About Lesson
Introduction to Sound
Introduction to waves
- The sound is produced by vibrating objects.
- They travel from one place to another in the form of waves. Hence, the name sound waves.

Wave and particle motion of waves
- Mechanical waves are waves that travel through a material medium.
- It is of two types: depending on the direction of motion of the particle of the medium and the wave propagation:
*transverse
*longitudinal

ransverse waves
- Particle motion is to perpendicular the direction of wave motion.
- This type of wave is a mechanical wave called a transverse wave. E.g.: Light, or even Mexican wave in a stadium.
Longitudinal waves
- When the particles of the medium travel parallel to the direction of the wave motion by means of successive compression or rarefaction.
- It is also a mechanical wave.
- Example: a slinky
Sound Properties
Introduction to sound waves
– Sound needs a medium to propagate. The matter or material through which sounds propagates is called a medium.
– Sound cannot travel in a vacuum. The moon does not have an atmosphere, hence, you can hear on the moon.
Sounds by Humans
How do humans produce sound?
- The sound produced in the voice box called larynx located at the upper end of the windpipe.
- 2 vocal cords get stretched across in the voice box. Has a slit, through which air is forced out by the lungs.
- Muscles attached to vocal cords make it tight or loose.
Hearing
Human ear
- Outer ear = pinna: collects sound from the surroundings.
- Sound passes through a tube called an auditory canal.
- Eardrum (tympanic membrane) → vibrates when the sound incident.
- Vibrations are sent to the inner ear, from there it goes to the brain as signals via the auditory nerve.

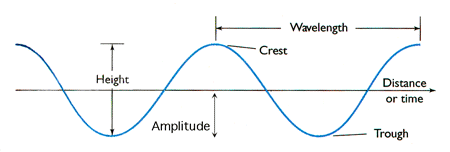
Amplitude, Time Period and Frequency
Amplitude, frequency and time period of vibrations
- The magnitude of disturbance in the medium on either side of the mean value is called as Amplitude(A). Larger the amplitude, louder the sound.
- The number of oscillations per second is called frequency. Expressed in Hertz (Hz).
- Time taken for one complete oscillation to travel across a point. T = 1/f. (Seconds)
Loudness and Pitch
- Volume or loudness of a sound depends on the amplitude. The force with which an object is made to vibrate gives the loudness.
- The number of oscillations per unit time. Directly proportional to frequency.

Audible and inaudible sounds
- Audible range = 20Hz to 20kHz known as the Sonic range.
- Below 20 Hz (inaudible) → infrasonic range
- Above 20 kHz (inaudible) → Ultrasonic range
Noise Pollution
Noise and music
– Sounds with the same pitch and loudness can be distinguished based on the quality. Music is pleasant to the ears while noise is not.
– Unpleasant sounds are called as noise.

Noise pollution and measures to control it
– Presence of excessive unwanted noise in our surroundings is called as noise pollution.
– Can cause hearing impairment, sleeplessness and also hypertension.
– Must be minimised by reducing noisy operations and honking in residential areas. Planting trees along roads also cut down the noise.

Join the conversation