Applied mechanics or Engineering mechanics is a branch of the physical sciences and the practical application of mechanics.
Pure mechanics describes the response of bodies or systems of bodies to external behavior of a body, in either a beginning state of rest or of motion, subjected to the action of forces.
Q. What is Force ?
Force , It may be defined as an agent which produce or tends to produce or destroy tends to destroy the motion of body.
It may be consider for:
- Change of motion of the body
- Retard the motion of the body
- Balance the forces which acts on the body
- Give rise the internal forces in the body.
The characteristics of the forces are:
- Nature of the force (Push or Pull)
- Line of action of the force
- Point at which the force acts on the body
- Magnitude of the force
S.I. Unit of the force is Newton(N). 1kgf = 9.81N
Q. What is Resultant Force ?
Resultant force is a single force which produce the same effect as produce by all the force acts on the body.
Resultant force can be found out by following method:
- Parallelogram Law
- Triangle Law
- Polygon Law
Q. The angle between two forces when the resultant is maximum and minimum respectively are:
0 and 180 degree.
Q. Concurrent forces are those forces whose lines of action:
meet at one point.
Q. If the resultant forces acting on a body is zero, then the body will be in Equilibrium. (Yes/No)
Yes.
Q. Process of finding out the resultant force is called _________ of the force?
Composition of the force.
Q. what are Coplaner Forces ?
Coplaner forces are those force whose line of action lies in the same plane.
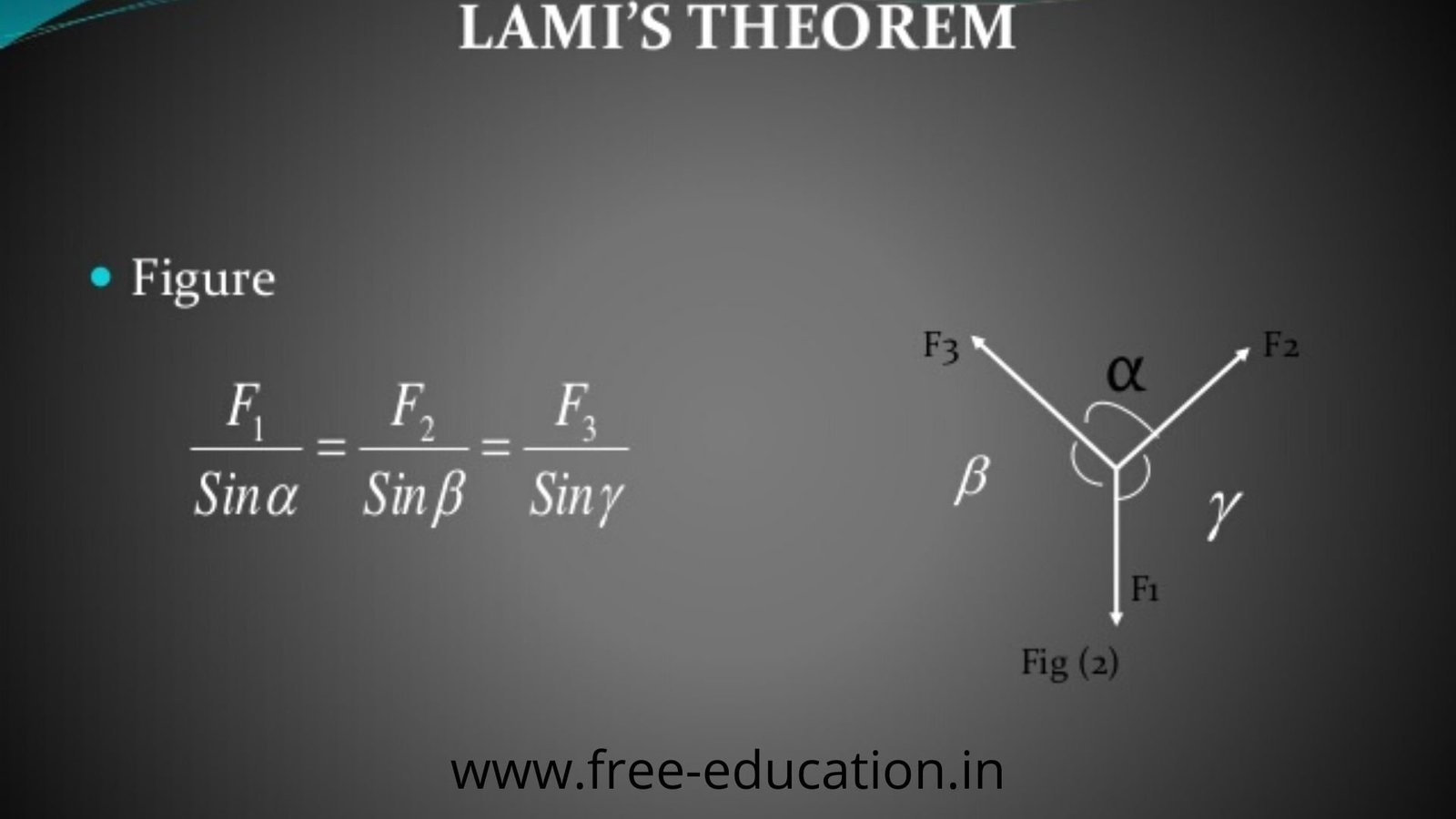
Q. Define Lami’s Theorem ?
If three coplaner force acting on a point are in equilibrium, then each force is proportional to the sine angle between the other two forces.
Q. The Moment of a force?
- The moment of force is the turning effect produced by a force, on the body, on which it acts.
- The moment of force is equal to the product of the force acting on the body and the perpendicular distance of a point and the line of action of the force.
- The moment of a force is equal to twice area of a triangle, whose base is the line representing the force and whose vertex is the point, about which the moment is taken.
Q. What is Varingon’s Theorem ?
The algebraic sum of their moments about the any point is equal to the moment of the resultant force about the same point.