CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
Pure Substances: Many substances around us contain only one type of constituent particles. Elements and compounds are pure substances. Some of the pure substances are iron, copper, water, salt, etc.
Impure Substances: Substances containing more than one type of constituent particles are called impure substances. Some of the impure substances are pond water, milk, etc.
Impurities: These are the unwanted particles present in a substance making it impure.
Mixtures: Substances which contain more than one component mixed in any ratio are called mixtures. For example, air is a mixture of many gases like nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, dust particles, etc.
Homogeneous Mixtures: The mixtures in which the particles of the substances present cannot be seen are called homogeneous mixtures. For example, solution of sugar and water, air, cold drinks, etc.
Heterogeneous Mixtures: The mixtures in which particles of the substances present can be seen easily are called heterogeneous mixtures. For example, water in oil, dust in air.
Need for Separation: We carry out the separation of the components of a mixture or an impure substance with the following purposes:
- To remove the unuseful or harmful component.
- To obtain the useful component.
- To remove impurities for getting a pure sample.
Principle of separation
- The substances present in a mixture retain their original properties like particle size, density, melting point, boiling point, volatility, etc.
- We use the difference in any one of these properties in the components of a mixture to separate them.
Methods of Separation: Handpicking, winnowing, sieving, magnetic separation, sedimentation, decantation, loading, filtration, evaporation, sublimation, distillation, churning, etc., are some common methods of separation.
Churning (or Centrifugation): It is the process of separation of the lighter particles of a suspended solid from a liquid. For example, to obtain butter from the curd or milk.
Condensation: The process of conversion of water vapour into its liquid form is called condensation.
Crystallisation: The process of crystallisation is used for obtaining pure crystalline substance from impure sample.
Decantation: It is the transfer of clean liquid from one vessel to the other without disturbing the settled (sedimented) particles.
Evaporation: It is the process of removing water (or moisture) from a mixture either by heating on flame or direct sunlight. For example, salt from sea water is obtained by this method.
Filtration: Filtration is used to separate solid particles from liquid by passing the mixture through a filter paper.
Handpicking: This method is used for separating small particles of dirt, stone, husk, etc., from the grains of wheat, rice, pulses, etc.
Loading: It is the process of faster sedimentation by suspending alum to a liquid.
Sedimentation: It is the process of settling of heavy solid particles in a mixture at the bottom of the vessel.
Sieving
- Sieving is used when two components of a mixture have different particle sizes.
- Sieving allows the fine particles to pass through the holes of the sieve, while the bigger particles remain on the sieve. For example, sieving of wheat flour, sieving of sand at construction sites.
Saturated solution: A solution in which no more soluble substance can be dissolved at room temperature is called saturated solution.
Solution: When a soluble substance is dissolved completely in a liquid (say sugar in water), a homogeneous mixture is formed. It is known as a solution.
Threshing: The process that is used to separate grain from stalks is threshing.
Winnowing: Winnowing can be used to separate lighter and heavier components of a mixture. For example, to separate husk from grain with the help of air.
Methods Of Separation:
Different methods are used for separating different substances that are mixed together. Let us learn about some common methods that are used.
Threshing:
Grains or seeds of plants like rice and wheat serve as sources of food. The flour (atta) that is used for making chapattis is made from wheat grains. After these crops have been harvested or cut, the grains need to be separated from the stalks (the dried stems). This is done by threshing.
The process of beating harvested crops to separate the grains from the stalks is called threshing. It is done manually (by hand) or with the help of machines. Manual threshing is done by holding a pile of crop and beating it on a rock or a hard surface (Fig. 3.1). This loosens and separates the grain from the stalk. Sometimes, threshing is also done by crushing the harvested stalks using bullocks.


Threshing is also done with the help of machines like the combine harvester (Fig. 3.2). Threshed grains may still contain seed coverings and tiny pieces of leaves or stem (collectively called chaff). These are separated by winnowing.
Winnowing:
The method used to separate chaff from the grain by wind or blowing air is called winnowing.
The mixture of chaff and grain is taken in a winnowing basket (Fig. 3.3). The farmer stands at a higher level and lets the mixture fall to the ground.
The grain, being heavier, falls almost vertically whereas the lighter chaff is carried away by the wind and forms a separate heap away from the grain.
The separated chaff is used as fodder for cattle. The direction of the wind plays an important role in the process of winnowing.

Hand-picking:
Rice, wheat, pulses, etc., that we buy from the market may contain impurities (unwanted or harmful particles) in the form of small stones, unwanted grains, etc. Often, these impurities look very different from the food item and can be spotted easily. The method of separation used in such a case is hand-picking (Fig. 3.4). This method is preferred when
- the quantity of the mixture is small,
- the unwanted substance is present in smaller quantities, and
- the size, shape, or colour of the unwanted substance is different from that of the useful one.

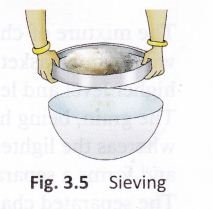
Sieving:
If the components of a mixture are of different sizes, they can be separated by sieving (Fig. 3.5). The smaller component passes through the pores of the sieve whereas the larger component (stones or husk) is left behind in it. This method is used in some homes to separate wheat bran (the bigger particles) from flour.
However, sieving wheat flour is not advisable as wheat bran, which is removed during sieving, is very rich in nutrients and is also a rich is better to remove visible impurities by hand picking.
The process of sieving is also used to separate pebbles and stones from sand at construction sites. The stones and pebbles present in the mixture remain in the sieve and the fine sand particles pass through the holes of the sieve.
Sedimentation and Decantation:
Have you seen pulses being washed in your home? When pulses are kept in a bowl of water, they settle down as they are heavy. However, dirt, insects, tiny pieces of straw, and other lighter impurities float at the top. The water, which contains these impurities, is then poured out and discarded. This process involves two methods: sedimentation and decantation.
The process of separating insoluble solids, suspended in a liquid, by allowing them to settle down is called sedimentation.
The solid particles that settle down during sedimentation are called sediments.
The process of pouring out the clear upper liquid without disturbing the sediments is called decantation.
The liquid above the sediments is called a supernatant.
A mixture of sand and water can also be separated by sedimentation and decantation.
The mixture is left undisturbed for some time.
Sand, being heavier, settles down and water is poured out into a separate container.

Filtration:
The process by which two substances (an insoluble solid and a liquid) are separated by passing the mixture through a filtering device is called filtration.
Filtration is commonly used in our homes. For example, after preparing tea, we filter out the tea leaves using a strainer. Filtration is also done to remove pulp from fresh fruit juice. Water may also contain solid impurities, which can be removed by filtration.
During filtration, the insoluble solid is retained in the filtering device whereas the liquid passes through it. It is important that the particles of the insoluble solid are bigger than the holes in the filtering device for them to be retained in it. A filter paper is a filtering device that has very fine pores in it.

Condensation:
The process in which gas changes into liquid is called condensation. Condensation is the opposite of evaporation. In nature, water vapour in the air condenses to form its liquid form, the dew. Condensation takes place only when water vapour hits a cold surface.
Solution And Solubility:
When some salt is added to water and stirred, the salt disappears. This is because the salt has dissolved in the water.

Dissolving is a change where substances mix completely with the liquid they have been added to.
Not all substances dissolve in water. Only some substances,Salt dissolves in water. like salt and sugar, dissolve in water and are known as soluble substances. Substances like chalk and sand do not dissolve in water and are known as insoluble substances.
The substance that dissolves is called the solute and the substance in which the solute dissolves is called the solvent. The resulting mixture is called the solution. Thus, solute + solvent = solution.
E.g., sugar + water = sugar solution.

If we keep adding spoonfuls of sugar to water and stir the solution each time, what will happen after some time? We will notice some grains of sugar at the bottom of the solution. This shows that no more sugar can be dissolved. We say that the solution has become saturated (Fig. 3.7).
A saturated solution is the solution in which no more of the solute can be dissolved.
But what if we heat the solution? Can we then dissolve that ‘extra’ sugar present in the saturated solution?
Yes, we can increase the solubility of a solute by heating the solution. Solubility is the ability of a substance to get dissolved in a given liquid. The quantity of a substance that can dissolve in hot water is much more as compared to that in cold water.
There are some other factors that increase the solubility of a solute.
Stirring We can observe this by taking two glasses of water and adding a spoonful of sugar to each glass. Then we keep one glass undisturbed and stir the other. Sugar dissolves faster when the solution is stirred.
Solute in powdered form We can observe this by taking two glasses of water and adding a whole sugar cube in one glass and powdered or crushed sugar cube in the other. Sugar in the powdered form dissolves first.
Different substances dissolve in different amounts of water while making a saturated solution.
Threshing The process of beating harvested crops to separate seeds from the stalks is called threshing.
Winnowing The method used to separate chaff from the grain by wind or blowing air is called winnowing.
Sedimentation The process of separating insoluble solids suspended in a liquid by allowing them to settle down is called sedimentation.
Decantation The process of pouring out the clear upper liquid without disturbing the sediments is called decantation.
Filtration The process by which an insoluble solid is separated from a liquid by passing the mixture through a filtering device is called filtration.
Saturated solution A solution that can dissolve no more of the solute is called a saturated solution.
Threshing is done either manually or by using machines to separate seeds or grains from the stalks.
Winnowing involves separating the chaff from the grain by letting the mixture fall to the ground from a height when the wind is blowing.
Hand-picking involves manually removing small stones, insects, etc. from the grains.
Sedimentation and decantation are used to separate an insoluble solid from a liquid.
Insoluble solid impurities present in water can be removed by filtration.
Common salt can be separated from seawater by evaporation.
Solubility of a solute can be increased by heating the mixture or it can also be increased by adding the solute in the powdered form.