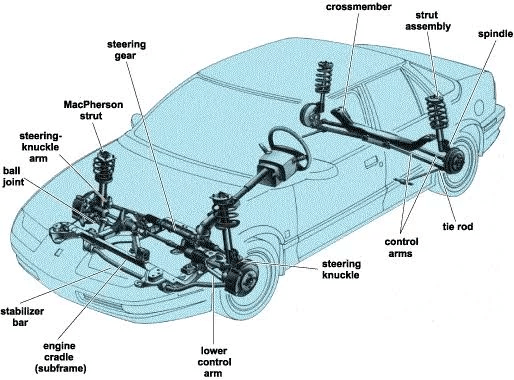
4. What is the components of a suspension system in an automobile?
A car’s suspension system consists of various components that work together to ensure a smooth and stable ride while also providing control and handling. Here are the primary components of a suspension system in a car:
- Springs:
- Springs are fundamental components of a car’s suspension system, responsible for absorbing shocks and vibrations from the road. They help maintain tire contact with the road surface and contribute to ride comfort. Two common types of springs used in cars are coil springs and leaf springs.
- Coil Springs: These are spiral-shaped springs made of steel or other materials. They compress and expand to absorb shocks and maintain the vehicle’s ride height.
- Leaf Springs: Leaf springs consist of multiple layers of curved metal strips stacked on top of each other. They are commonly used in the rear suspension of trucks and some older car models.
- Shock Absorbers (Dampers): Shock absorbers, often referred to simply as dampers, work in conjunction with springs to control the movement of the suspension. They dampen and reduce the oscillations of the springs, preventing the car from bouncing excessively after hitting bumps or irregularities in the road.
- Control Arms (A-arms): Control arms, also known as A-arms, connect the suspension system to the car’s frame or body. They play a critical role in controlling the motion of the wheels. Most vehicles have upper and lower control arms, which help maintain proper wheel alignment and facilitate smooth wheel movement.
- Sway Bar (Stabilizer Bar): The sway bar, or stabilizer bar, connects the left and right wheels on the same axle. Its purpose is to reduce body roll during cornering, thereby improving the car’s stability and handling. When the car tilts during a turn, the sway bar transfers some of the load from one wheel to the other.
- Bushings and Bearings: Bushings are rubber or polyurethane components that isolate vibrations and noise from the suspension system. They are found at various points, such as the control arms. Bearings are used to facilitate smooth rotation in components like wheel hubs.
- Struts: Struts are a type of suspension component commonly used in the front suspension of many modern cars. They combine the functions of a shock absorber and a structural support for the suspension. Struts typically include a coil spring encased in a structural housing.
- Torsion Bars: Torsion bars are a type of spring used in some vehicles, especially trucks and SUVs. They store and release energy by twisting along their length, providing support and ride comfort.
- Air Springs (Airbags): High-end vehicles and certain trucks use air springs (also known as airbags) that can be adjusted electronically to vary the car’s ride height and stiffness. Inflating or deflating these airbags allows the suspension to adapt to different driving conditions.
- Suspension Bushings: Suspension bushings are made of rubber or polyurethane and are used to isolate vibrations while allowing controlled movement of suspension components. They can be found in various locations within the suspension system.
Understanding these components is essential for car engineers, mechanics, and enthusiasts as they design, maintain, and optimize the suspension system to ensure a balance between ride comfort, handling, and safety in automobiles.
Transgender man becomes a bodybuilder to overcome his insecurities 1 month deca results black bodybuilder with huge cock fuck a white gym guy5. What are the different types of brakes used in automobiles?
There are several types of brakes used in automobiles, including disc brakes, drum brakes, and regenerative brakes. Disc brakes use calipers to squeeze brake pads against a rotor, creating friction and slowing down the vehicle. Drum brakes use brake shoes and drums to achieve the same result. Regenerative brakes, commonly used in hybrid and electric vehicles, use the electric motor to slow down the vehicle and convert kinetic energy into electrical energy.
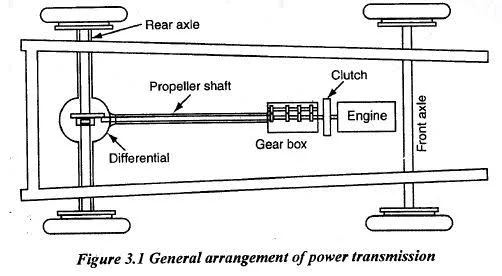
6. What is the purpose of a differential?
A differential is a device that allows the wheels of a vehicle to rotate at different speeds. It is commonly used in rear-wheel-drive vehicles to enable smooth cornering. Without a differential, the wheels would be forced to rotate at the same speed, making it difficult to turn.
7. What is the role of an alternator in a vehicle?
An alternator is responsible for generating electrical power in a vehicle. It converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, which is used to power the vehicle’s electrical system and recharge the battery.
8. What is the purpose of a transmission?
A transmission is a device that transmits power from the engine to the wheels of a vehicle. It allows the driver to change gears and control the speed and torque of the vehicle. It also helps to multiply engine torque to improve vehicle performance.
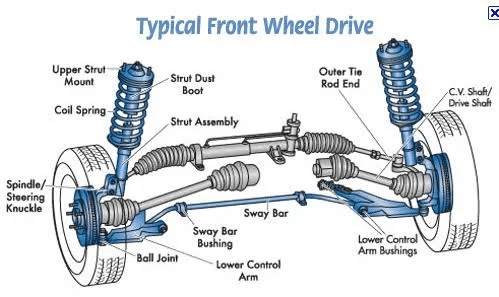
9. What is the difference between front-wheel drive and rear-wheel drive?
In a front-wheel-drive vehicle, power is transmitted to the front wheels, which are responsible for both steering and propelling the vehicle. In a rear-wheel-drive vehicle, power is transmitted to the rear wheels, which are responsible for propelling the vehicle. Rear-wheel drive offers better acceleration and handling, while front-wheel drive provides better traction in slippery conditions.
10. What is the function of an engine control unit (ECU)?
The engine control unit (ECU) is a computer that controls various aspects of the engine’s operation, such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and emission control. It receives input from various sensors and makes adjustments to optimize engine performance and efficiency.
11. What are the safety features in modern automobiles?
Modern automobiles are equipped with a wide range of safety features to protect occupants in the event of a collision. These include seat belts, airbags, anti-lock braking systems (ABS), electronic stability control (ESC), and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) like lane departure warning and adaptive cruise control.
12. How will you differentiate between two stroke engine and four stroke engines?
| TWO STROKE ENGINE | FOUR STROKE ENGINE |
| 2-stroke piston engine has an intake and an exhaust stroke. All air, fuel, and combustion products must be moved in those 2 strokes. | A 4-stroke engine has a separate stroke for moving burned (or burning) and unburned mixtures – intake, compression, expansion, and exhaust. Using 4-stroke results in cleaner emissions at the expense of specific power. |
| A 2-stroke engine completes a power cycle in two strokes of the piston, | while a 4-stroke engine completes it in four strokes. |
| 2-stroke engine: Combustion occurs every revolution of the crankshaft. | 4-stroke engine: Combustion occurs every two revolutions of the crankshaft. |
| 2-stroke engines are simpler, lighter, and have higher power-to-weight ratio. | 4-stroke engines are more fuel-efficient and have better emissions control. |
| But two stroke is powerful than four stroke. | Four stroke is highly efficient than two stroke. |
| Examples: 2-stroke – chainsaws, motorcycles. | Examples: cars, trucks. |
13. How does the thermostat work?
When the engine temperature is too low, the thermostat closes the main valve, cutting off the flow to the radiator. When the engine becomes too hot, the primary valve opens to allow regular circulation of coolant via the radiator.
14. Why we not use 2 stroke engine?
Because of their greater emissions, worse fuel efficiency, and shorter lifespan, two-stroke engines are rarely used.
- When compared to 4 stroke engines, 2 stroke engines emit greater pollution.
- They are less fuel efficient because they use more gasoline each power stroke.
- The lubricating mechanism of two-stroke engines is inefficient, resulting in a reduced engine lifespan.
- Some motorcycles, chainsaws, and outboard motors are still powered by two-stroke engines.
15. Why we use 4 stroke engine?
Automobiles employ four-stroke engines because of their efficiency, power production, and low emissions.
- When compared to two-stroke engines, four-stroke engines use less fuel.
- They produce more power since they have independent intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes.
- Because they have a designated exhaust stroke, four-stroke engines emit fewer emissions.
- Automobiles powered by four-stroke engines include cars, trucks, motorbikes, and buses.
16. What is BS standard in India?
BS stands for Bharat Stage, which is the Indian government’s car emission standards:-
- In India, BS standards are used to regulate pollution emissions from vehicles.
- These regulations are based on European emission norms.
- Each stage of BS standards establishes tougher limitations on pollutant emissions like as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter.
- The goal of BS regulations is to improve air quality and reduce vehicular emissions.
- For example, in 2017, BS-IV standards were adopted, requiring automobiles to fulfil tougher pollution regulations than the prior BS-III standards.
17. Difference between petrol and diesel engine?
Spark ignition is used in gasoline engines, while compression ignition is used in diesel engines.
- RPMs are higher in petrol engines, whereas torque is higher in diesel engines.
- Diesel engines are heavier and noisier, but petrol engines are lighter and quieter.
- Petrol engines accelerate faster, whereas diesel engines consume less fuel.
- Diesel engines emit more NOx and particulate matter than petrol engines.
- Diesel engines are better suited for larger cars and heavy-duty purposes, whilst petrol engines are better suited for smaller vehicles.
18. What is S.I. and C.I. engine?
The S.I stand for Spark Ignition engine while C.I represent for Compression Ignition engine.
- The spark plug in a S.I engine ignites the fuel-air combination, whereas compression in a C.I engine ignites the fuel.
- S.I engines are utilized in petrol vehicles, whilst C.I engines are used in diesel vehicles.
- In comparison to C.I engines, S.I engines have poorer efficiency and higher emissions.
- Petrol engines used in cars and motorcycles are examples of S.I engines, while diesel engines used in trucks and buses are instances of C.I engines.
19. About engine and basic components of an automobile.
The engine contributes to the vehicle’s self-propulsion. Which consists primarily of the law of energy conservation.Chemical energy is converted into thermal energy, which is then converted into rotary motion…parts such as pistons, crankshafts, camshafts, piston pins, connecting rods, valves, and so on….
20. What is Hybrid engine vehicle?
A hybrid engine vehicle combines two or more power sources, most commonly an internal combustion engine with an electric motor.
- Hybrid automobiles replenish their batteries through regenerative braking.
- They can run on an internal combustion engine, an electric motor, or both.
- Hybrid engines increase fuel economy while decreasing pollution.
- Toyota Prius, Honda Insight, and Ford Fusion Hybrid are examples of hybrid vehicles.
A hybrid engine vehicle/hybrid vehicle is a type of vehicle that contains two power sources. Typically, an IC engine and an electric motor are used. Based on the conditions under which the vehicle is operated, these can operate separately or in tandem.
21. What is automobile engine? Brief description.
An automobile engine is a device that converts fuel into mechanical energy to power the vehicle.
- An automobile engine is the heart of a vehicle, responsible for generating power to propel the vehicle forward.
- It works on the principle of internal combustion, where fuel is burned inside the engine to produce energy.
- There are different types of automobile engines, such as gasoline engines, diesel engines, and electric motors.
- The engine consists of various components, including cylinders, pistons, crank shafts, valves, and a fuel injection system.
- The engine’s power output is measured in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW).
- For example, a V6 engine has six cylinders arranged in a V shape, while a four-cylinder engine has four cylinders in a straight line.
- Modern automobile engines are designed to be more fuel-efficient, environmentally friendly, and technologically advanced.
- Engine performance can be enhanced through turbocharging, supercharging, or hybrid technology.
22. What is Vernier caliper?
A Vernier Caliper may have a minimum count of 0.02 mm (Least Count). It is widely used for precisely determining the outside diameters of shafts. thicknesses of various pieces.
A Vernier calliper is a measuring tool that is used to accurately measure an object’s internal and external dimensions.
- There are two scales, one fixed and one movable.
- The movable scale moves together with the main scale and can be locked into place.
- Engineering, machining, and scientific research all use it.
- It is capable of measuring length, depth, and thickness.
- For example, measuring the diameter of a bolt or the thickness of a metal sheet.
23. What happens if gasoline is used in a Diesel engine? Diesel engine will work?
No, because the compression ratio of a petrol engine is 6 to 10 and that of a diesel engine is 15 to 22. As a result of such tremendous compression, petrol becomes severely compressed and may explode.
24. What does it mean when your car emits white smoke?
White smoke, as well as creamy brownish oil, indicate a coolant leak. This could be caused by a faulty head gasket or a broken block. Oil smoke is typically more bluish in colour. White smoke is commonly connected with a coolant leak, although it can also be caused by burning oil.
Automobile Interview Questions
25. How air conditioners work in cars?
Air conditioners work on the principles of evaporation, condensation, compression, and expansion. The heated air from the car is evacuated via evaporation, and then condensation of the evaporated air occurs, which is subsequently compressed by the compressor and finally expanded to us in the form of a cold breeze. The energy required to evacuate the hot air and then compress and expand reduces the average of the car in some way.
26. What do you understand by CC of engine?
CC stands for cubic centimeters. It represents the engine cylinder’s overall volume. This represents the fact that engines with higher CC can produce greater power than other engines. CC can also be thought of as being inversely proportional to fuel usage.
27. Explain the significance of governor in automobiles?
A governor is a key component of an automobile engine. It is used to regulate the engine’s main speed when the load changes. Fuel supply has to be maintained throughout variations in load. The governor is in handling this responsibility. When there is a large load on the engine, the speed falls, so the fuel supply must be increased to increase the power, and when the load decreases, the fuel supply must be decreased.
28. What is oil grade SAE stands for?
“SAE” stands for “SOCIETY OF AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERS” (USA).
29. By mixing oil in fuel of four stroke bike will it damage engine, performance? If not than what happen?
Yes, without a doubt. It can wear and tear on the cylinder liners and piston, as well as piston damage. It can also cause knocking and detonation, where irregular combustion occurs and the engine produces dark smoke and a harsh sound.
30. Why are car steering wheels round?
- A steering wheel is round so that your hands stay in the same spot no matter which way the steering wheel is turned.
- It is the most ergonomic design for turning and guiding the car.
- Also, because the design is round, there are no edges to collide with while turning or steering because the circle location remains constant.
- From the standpoint of design, it should be able to provide uniform force, i.e. torque, by adjusting the distance from the centre.
31. Why big tyre used in rear of Tractors?
Tractors have large rear tyres because the surface area of the tractor’s wheels touching the ground increases pulling force. Tractor pullers, for example, have huge tyres.
Another advantage is that the tractor does not have to run at a higher speed to get the same ground speed as larger tyres. Because of the larger tyres, gear ratios do not need to be as high.
32. What will happen if someone adds oil to the fuel of four stroke bike engine?
Mixing oil with the fuel in a four-stroke engine is a bad idea because it will harm the engine. When you add oil, it will cause the cylinder liner and piston to wear out more quickly, and it can even damage the piston.
Due to this some unusual and harmful things happening inside the engine, like strange fires & loud noises. So, it is important not to mix oil with the fuel in a four-stroke engine.
33. What is SAE? Mention the importance of SAE to the automobile domain.
Full form of SAE stands for the Society of Automotive Engineers.
SAE make rules for how all kinds of vehicles are built, like cars, boats, trucks and airplanes.
SAE has rules for vehicles that go on the ground and ones that fly in the sky.
SAE help & support students who are learning about engineering, technology, science and math.
SAE has been sharing technical information since 1906.
34. State the function of flywheel in IC engine.
Function of Flywheel :- A flywheel controls the speed variations caused by the fluctuation of the engine turning moment during each cycle of operation.
A flywheel used as a reservoir, which stores energy during the period when the supply of energy is more than the requirement, and releases it during the period when the requirement of energy is more than the supply.
35. What Are Airbags in a Car and How Do They Work?
In an automobile, airbags are designed to protect the driver and front-seat passenger in case of a collision. in the majority of instances, these inflatable bags are hidden under the front dashboard and steering wheel.
In the 1950s, an industrial engineer was involved in an accident that made him understand cars needed a piece of safety equipment. Engineers have since tried to figure out how to create a “safety cushion assembly” for a car. Within a short time, the prototype was adopted, and the usage of airbags in automobiles became common.
Airbags are cushions inside cars that inflate when the car is hit in the front to protect the people inside. Initially, cars had front airbags, but later, side airbags were added. Both types of airbags have saved lives, reducing driver fatalities by 29% and front-seat passenger fatalities by 32% with frontal airbags. Side airbags have also made a big difference in reducing risks.
Airbags in a car have special sensors that can tell how hard a crash is. They only inflate really fast if the crash is really bad.
People might wonder if using the emergency brake makes the airbags inflate. The answer is no. They only inflate if the crash is very severe, like more than 20 times the force of gravity.
So, the car’s airbag system relies on a sensor called an accelerometer. It takes about 12 to 20 milliseconds for the front airbag to start coming up, and then it takes around 60-65 milliseconds to fully inflate.
36. What is the car insurance claim process for own damage car or vehicle ?
In September 2019, the Insurance Regulatory Development Authority of India (IRDAI) made it mandatory for insurance companies to offer a special type of insurance called “Own-Damage Insurance” as a separate policy.
Here are the steps to follow when you want to claim insurance for car damage:
- Step 1: Notify Your Insurance Company : When an incident occurs, get in touch with your insurance company to report it and provide information about the damage to your car. It’s crucial to be completely honest and transparent with them, as withholding information can complicate the resolution process and lead to disputes.
- Step 2: Report an FIR to the Police : In case of significant incidents like theft, car accidents, or fires, it’s crucial to promptly file a First Information Report (FIR) with the police. However, for minor scrapes and dents where no third party is involved, an FIR may not be necessary. It’s important to assess the situation and involve the police when required to ensure a smooth insurance claim process.
- Step 3: Use Photographic Proof : Take numerous photos of the accident scene and the damage to your vehicle. Clear, well-documented images are essential for your own damage insurance provider to evaluate the extent of the damage and process your claim accurately.
- Step 4: Provide the Insurance Company with the Necessary Documents: For your claim, you’ll need to provide documents like insurance policy copy, FIR, owner’s license, driver’s car registration, and other necessary paperwork.
- Step 5: Fix Your Car : You can choose to get your car fixed at a shop or ask your insurance company to cover the repair costs. If they approve, you’ll be reimbursed for your loss.
- Step 6: Claim Settlement Process: With cashless claim settlement, repair costs go to the network garage after the surveyor’s report. For reimbursement, you submit repair receipts, but remember you’ll likely have a deductible.
37. What are Documents Required to Claim Car Insurance For Own Damage ?
To settle a reimbursement claim for damaged cars, you’ll need these documents: insurance contract (Policy), FIR report (if required), signed claim form, vehicle registration (RC), driver’s license, repair cost estimates, medical receipts (for injuries), and receipts for additional costs.
38. List of Insurance of Company who provide motor Insurance.
- Bajaj Allianz General Insurance Company Limited
- IFFCO Tokio General Insurance Company Limited
- National Insurance Company Limited
- The New India Assurance Company Limited
- The Oriental Insurance Company Limited
- Reliance General Insurance Company Limited
- Liberty General Insurance Company Limited
- SBI General Insurance Company Limited
- Universal Sompo General Insurance Company Limited
- HDFC Ergo General Insurance Company Limited
- TATA AIG General Insurance Company Limited
- ICICI Lombard General Insurance Company Limited
- United India Insurance Company Limited
- Royal Sundaram General Insurance Company Limited
- Cholamandalam MS General Insurance Company Limited
- Future Generali India Insurance Company Limited
- Shriram General Insurance Company Limited
- Raheja QBE General Insurance Company Limited
- Magma HDI General Insurance Company Limited
- Kotak Mahindra General Insurance Company Limited
- DHFL General Insurance Company Limited
- Acko General Insurance Company Limited
- Go Digit General Insurance Company Limited
39. List the car body part names.
Following are the main parts of car body:
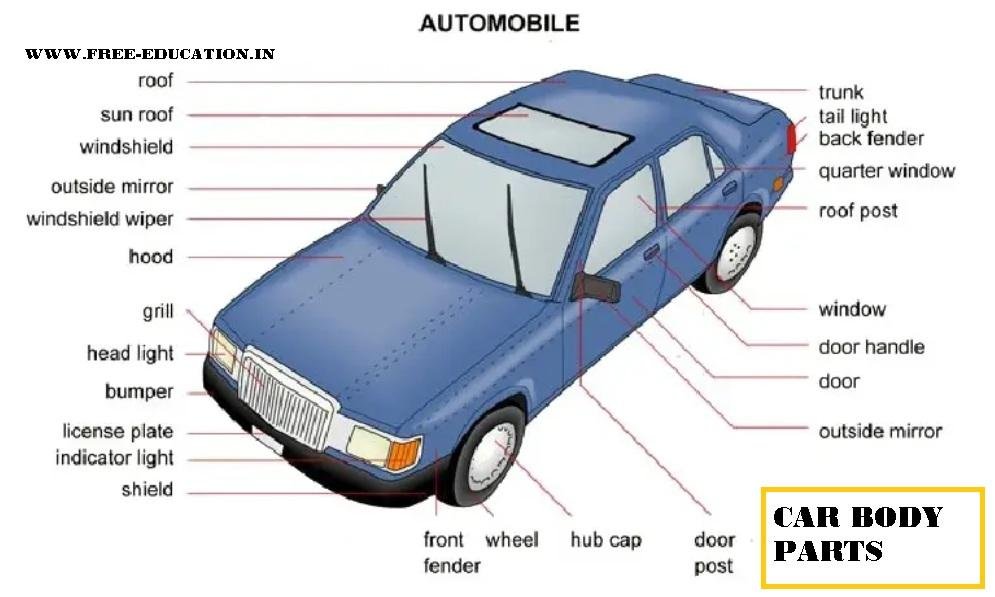
- Body shell
- Hood or bonnet
- Front bumper
- Rear bumper
- Bumper grille
- Crash guard or bull bar
- Head light
- Fog lamp
- Indicator lights
- Wiper blade
- Radiator
- Radiator supports
- Cowl panel
- Quarter panel
- Fender
- Fender liners
- Roof
- Sunroof
- Mirrors
- Doors
- Door handle
- Window glass
- Quarter window
- Trunk or deck-lids
- Mud flaps
- Wheels
- Hubcap
- Dashboard
- Number plate
- Tail lights
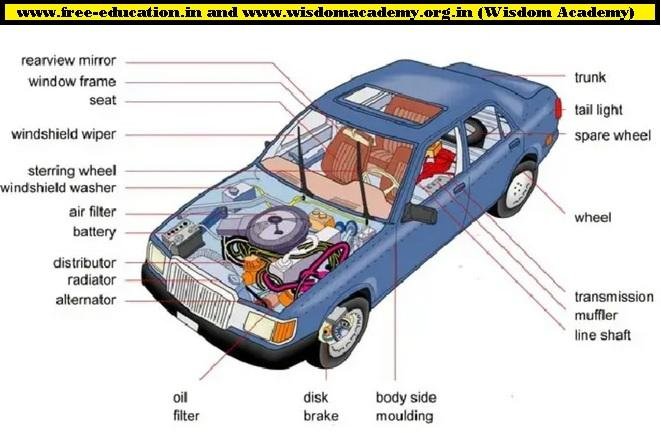
40. Explain how you keep a car in good working condition.
To maintain my car well, I do regular maintenance like changing oil and filters, checking belts, hoses, battery, tires, brakes, and more. I also keep fluids at the right levels and ensure fuel system and wheel lubrication. For heavily used cars, yearly servicing is crucial.
41. What do you check before buying a used car?
When I look at used cars, I’m concerned about leaks. I check for oil and coolant leaks, and I pay attention to the battery, engine, and exhaust. I also inspect for burning smells, check the tires for damage, and make sure all the meters work properly.
42. How is a crankshaft different from a camshaft?
A crankshaft and a camshaft are both essential components in an engine, but they serve different purposes and have distinct functions:
Crankshaft:
- Function: The crankshaft is responsible for converting the reciprocating motion of the pistons (up and down) into rotational motion that powers the vehicle’s wheels.
- Location: Typically located in the lower part of the engine block.
- Design: It has eccentric lobes or throws where connecting rods from the pistons are attached.
- Movement: Rotates continuously as long as the engine is running.
- Timing: Not involved in controlling valve opening and closing.
Camshaft:
- Function: The camshaft controls the opening and closing of the engine’s intake and exhaust valves, regulating the flow of air and fuel into and out of the cylinders.
- Location: Positioned in the engine block or cylinder head, above the cylinder head gasket.
- Design: Contains a series of lobes or cams that press against valve lifters or pushrods to open and close valves at specific times.
- Movement: Rotates at half the speed of the crankshaft and has a synchronized timing relationship with it.
- Timing: Critical for precise valve timing, which affects engine performance and efficiency.
In summary, the crankshaft converts linear piston motion into rotational motion to generate power, while the camshaft controls the opening and closing of valves to manage the air-fuel mixture and exhaust gases. Both components work together to ensure proper engine operation.
43. What is the injector pressure in heavy vehicles?
The injector pressure in heavy vehicles, such as trucks and buses, can vary depending on the specific engine and fuel injection system used.
However, in today’s modern heavy-duty diesel engines, the injector pressure can range from 30,000 to 40,000 pounds per square inch (psi) or even higher. Some advanced diesel engines may have injector pressures exceeding 40,000 psi for improved fuel atomization and combustion efficiency.
It is important to understand that injector pressures can vary between different engine manufacturers and models. It can also depend on factors like the engine’s design, fuel type and emission standards. To determine the exact injector pressure for a particular heavy vehicle, it is best to consult the vehicle’s specifications or the manufacturer’s documentation.
44. What are the potential causes of an overheating engine?
An overheating engine can be caused by several factors, and it’s essential to address the issue promptly to prevent serious damage to the vehicle. Potential causes of engine overheating include:
- Coolant Low or Contaminated:
Low coolant levels due to leaks or evaporation can reduce the engine’s ability to dissipate heat.
- Contaminated coolant, such as mixing different types or using improper coolant, can lead to overheating.
- Coolant Leaks:
Leaks in the cooling system, including hoses, radiator, water pump, or gaskets, can result in coolant loss and overheating.
- Faulty Thermostat:
A malfunctioning thermostat may not open and close properly, disrupting the flow of coolant through the engine.
- Radiator Issues:
Clogged or damaged radiators can restrict the flow of coolant and cause overheating.
- Water Pump Failure:
A faulty water pump can reduce the circulation of coolant through the engine, leading to overheating.
- Cooling Fan Problems:
The engine’s cooling fan may not work correctly, preventing adequate airflow through the radiator.
- Faulty Temperature Sensor:
A malfunctioning engine temperature sensor can lead to incorrect temperature readings and cooling system issues.
- Blocked Coolant Passages:
Blockages in the coolant passages within the engine can impede the flow of coolant and result in overheating.
- Engine Oil Issues:
Low engine oil levels or poor-quality oil can reduce lubrication and heat dissipation, contributing to overheating.
- Faulty Belts and Hoses:
Worn or damaged drive belts and hoses can affect the operation of the water pump and cooling system.
- Excessive Engine Load:
Towing heavy loads or driving in extreme heat conditions can place additional strain on the engine, leading to overheating.
- Head Gasket Failure:
A blown head gasket can allow coolant to mix with engine oil or enter the combustion chambers, causing overheating and potential engine damage.
- Exhaust System Restriction:
A blocked catalytic converter or exhaust system can increase engine heat.
- Air Pocket in Cooling System:
Air pockets in the cooling system can disrupt the flow of coolant and lead to localized overheating.
- Faulty Radiator Cap:
A malfunctioning radiator cap can affect pressure in the cooling system, potentially causing overheating.
It’s crucial to diagnose and address the specific cause of engine overheating to prevent long-term damage and maintain the vehicle’s performance and reliability. If your engine is overheating, it’s advisable to stop driving, let the engine cool down, and seek professional assistance to identify and resolve the issue.
45. How can you judge whether the problem is because of the alternator or the battery?
Determining whether a problem is caused by the alternator or the battery in your vehicle can be done through some simple diagnostic steps. Here’s how you can judge which component may be at fault:
Symptoms of a Battery Problem:
No Electrical Power: If you turn the key, and the dashboard lights, interior lights, and accessories (like the radio) don’t come on or are very dim, it’s likely a battery issue.
Slow Cranking: If the engine cranks very slowly when you try to start the car, and you hear a clicking sound, the battery may be weak or dead.
Jump Start Works: If you can jump-start the car, and it starts fine afterward, the battery is a likely culprit.
Symptoms of an Alternator Problem:
Dimming Lights: When you’re driving, if you notice that the headlights and interior lights become noticeably dimmer or flicker, it could indicate an alternator problem.
Warning Lights: If the “Battery” or “Charging System” warning light on the dashboard comes on and stays lit while driving, the alternator might be failing.
Car Stalls or Dies: If the car stalls while running or dies shortly after starting, especially if it can’t be jump-started, the alternator may not be charging the battery.
Testing:
To confirm whether it’s the battery or alternator, you can use a multi meter or have your vehicle tested at an auto repair shop or parts store:
Battery Test: A battery test will measure its voltage. A healthy battery should have around 12.6 volts when the engine is off. If it’s significantly lower, the battery may be the issue.
Alternator Test: An alternator test will determine if it’s charging the battery properly. With the engine running, the alternator should output around 13.5 to 14.5 volts. If it’s not, the alternator may be the problem.
It’s worth noting that sometimes both the battery and alternator can fail simultaneously or one may have caused the other to fail. Therefore, it’s a good idea to check both when experiencing electrical issues. If you’re uncertain or not comfortable performing these tests yourself, it’s best to consult a professional mechanic who can diagnose the problem accurately and recommend the necessary repairs or replacements.
46. Define octane number and a cetane number.
Octane Number:
The octane number, also known as the octane rating, measures a fuel’s ability to resist knocking in spark-ignition engines like those in cars. Higher octane numbers mean better resistance to knocking and can allow for more efficient engine performance.
Cetane Number:
The cetane number gauges the ignition quality of diesel fuel in compression-ignition engines found in diesel-powered vehicles. A higher cetane number indicates better ignition quality, leading to smoother combustion, reduced engine noise, improved fuel efficiency, and lower emissions.
47. Why are hydrogen and natural gas used in automobiles?
Hydrogen and natural gas are used in automobiles for several reasons, primarily related to their potential as alternative fuels that offer certain advantages over traditional gasoline and diesel fuels:
- Reduced Emissions: They produce fewer harmful emissions, contributing to cleaner air and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: They can lead to improved fuel efficiency and reduced fuel consumption in certain engine types.
- Diverse Sources: They can be produced from various sources, including renewables, enhancing energy security.
- Reduced Oil Dependency: Less dependence on petroleum enhances energy security and reduces vulnerability to oil supply disruptions.
- Lower Fuel Costs: In some regions, they are cost-effective compared to gasoline or diesel.
- Technology Development: Promotes innovation in alternative fuel technologies like hydrogen fuel cells and CNG engines.
- Regulatory Incentives: Some governments offer incentives to encourage their use, aligning with environmental and energy policies.
48. What is a kingpin offset and how is it used?
The kingpin offset is a key parameter in the front suspension system of many vehicles, and it plays a crucial role in steering stability, handling, tire wear, and overall safety. Properly adjusting the kingpin offset is essential for maintaining a vehicle’s optimal performance and extending the lifespan of its components.
Here’s how kingpin offset is used and why it’s important:
- Steering Stability: Kingpin offset is designed to enhance steering stability and straight-line tracking of the vehicle. It helps the vehicle maintain a straight path when driving without the need for constant steering corrections.
- Cornering Control: Kingpin offset influences the vehicle’s handling characteristics, especially during turns and corners. It contributes to steering effort and responsiveness, helping the driver maintain control while navigating curves.
- Alignment and Tire Wear: Proper kingpin offset alignment is essential for even tire wear. If the kingpin offset is not correctly adjusted, it can lead to uneven tire wear patterns, reducing tire lifespan and increasing maintenance costs.
- Safety: Incorrect kingpin offset settings can affect a vehicle’s stability and handling, potentially leading to safety issues. Proper alignment, including kingpin offset, is essential for safe operation, especially in heavy-duty and commercial vehicles.
- Tire and Suspension Wear: Kingpin offset can impact the wear and tear on various suspension components. Proper alignment ensures that these components, including bushings and bearings, wear evenly and last longer.
- Alignment Adjustments: Automotive technicians use specialized equipment to adjust the kingpin offset and other alignment parameters during routine maintenance or after suspension repairs to ensure the vehicle’s optimal performance and safety.
49. Why are car tyres always black? What is the advantage?
Car tires are predominantly black due to the presence of carbon black in their composition, which serves several important purposes:
Reinforcement: Carbon black is a type of finely divided carbon used as a reinforcing filler in tire rubber compounds. It strengthens the rubber, improving its durability and resistance to wear and tear. This reinforcement is essential for withstanding the stresses and strains tires experience on the road.
Heat Dissipation: Black color absorbs and dissipates heat more effectively than lighter colors. As tires heat up during driving, particularly at high speeds, the black color helps manage and disperse the heat generated by friction with the road. Efficient heat dissipation is crucial for maintaining tire integrity and preventing overheating.
UV Protection: Carbon black provides UV (ultraviolet) protection, shielding the tire’s inner layers from the damaging effects of sunlight and ozone exposure. This UV protection helps extend the lifespan of the tire.
Traction: The unique tread patterns and compounds used in tire manufacturing are designed to provide optimal traction on the road surface. Carbon black’s presence enhances the tire’s grip, contributing to better traction in various weather conditions, including wet and dry roads.
Aesthetic Appeal: While the functional aspects of carbon black are essential, the color also contributes to the traditional and aesthetic appearance of tires. Black tires are often considered visually appealing and are a common choice for vehicle design.
Cost-Efficiency: Carbon black is a cost-effective and readily available material. It allows tire manufacturers to produce high-quality tires at a reasonable cost, making them accessible to a wide range of consumers.
While black is the standard color for most tires, some manufacturers have experimented with colored sidewalls or treads for cosmetic reasons or to indicate specific tire characteristics. However, the black color remains the industry standard due to its numerous functional advantages in terms of tire performance, longevity, and safety.
50. Under which conditions does a car emit white smoke? How do you prevent it?
White smoke emitting from a car’s exhaust can indicate various underlying issues, and the causes can vary. Here are some common conditions under which a car may emit white smoke and steps to prevent it:
1. Cold Weather or Cold Start: In cold weather, it’s normal for a car to produce white vapor-like exhaust when first starting, especially if the engine is running rich (using more fuel). This is typically harmless and should disappear once the engine warms up.
2. Condensation: During cold weather or when the engine is cold, condensation can form in the exhaust system. When you start the car, this moisture may turn into white steam that exits the tailpipe. This is also normal and should dissipate as the engine warms up.
3. Coolant Leak: One of the more concerning reasons for white smoke is a coolant leak into the combustion chamber. This can be due to a damaged head gasket, a cracked cylinder head, or a damaged engine block. If coolant mixes with the combustion process, it can produce white smoke. To prevent this, ensure your vehicle’s cooling system is properly maintained and promptly address any signs of coolant loss or overheating.
4. Faulty Fuel Injector: A malfunctioning fuel injector can cause excess fuel to enter the combustion chamber, leading to incomplete combustion and white smoke. Regular maintenance and fuel system cleaning can help prevent this issue.
5. Incorrect Fuel Mixture: An incorrect air-fuel mixture, such as running too rich (too much fuel), can lead to white smoke. Regularly check and maintain the vehicle’s fuel system and ensure it’s tuned properly to prevent this problem.
6. Engine Oil Leak: If engine oil leaks into the combustion chamber, it can produce white smoke. Regularly check for oil leaks and address them promptly. Ensure proper maintenance, including regular oil changes.
7. Cracked Engine Block or Cylinder Head: In rare cases, a cracked engine block or cylinder head can allow coolant or oil to enter the combustion chamber, causing white smoke. Preventing this requires regular engine inspections and addressing any issues promptly.
To prevent white smoke and ensure your vehicle’s health:
- Perform Regular Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, including oil changes, cooling system checks, and fuel system inspections.
- Monitor Fluid Levels: Regularly check your engine’s oil and coolant levels and look for signs of leaks.
- Address Warning Signs: If you notice white smoke that persists or other unusual symptoms like engine overheating, have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic promptly.
- Use High-Quality Fuels and Oils: Use the recommended fuels and high-quality engine oils for your vehicle to maintain proper combustion and lubrication.
- Keep Your Vehicle Tuned: Ensure your vehicle’s engine is properly tuned to maintain the correct air-fuel mixture.
Remember that white smoke from the exhaust should not be ignored, especially if it persists or is accompanied by other symptoms like engine misfires, reduced power, or unusual noises. Prompt diagnosis and repair can prevent more significant and costly issues.
51. How does the clutch system work? What is a dual-clutch transmission?
A clutch system is an essential component in manual transmission vehicles, and it’s responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels by connecting and disconnecting the engine’s power to the transmission. Here’s how it works:
Clutch System:
Step 1: Clutch Assembly: The clutch system in a manual transmission vehicle consists of key components: the clutch pedal, clutch disc, pressure plate, and flywheel.
Step 2: Clutch Pedal: When the driver presses the clutch pedal, it disengages the clutch, separating the clutch disc from the flywheel.
Step 3: Clutch Disc: Positioned between the engine’s flywheel and the transmission input shaft, the clutch disc is released from the flywheel when the clutch pedal is depressed.
Step 4: Flywheel: The flywheel is connected to the engine’s crankshaft and rotates with the engine. It provides a smooth surface for the clutch disc to engage when the clutch is activated.
Step 5: Engagement and Disengagement: Releasing the clutch pedal applies pressure to the clutch disc via the pressure plate, pressing it against the flywheel. This creates a solid connection between the engine and the transmission, allowing power to flow to the wheels. Pressing the clutch pedal disengages the clutch, moving the clutch disc away from the flywheel and interrupting power transfer.
A dual-clutch transmission (DCT) is a type of automatic transmission that combines elements of both manual and automatic transmissions. It uses two separate clutches, one for odd-numbered gears (1st, 3rd, 5th, etc.) and another for even-numbered gears (2nd, 4th, 6th, etc.). Here’s how a DCT works:
Step 1: Dual Clutches: A DCT employs two separate clutches, often called the “wet” and “dry” clutches. The wet clutch is submerged in oil and handles odd-numbered gears (1st, 3rd, 5th, etc.), while the dry clutch manages even-numbered gears (2nd, 4th, 6th, etc.).
Step 2: Gear Selection: The DCT’s control unit continually assesses driving conditions, throttle input, and vehicle speed to decide which gear to engage. For instance, during acceleration, it may prepare to shift to the next higher gear.
Step 3: Seamless Gear Changes: When a gear change is needed, the DCT preselects the next gear using one clutch while keeping the other clutch engaged. This enables extremely fast and smooth gear changes.
Step 4: Engagement: When it’s time to switch gears, the currently engaged clutch disengages, and the other clutch engages almost instantly. This seamless transition ensures smooth acceleration with minimal power interruption.
Step 5: Effiffiffiffiffiff fficiency: DCTs are highly efficient because they can shift gears quickly and without power loss compared to traditional automatic transmissions with torque converters.
DCTs are often found in high-performance and sports cars as they provide swift gear changes and can be operated either in full automatic mode or manually via paddle shifters or a gear lever. They offer the convenience of an automatic transmission with the performance and control of a manual transmission.
52. What do you mean by independent suspension?
In cars, independent suspension allows each wheel to move independently of the others, improving ride comfort, handling, and stability. It isolates wheel movements, which improves road comfort and reduces body roll during turns. This technology, which provides accurate wheel alignment adjustments, is extensively employed in current cars, SUVs, and high-performance vehicles, however it is more sophisticated and expensive than solid axle suspensions. There are several varieties, including as double wishbone and multi-link configurations, that are customised to particular vehicle needs. Because of their durability and simplicity, solid axles, which connect wheels on one side, are employed in heavy-duty and off-road vehicles.
53. What different types of smoke ?
Different colors of smoke indicate a different set of problems.
Black Smoke:
Black smoke is the most common type of smoke generated by vehicle on the road. Which indicates the amount of carbon generated. However, there are many reasons of black smoke coming from the car. The primary possibility is that your engine is burning more fuel than usual. This eventually leads to your petrol draining too quickly.
Another reason is clogged air filters. Dirty air filters prevent clean air from entering the combustion chamber. Black smoke might also be caused by faulty fuel injectors.
Black smoke also generated if your car has faulty sensors, it can offer inaccurate pressure readings, resulting in excessive fuel injection.
White Smoke
White smoke from a vehicle typically indicates overheating due to a faulty cooling system or coolant issues. Coolant, used to regulate temperature, can enter the cylinder through a faulty gasket, burning with fuel and causing overheating and white smoke. This is often seen in poorly maintained cars, resulting from engine oil deficiency, damaged gaskets, or engine block/cylinder problems. Inadequate lubrication leads to accelerated engine component wear, overheating, and white smoke emission.
Blue Smoke
Seeing blue smoke from your car’s tailpipe indicates burning engine oil. This occurs when oil leaks from its intended path, failing to lubricate essential engine parts. The leakage may be caused by worn piston rings, gaskets, or a malfunctioning PCV valve. In some cases, oil might mix with fuel and even combust. Continued use with oil leakage can lead to damage to your car’s spark plugs. If the smoke appears during acceleration, it’s likely related to the cylinder head, and during deceleration, it may be due to damaged piston rings.
Gray Smoke
Gray smoke from a car’s exhaust can result from various under-the-hood issues, such as burning transmission fluid or a faulty turbocharger, particularly in diesel engines. This smoke often has a burning odor.
A malfunctioning turbocharger is a common cause of gray smoke, leading to incomplete combustion, akin to the causes of blue smoke (burning oil).
Leaking automatic transmission fluid is another potential reason for gray smoke. This fluid serves critical roles in lubrication, cooling, wear prevention, and gasket sealing. A broken transmission modulator can cause the fluid to leak into the combustion chambers, where it’s burned.
A jammed PCV (Positive Crankcase Ventilation) valve can also produce gray smoke. The PCV valve’s role is to direct air and gas into the combustion chambers while reducing emissions. A broken or stuck PCV valve can create pressure buildup in the ventilation system, resulting in leaks and gray smoke.
54. What is the use of left feet in the automatic car?
In an automatic car, it’s best to use your right foot for the accelerator and brake pedals during regular driving since there’s usually no need to use both simultaneously. Using both feet can pose risks, such as accidentally pressing both pedals during emergencies, activating brake lights unintentionally, causing conflicting actions, and perpetuating habits from manual driving. Thus, for safety and efficiency, stick to using only your right foot for the accelerator and brake in automatic vehicles.
So on that basis, In automatic car, Left feet has no use. It is completely on rest foot in automatic car.
55. What is the position of the valve in the compression stroke of a 4 stroke engine ?
Both Valve Remain Close
56. What is safety need take in car workshop ?
Safety is paramount in a car workshop to protect both workers and the environment. Here are key safety measures that should be taken:
Protective Gear: Mechanics should wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety goggles, gloves, ear protection, and overalls, to shield against potential hazards.
Ventilation: Proper ventilation is essential to disperse fumes from exhaust and chemicals. Install exhaust fans or use air filtration systems.
Fire Safety: Maintain fire extinguishers, ensure they are easily accessible, and conduct fire drills. Store flammable materials safely.
First Aid: Have a well-equipped first aid kit on hand and ensure employees are trained in basic first aid procedures.
Tool Safety: Regularly inspect and maintain tools to prevent accidents. Follow manufacturer’s guidelines and provide proper tool storage.
Lifts and Hoists: Inspect and maintain vehicle lifts and hoists regularly, ensuring they meet safety standards. Train employees in their safe operation.
Chemical Safety: Store chemicals properly, label containers, and provide Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for reference. Use chemicals in well-ventilated areas and wear appropriate protective gear.
Spill Control: Implement spill control measures for oil, coolant, and other fluids. Have absorbent materials and spill kits available.
Electrical Safety: Ensure wiring and electrical systems are up to code. Provide proper grounding and insulation. Train staff in electrical safety.
Machine Guards: Install safety guards on machinery and equipment to prevent accidents.
Training: Train all employees in workshop safety procedures and protocols, including handling hazardous materials, using equipment, and responding to emergencies.
Emergency Response: Establish clear emergency response protocols for accidents, fires, and chemical spills. Maintain accessible emergency exits.
Vehicle Safety: Use wheel chocks and safety stands when working under vehicles. Ensure proper lifting points are used.
Housekeeping: Keep the workshop clean and organized to reduce tripping hazards and fire risks.
Safety Signs: Display safety signs and labels for potential hazards, safety equipment locations, and emergency exits.
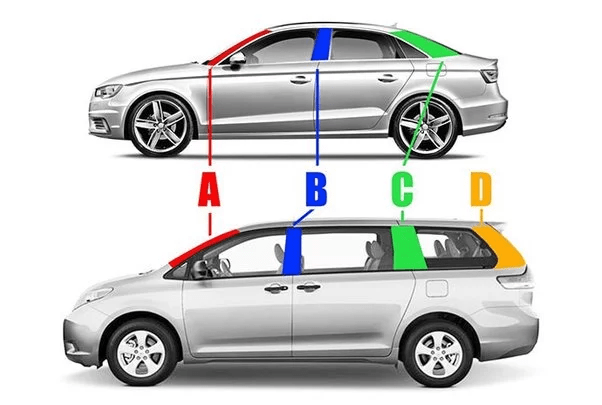
57. How many types of Pillars in Cars ?
Vehicle frames rely on key pillars: A, B, C, and sometimes D. These support the car’s body, like pillars in a house. They stand nearly vertical or inclined to uphold the roof and structure.
58. How many types of car insurance ?
Motor insurance comes in various types, such as:
- Liability Insurance: Covers damages and injuries to others.
- Collision Insurance: Pays for your vehicle’s collision-related repairs.
- Comprehensive Insurance: Covers non-collision damage like theft or vandalism.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Coverage: Protects against drivers with inadequate insurance.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP) or MedPay: Covers medical expenses.
- Gap Insurance: Covers the gap between your car’s value and what you owe.
- Towing and Labor: Pays for roadside assistance and towing.
- Rental Reimbursement: Covers rental car expenses during repairs.
- Classic Car Insurance: For vintage or classic cars.
- Usage-Based Insurance (UBI): Premiums based on driving habits.
- Commercial Auto Insurance: For business vehicles.
59. Explain the working of the 4 Stroke Engine ?

60. What is Engine Firing Order ? Why is it very important ?
The firing order of engine cylinders is crucial for optimal performance and engine balance. It’s not a simple 1-2-3 sequence; manufacturers carefully arrange it to prevent crankshaft damage. Firing order affects vibration, back pressure, engine balance, power flow, and cooling. Here are some common firing orders:
- 3 cylinders: 1-2-3 for Perodua, 1-3-2 for BMW K75 and Subaru Justy.
- 4 cylinders: 1-3-2-4 for Ford Taunus V4, 1-2-4-3 for British Ford and relay, 1-3-2-4 for Yamaha R1 and Subaru, 1-4-3-2 for Volkswagen air-cooled.
- 5 cylinders: 1-2-4-5-3 for Volvo 850 and Audi 100, 1-3-5-4-2 for GM Atlas.
- 6 cylinders: Various orders like 1-5-3-6-2-4 for Volkswagen VR6, 1-4-3-6-2-5 for Mercedes-Benz M272, and more for different engines.
61. What is the meaning of acceleration enrichment in automobile ?
In vehicles, acceleration enrichment is a technology that briefly enhances fuel delivery during high acceleration in order to retain engine performance and responsiveness. When you push the gas pedal for speedy acceleration, it ensures that the engine receives enough fuel, preventing issues such as poor performance or engine damage caused by a lean fuel mixture.
62. What are important Engine Part and Also mention other part which are important for vehicle ?
The engine in your car is like the heart, converting heat from burning gas into the force needed to turn the wheels for propulsion during a complex process. Different types of engines are available, and drivers can modify them for performance. Key engine parts include the connecting rod, piston, crankshaft, flywheel, cylinder, cylinder head, camshaft, intake, exhaust manifold, and sometimes a carburetor or throttle body for fuel control.
Other crucial auto parts include:
- Alternator: Generates electrical power to charge the battery and run electrical components.
- Battery: Provides power to all electrical components in modern vehicles.
- Radiator: Keeps the engine cool by dissipating heat.
- Muffler: Reduces engine noise and dampens emissions.
- Catalytic Converter: Converts harmful emissions into less harmful compounds.
- Transmission: Manages speed and torque using gears and gear trains.
- Axle: Connects and supports the wheels.
- Fuel Tank: Stores fuel for the engine.
- Center Console: Located between the front seats, contains various controls and storage compartments.
63. What is the difference between manual and automatic transmission.
| Aspect | Manual Transmission | Automatic Transmission |
|---|---|---|
| Gear Shifting | Driver manually operates clutch and gear lever | Transmission system automatically selects gears |
| Clutch vs. Torque Converter | Uses a clutch mechanism | Uses a torque converter |
| Ease of Use | Requires learning to operate clutch and manual gear changes | Offers a simpler, no-gear-shifting driving experience |
| Fuel Efficiency | Historically more fuel-efficient due to less power loss | Modern automatics have improved efficiency |
| Maintenance and Repairs | Fewer components, less complex, and often less expensive to maintain | More complex, potential for costlier repairs |
| Driving Experience | Engaging and connected driving experience, preferred by enthusiasts | More relaxed and convenient driving experience |
| Resale Value | May have lower resale value in some markets | Often results in higher resale value in many markets |
Keep in mind that the choice between manual and automatic transmissions depends on individual preferences, driving conditions, and the intended use of the vehicle. Modern technology has narrowed the efficiency gap between the two types, and some vehicles offer options that provide a blend of manual and automatic control.
| Aspect | Manual Transmission (MT) | Automatic Transmission (AT) |
|---|---|---|
| Clutch Engagement | The driver operates the clutch pedal, disengaging the engine from the transmission, interrupting power flow. | The engine is always connected to the transmission via a torque converter, maintaining continuous power transmission. |
| Gear Shifting | The driver selects gears manually by using a gear lever, altering the gear ratio by engaging different sets of gears. | Gear selection is managed automatically through a hydraulic system, with no manual gear lever operation by the driver. |
| Clutch Disengagement | After selecting a new gear, the driver releases the clutch pedal gradually, engaging the engine with the transmission. | Automatic, no clutch pedal; gear changes occur without manual input, controlled by the Transmission Control Unit (TCU). |
| Direct Driver Control | Provides the driver with direct control over gear selection and clutch engagement timing, offering a hands-on experience. | Offers automatic and smooth gear changes, reducing the need for manual involvement, ideal for convenience. |
| Smooth Transitions | Gear changes may require driver skill, and shifts can be abrupt, depending on driver proficiency. | Provides smooth and seamless gear changes, enhancing comfort, especially in heavy traffic. |
In summary, manual transmissions require the driver’s active involvement in clutch operation and gear selection, while automatic transmissions manage gear changes automatically through a torque converter and hydraulic system, providing a more convenient and relaxed driving experience.
64. What is ACC (Adaptive Cruise Control) ?
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) is an advanced driver assistance system (ADAS) that enhances traditional cruise control by automatically adjusting a vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe following distance from the vehicle ahead. ACC uses a combination of sensors, such as radar, lidar, cameras, or a combination of these, to monitor traffic conditions and control the vehicle’s acceleration and braking accordingly.
The adaptive cruise control (ACC) system depends on two infrared sensor to detect ahead car. Each sensor has an emitter, which sends out a beam of infrared light energy, and a receiver, which captures light reflected back from the vehicle ahead.
The first sensor, called the sweep long-range sensor, uses a narrow infrared beam to detect object six to 50 yards away. At its widest point, the beam covers no more than the width of one highway lane, so this sensor detect vehicle only up ahead and does not detect cars in other lanes. Other sensor, called cut-in sensor, comes in. It has two wide beams that “look” into adjacent lanes, up to a distance of 30 yards ahead.
65. What is Automobile Engineering ?
Automobile engineering is a branch of engineering which deal with design, manufacturing and operation of automobile. An Automobile engineer has to deal with motorcycles, buses, trucks, etc. It also include the segments of mechanical, electrical, electronic, software and safety elements.
The work of an automobile engineer breaks down into three categories:
Design: Designing new product and improve the existing ones.
Research and Development: Finding solutions to engineering problems.
Production/Manufacturing:- Planning and Designing new production process to manufacture the vehicle and its spare parts.
66. What is the function of ABS (Anti-Lock Breaking) System ?
The Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS) prevents wheel lockup during hard braking by rapidly pulsing the brakes. This helps drivers maintain steering control, reduces stopping distance, and enhances stability on slippery surfaces. ABS is a vital safety feature in modern vehicles.
67. What is CRDI ?
CRDI is the short form for “Common Rail Direct Injection.” It is an advanced technology which is used in diesel engines to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and improve overall engine performance. CRDI is a highly precise and effective way of injecting fuel directly into each engine cylinder’s combustion chamber.
Advantage:- CRDi engine are advantageous in many ways. Cars fitted with this new engine technology are believed to deliver 25% more power and torque than the normal direct injection engine. It offers good pickup, lower level of noise and vibration, high mileage, lower emission, lower fuel consumption, and improved performance.
Disadvantage:- Like all good things have a negative side, this engine also have some disadvantages. The main disadvantage of the CRDi engine is that is costly than conventional engine. The list also includes high costly spare parts.
Application:- The most common application of CRDi engines are marine and locomotive applications. Also, in the present day they are widely used in a variety of car models ranging from city cars to premium executive cars.
68. What is DTSI ?
DTSI, or Digital Twin Spark Ignition, is a technology used in Bajaj Auto motorcycles.
Digital twin spark ignition engine has two spark plugs which is located at opposite sides of combustion chamber. This technology has greater combustion rate because of twin spark plug. increased power, lower emissions, smoother idling, and lower vibrations. DTSI technology is exclusive to Bajaj motorcycles and attempts to improve engine performance while still being environmentally friendly. It also has some disadvantages like high NOx emission, If one spark plug get damaged then we have to replaced both. Due to which it cost is relatively more.
69. What is spark plug ?
It is device which used to produce electric spark to ignite the compressed air-fuel mixture in cylinder.
A spark plug consist of mainly three parts :-
- Center electrode or insulated electrode.
- Ground electrode or outer electrode
- Insulation separating the two electrodes.
70. What is the function of Turbocharger ?
A turbocharger, often called a “turbo,” is like a supercharger for your car’s engine. It does this by pushing more air into the engine’s combustion chamber. Here are the important things to know about how a turbocharger works:
Forced Induction: Think of a turbocharger as a special air pump. It squeezes the air going into the engine, making it denser. This denser air has more oxygen, which helps the engine burn fuel better.
More Power: By packing more air into the engine, a turbocharger makes the engine burn more fuel. This extra fuel burning results in more engine power. So, even a small engine with a turbocharger can perform like a bigger, more powerful one.
Better Fuel Efficiency: Turbos can also make engines more fuel-efficient. They get more power from the same amount of fuel, which is great for saving on gas.
Stronger Low-Speed Performance: Turbos are excellent at boosting power, especially when you’re driving slowly. This means better acceleration and the ability to tow heavy stuff.
High Altitude Help: Turbochargers are handy in places with thin air, like high mountains. They stuff more air into the engine, making up for the lack of oxygen in the air.
Cleaner Emissions: Turbos can help reduce harmful stuff in car emissions. When the engine burns fuel more efficiently, it produces fewer bad things like carbon monoxide and unburned fuel particles.
Smaller Engines, Same Power: Car makers use turbos to put smaller, more efficient engines in vehicles without sacrificing power. Smaller engines are lighter and use less space, which can make cars more efficient.
Performance Boost: Some people love to soup up their cars for extra power. They use turbos to add more “oomph” to the engine, making it faster and more powerful.
One thing to remember is that turbos use exhaust gases to work. They spin a special fan to compress the air going into the engine. But, they can be a bit tricky to manage. If not designed or maintained correctly, they can cause issues like “turbo lag” (a delay in power) or overheating. So, taking good care of your turbocharged engine is key for a smooth ride.
71. What is the role of Blink Code in Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS) ?
The blink code in an Antilock Braking System (ABS) is a diagnostic tool that is used to identify potential flaws or defects in the ABS system. When the ABS control unit detects a defect, it can initiate a preset sequence of blinking lights on the ABS warning lamp or ABS indication on the dashboard. These blink codes are intended to assist technicians and mechanics in determining the source of the problem and performing the necessary repairs.
The exact blink code patterns can vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle, as well as the manufacturer of the ABS system. Each blink code corresponds to a specific error or fault, such as a sensor malfunction, hydraulic pump failure, or other issues within the ABS system.
To interpret a blink code in an ABS system, you would typically need the vehicle’s service manual or access to a diagnostic tool that can read and interpret the ABS fault codes. In most cases, the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic (OBD) system can also provide information about ABS faults alongside other diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
Here’s a general example of how blink codes might work:
- The ABS warning light on the dashboard will start blinking a specific number of times.
- The number of blinks represents a numeric code (e.g., two blinks followed by a pause, then three blinks would represent code 23).
- You would consult the vehicle’s service manual or an ABS diagnostic code reference to determine what code 23 corresponds to. This would tell you the nature of the ABS fault.
It’s important to note that diagnosing and repairing ABS issues usually requires specialized knowledge and equipment, and it’s typically not a DIY task for most car owners. If your vehicle’s ABS warning light is blinking, it’s advisable to have it checked by a qualified mechanic or at an automotive service center to identify and address the specific problem. Ignoring ABS issues can compromise your vehicle’s braking performance and safety.
72. How car operate ? Explain step by step.
Let’s learns more about how a car get start :-
Step 1 :- Turns the Key in the ignition
Step 2 :- When we give ignition, The car battery power up
Step 3 :- Car battery power up and sending the power to the starter motor
Step 4 :- Now starter motor turns the crankshaft (Rotational) due to which piston gets motion (Reciprocating)
Step 5 :- With the piston moving the engine fires up and tick over
Step 6 :- A fan draws air into the engine via an air filter (which removes the dirt and grit from the air)
Step 7 :- The cleaned air is drawn into a chamber where fuel (Petrol or Diesel) is added
Step 8 :- This fuel-air mix (a vaporised gas) is stored in the chamber
Step 9 :- Driver presses the accelerator pedal & the throttle valve is opened
Step 10 :- The gas-air mix passes through an intake manifold and is distributed, through intake valves, into the cylinder. (Here camshaft control the opening and closing of the valves)
Step 11 :- The distributor makes the spark plugs, which ignites the fuel-air mix. The resulting explosion forces a piston to move down which in turn causes the crankshaft.
Step 10 :- Flywheel is connected to crankshaft. As the crankshaft rotate, Flywheel also rotate (Flywheel used to stored the mechanical energy of the engine).
Step 11 :- Now clutch comes into the play which is used to connect or disconnect the flywheel and gear box. When press the clutch flywheel get disconnect from the gearbox shaft) Then We can easily change the gear box without any load on the gearbox.
Step 12 :- Gear box is connected to differential through the propeller shaft. Now rotating power goes to differential. And Differential rotate the Wheel of car.
As Car start moving on the road. That’s how a car work.
74. What are different types of car layout ?
Layouts can roughly be divided into following categories:-
Front Wheel Drive : Front engine, Mid-engine, Rear engine
Rear Wheel Drive : Front engine, Mid-engine, Rear engine
Four Wheel Drive : Front engine, Mid-engine, Rear engine
75. What is the voltage required to run a car for battery, bus and truck ?
12-Volt System: Most passenger cars, as well as many light-duty trucks and SUVs, use a 12-volt electrical system.The 12-volt system powers various components in the vehicle, including the starter motor, lights, radio, and accessories.
24-Volt System: Some larger trucks and commercial vehicles, such as buses and heavy-duty trucks, use a 24-volt electrical system.
48-Volt System: In recent years, there has been a trend towards using 48-volt electrical systems in certain vehicles, especially in hybrid and electric vehicles. These systems provide more power than a traditional 12-volt system and can support advanced features like mild hybrid technology and regenerative braking.
76. List the types of Brakes Used in Vehicle.
- Frictional Brake
- Pumping Brake
- Electromagnetic Brake
- Hydraulic Brake
- Air Brake
- Anti-Lock Braking System.
77. What is the full form of ECU and It function ?
ECU: Engine Control Unit
- The electronic control unit that manages and controls various aspects of the engine’s operation, including fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions.
It is also known as ECM (Engine Control Module)
78. What is CVT ?
CVT: Continuously Variable Transmission
- Function: Utilizes a continuous range of gear ratios for smoother acceleration and improved fuel efficiency.
79. What is the full form of PHEV ?
PHEV: Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle
- Function: Combines an internal combustion engine with an electric motor and a rechargeable battery, offering both electric and hybrid driving modes.
80. What is the full form of FWD, RWD, AWD and 4WD ?
FWD : Front Wheel Drive
RWD : Rear Wheel Drive
AWD : All Wheel Drive
4WD : Four Wheel Drive
81. What are the power losses in running engine and How much actual power output ?
There are diffrent types of power losses in running engine which are given below:-
- 30 % Due to Cooling
- 30% Due to Exhaust
- 10% Due to Friction
- 5% Due to Pumping
- Actual Power Output, We obtatin from engine 25%
82. What is Gear Ratio ?
The gear ratio of a gear train is the ratio of the angular velocity of the input gear to the angular velocity of the output gear, also known as the speed ratio of the gear train. The gear ratio can be computed directly from the number of teeth in the various gears that engage to form the gear train.
In simple words, gear ratio defines the relationship between multiple gears.
Gear Ratio = Output gear teeth / Input gear teeth
Example 1:-If our motor is attached to a gear with 80 teeth and this gear is then attached to a gear with 40 teeth that drives a wheel, our gear ratio is 80:40 or more accurately 2:1
Example 2:-if our motor is attached to a gear with a 1″ diameter and this gear is connected to gear with a 2″ diameter attached to a wheel, From the centre to edge of our input gear is 0.5″ and From the centre to edge of our ouput gear is 1″ So Our ratio is 1/0.5 = 2:1
83. How does gear ratio affect torque?
Firstly , We need to understand – What is Torque?
Torque is a twisting force (it does not do any work itself – it is simple an application of energy). Work occurs, when torque is applied and movement occurs.
“Torque is a force that tends to rotate or turn things. We generate a torque any time you apply force using a wrench. Tightening the lug nuts on wheels is a good example.
Torque = Force x Distance
How does gear ratio affect Torque ?
Simply Take, Torque at work (such as at a wheel) is your motor’s torque times your gear ratio.
Motor Torque x Gear Ratio = Torque at the wheels
Let’s say we have 10 rpms motor that is capable of 5 oz. Torque (We know this from our motor spec.)
Gear Ratio is 5:1 , Then Torque at wheel = 5 x 5/1 = 25 oz
What if gear ratio were 1:3 then, 5 x 1/3 = 1.6 oz
84. What is the principle of Suspension System ?
- To restric road vibration from being transmitted to the various components of the vehicle.
- To protect the passengers from road shocks.
- To maintain the stability of the vehicle in pitching and rolling.
85. List the Components of Suspension System?
- 1. Control Arm :- A movable lever that fastens the steering knuckle to the frame of the vehicle.
- 2. Control Arm Bushing:- This is a sleeve which allows the control arm to move up and down on the frame.
- 3. Strut Rod:- Prevents the control arm from swinging forward and backwards.
- 4. Ball Joint:- A joint that allows the control arm and steering knuckle to move up and down and sideways as well.
- 5. Shock Absorbers or Struts:- Prevents the supension from bounce after spring compression and extension.
- 6. Stabilizer Bar:- Limits body roll of the vehicle during cornering.
- 7. Spring:- Supports the weight of the vehicle.
86. What is the range of engine efficiency in case of two stroke engine?
The efficiency of a two-stroke engine can vary widely depending on several factors, including design, operating conditions, and the specific application. However, two-stroke engines typically have lower thermal efficiency compared to four-stroke engines. The range of engine efficiency for two-stroke engines can vary, but it is generally lower than that of four-stroke engines.
In practice, the efficiency of a two-stroke engine can range from around 20% to 30% for small, simple two-stroke engines used in applications like chainsaws or leaf blowers. These engines tend to have lower efficiency due to their design and the presence of unburned fuel-air mixture that can escape during the exhaust process.
87. What is the use of hydrogen in automobile?
Hydrogen can be used in automobiles as a fuel source in hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). Here are some key uses and advantages of hydrogen in the context of automobiles:
- Fuel for Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs):
- Hydrogen can be used as a fuel in fuel cell vehicles. In these vehicles, hydrogen is stored in high-pressure tanks and is fed into a fuel cell stack.
- Inside the fuel cell stack, hydrogen reacts with oxygen from the air to produce electricity through an electrochemical process.
- This electricity powers an electric motor, which drives the vehicle’s wheels, providing propulsion.
- The only byproduct of this process is water vapor, making FCVs a zero-emission technology at the tailpipe.
- Zero Emissions:
- Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions. The only emission is water vapor, which makes them environmentally friendly and a potential solution for reducing greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector.
- High Energy Density:
- Hydrogen has a high energy density, which means it can store a large amount of energy in a relatively small volume.
- This high energy density makes hydrogen a viable option for vehicles where long driving ranges and quick refueling times are important.
- Fast Refueling:
- Hydrogen fueling stations can fill up a hydrogen tank in a matter of minutes, similar to the time it takes to refuel a gasoline or diesel vehicle. This is in contrast to electric vehicles that typically require longer charging times.
- Potential for Sustainable Production:
- Hydrogen can be produced through various methods, including electrolysis of water using renewable energy sources like wind or solar power.
- When hydrogen is produced using renewable energy, it is considered “green hydrogen” and can contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable transportation system.
- Application in Heavy-Duty Vehicles:
- Hydrogen fuel cell technology is often considered for heavy-duty vehicles like buses, trucks, and trains where battery-electric solutions may face challenges related to weight and range.
Despite these advantages, there are also challenges associated with hydrogen as a vehicle fuel. These challenges include the need for a hydrogen infrastructure, energy efficiency concerns in the production and distribution of hydrogen, and the overall cost of fuel cell vehicles. However, ongoing research and development efforts aim to address these issues and make hydrogen a more viable and sustainable option for future transportation.
88. List out the various materials used in the construction of chassis frames.
- Low Carbon Steel – 0.18 or 0.20 % Carbon content
- High Carbon Steel – 0.25 % carbon content
- Alloy Steel – With alloying elements like Ni & Cr.
89. Write down any two main sections of vehicle construction.
- Chassis Construction
- Body Construction
90. What are two types of vehicle suspensions?
- Rigid axle suspension
- Independent Suspension
91. How to Evaluate the car step by step process?
Step 1:- Check the Vehicle was Accident or not.
Check the pillar of the vehicle A, B & C Pillar (Note:- Check the Welding on pillar after removing the rubber)
Also check the door is company fitted or Replaced (Sealer is attached on door which is company fitted)
Step 2:- Check the Engine Mounting, Engine Leakage, Mark on Engine Nut.
By this process, We can check engine is repair or not.
Step 3:- Check document of RC, Insurance and Pollution.
We can check the insurance is Own damage or Third Party. (if the vehicle value is not mentioned on insurance it means it is third party insurance)
Step 4:- Check the Odometer Reading, Steering, Power Window working or not, Interior condition of the vehicle.
Note all the details like odometer reading, steering wheel noise, Power Window and Interior Condition or Any other noise.
Step 5: Check the Vehicle is repaint or original.
Check the paint on roof, hood, door, tail dicky etc. by paint thickness gauge, By Visual Inspection, Car history, UV light.
Step 6: Check the Tyre depth.
Check the Tyre depth by Tyre depth gauge (Minimum depth required 2mm, if below 2 mm it means Tyre wear)
92. How to Inspect and Buy a Used Car ? or How to do Second Hand Car Inspection ?
Here is a checklist for Car Inspection :-
The Basic :- Make and Model, Year, Variant, Asking price
The Body:- Scratches, Dents, Windshield (chips or cracks), Headlights (foggy/scratched/cracked)
The Wheel:- Treads, Rim/Alloy Damage, Brake Disc Condition.
The Interior:- Power Window Controls, Power Mirror Controls, Lights & Washer, AC Controls,Pedals, Steering Wheel, Gear Knob.
The Underbody:- Front Bumper, Left Sideskirt, Rear Bumper, Right Sideskirt, Engine Sump, Exhaust Assembly.
93. Tell us the 5- 5 name of car or vehicle of different Brands ?
| Brand | Car Models in the Indian Market |
|---|---|
| Maruti Suzuki | Swift, Baleno, Alto, Vitara Brezza, Dzire |
| Mahindra & Mahindra | Scorpio, XUV500, Thar, Bolero, KUV100 |
| Tata | Nexon, Harrier, Tiago, Tigor, Safari |
| BMW | 3 Series, X5, 7 Series, X3, 5 Series |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class, E-Class, GLC, GLE, A-Class |
| Volvo | XC60, S60, XC90, XC40, V90 Cross Country |
| Hyundai | Creta, i20, Venue, Verna, Santro |
| Toyota | Innova Crysta, Fortuner, Glanza, Corolla Altis, Urban Cruiser |
| Honda | City, Amaze, WR-V, Jazz, Civic |
| Chevrolet | (Note: GM exited the Indian market in 2017) |
| Ford | EcoSport, Endeavour, Figo, Freestyle, Aspire |
| MG (Morris Garages) | Hector, ZS EV, Gloster, Hector Plus, Astor |
94. What is the difference between two wheeler, three wheeler and four wheeler engine ?
| Aspect | Two-Wheeler Engines | Three-Wheeler Engines (Auto Rickshaws) | Four-Wheeler Engines (Cars) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engine Placement | Between the two wheels | At the rear, driving one of the rear wheels | Front of the vehicle |
| Engine Types | Single-cylinder, twin-cylinder, sometimes multi-cylinder | Typically single-cylinder, four-stroke | Four-cylinder, six-cylinder, eight-cylinder, etc. |
| Engine Size/Displacement | Smaller | Smaller | Larger |
| Cooling System | Air-cooled (smaller models), liquid-cooled (larger models) | Air-cooled (common), sometimes liquid-cooled | Liquid-cooled |
| Transmission Options | Manual transmission with gears and clutch, or automatic (e.g., CVT) | Manual transmission with gears and clutch, or automatic (e.g., CVT) | Manual, automatic, CVT, dual-clutch, etc. |
| Purpose/Application | Lightweight, compact | Efficiency, short-distance transportation | Wide range of applications |
| Load Capacity | Limited | Relatively lighter loads | Heavier loads |
95.What is the full form of MRF ? (Tyre Company)
Madras Rubber Factory
96. Clutch, Gear, Wheel, Axle, Shaft Put together form the ?
Transmission System
97. Double Wishbone is a type of ______?
Suspension Type
98. Which is the largest two-wheeler company in the World in terms of Sales ?
Hero MotoCorp
99. Who invented the 4 stroke petrol engine ?
Nkolaus Otto
Here, Also find the Some Important Automobile Engineering Question Given Below:-
- “What is the difference between torque and horsepower?”
- “Explain the working principle of an internal combustion engine.”
- “How do you calculate the compression ratio of an engine?”
- “What are the advantages of using turbochargers in engines?”
- “What is the purpose of a differential in a vehicle?”
- “Describe the function of a catalytic converter in an exhaust system.”
- “What is the role of a transmission in a vehicle?”
- “What are the main components of a suspension system?”
- “How do you diagnose and fix engine knocking?”
- “Explain the concept of oversteer and understeer in vehicle handling.”
- “What is the importance of vehicle aerodynamics?”
- “How is engine displacement measured?”
- “Discuss the working principle of an automatic transmission.”
- “What is the function of an EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) system?”
- “What are the different types of braking systems used in vehicles?”
- “Explain the term ‘valve overlap’ in engine timing.”
- “What is the purpose of a crankshaft in an engine?”
- “Describe the advantages of using a hybrid drivetrain.”
- “How does a fuel injection system work in modern engines?”
- “What are the factors affecting tire wear in a vehicle?”
- “Explain the difference between front-wheel drive and rear-wheel drive.”
- “What is a drivetrain and how does it work?”
- “Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of electric vehicles (EVs).”
- “What are the key components of an exhaust system?”
- “Explain the concept of regenerative braking in hybrid and electric vehicles.”
- “What is the function of a camshaft in an engine?”
- “How do you calculate the gear ratio in a transmission?”
- “What are the key safety features in modern automobiles?”
- “Explain the purpose of an anti-lock braking system (ABS).”
- “What is the role of an alternator in a vehicle’s electrical system?”
- “How is engine efficiency measured, and what factors affect it?”
- “Discuss the differences between a carburetor and fuel injection.”
- “What is the significance of engine timing in combustion engines?”
- “How do you calculate a vehicle’s miles per gallon (MPG) fuel efficiency?”
- “What are the challenges and benefits of autonomous vehicles?”
- “Explain the concept of all-wheel drive (AWD) and when it’s advantageous.”
- “What is the importance of proper wheel alignment in vehicle handling?”
- “Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using aluminum in engine construction.”
- “What is the role of a powertrain control module (PCM) in modern vehicles?”
- “How do you diagnose and troubleshoot engine misfires?”
- “What is the function of a supercharger in an engine?”
- “Explain the differences between naturally aspirated and forced induction engines.”
- “What is the role of a torque converter in an automatic transmission?”
- “How does a differential lock work, and when is it useful?”
- “Discuss the environmental impact of emissions from internal combustion engines.”
- “What is the purpose of a serpentine belt in a vehicle’s engine?”
- “How are vehicle emissions controlled, and what are emission standards?”
- “Explain the concept of variable valve timing (VVT) in engines.”
- “What is the significance of engine balancing?”
- “Discuss the importance of tire pressure maintenance for safety and efficiency.”
- “What is the difference between a V6 and a V8 engine?”
- “Explain the role of an air filter in an engine.”
- “How is engine oil viscosity important for engine performance?”
- “What is the function of a throttle body in the engine?”
- “Discuss the differences between front-engine and mid-engine layouts.”
- “Explain the purpose of a transmission fluid cooler.”
- “What are the key components of a fuel delivery system in a vehicle?”
- “How does regenerative suspension technology work in vehicles?”
- “What are the primary factors affecting vehicle fuel efficiency?”
- “Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of diesel engines.”
- “What is the role of a radiator in engine cooling?”
- “Explain the significance of engine timing belts or chains.”
- “How do you diagnose and fix engine overheating issues?”
- “What is the importance of a catalytic converter in reducing emissions?”
- “Discuss the differences between an inline engine and a V-shaped engine.”
- “What is the function of a transmission control module (TCM)?”
- “Explain the concept of hybrid vehicle regenerative braking.”
- “How are vehicle emissions tested and measured?”
- “What are the benefits of using lightweight materials in vehicle design?”
- “Discuss the purpose of a crankcase ventilation system.”
- “How does a limited-slip differential work, and when is it used?”
- “What are the main factors affecting vehicle suspension tuning?”
- “Explain the advantages of direct fuel injection in engines.”
- “What is the significance of vehicle chassis design for safety and performance?”
- “Discuss the differences between rear-wheel steering and front-wheel steering.”
- “What are the key components of a hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) drivetrain?”
- “How does a continuously variable transmission (CVT) work?”
- “Explain the role of a fuel pressure regulator in an engine’s fuel system.”
- “What is the function of a power steering system in a vehicle?”
- “Discuss the impact of engine size on vehicle performance and efficiency.”
- “How is engine efficiency affected by the air-fuel ratio?”
- “What are the key factors influencing engine knock and detonation?”
- “Explain the differences between an inline-four and an inline-six engine.”
- “What is the significance of a transmission torque converter lockup?”
- “How does a hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) differ from a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV)?”
- “Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using hydrogen as a vehicle fuel.”
- “What is the role of electronic stability control (ESC) in vehicle safety?”
- “Explain the concept of variable displacement technology in engines.”
- “How do you diagnose and address engine oil leaks?”
- “What is the importance of a vehicle’s center of gravity in handling?”
- “Discuss the impact of vehicle weight on fuel efficiency and performance.”
- “What are the key components of a vehicle’s electrical system?”
- “Explain the function of an exhaust gas temperature (EGT) sensor.”
- “How does a turbocharged engine differ from a naturally aspirated engine?”
- “What are the primary factors affecting tire grip and traction?”
- “What is the significance of vehicle wheelbase length?”
- “Discuss the importance of proper vehicle maintenance for longevity and safety.”
- “How are vehicle emissions regulated on a global scale?”
- “What are the future trends and innovations in automobile engineering?”
Conclusion [Automobile Interview Questions]
By familiarizing yourself with these top 10 automobile engineering interview questions and their answers, you will be better prepared for your next interview. Remember to also research the company and industry trends to demonstrate your knowledge and passion for the field. Good luck!
Automobile Engineering Course [Video]
Automobile Engineering Course: Ignite Your Passion for Automotive Innovation! [Blogs]
Mohd. Sharif Qualification: B.Tech (Mechanical Engineering) [Founder of Wisdom Academy] [Aim Foundation & Free-Education.In] [Engineer By Profession | Teacher By Choice] [Blogger, YouTube Creator]


