About Lesson
Introduction to Reproduction
- Reproduction is the process of giving rise to an offspring.
- Reproduction is essential for the continuation of a species.
- There are two modes of reproduction:
- Sexual reproduction and
- Asexual reproduction
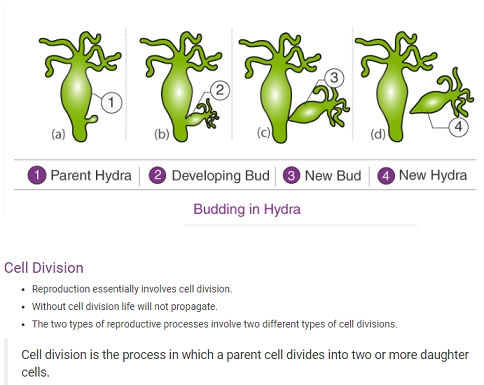
Asexual reproduction
The type of reproduction in which only a single parent is involved is called asexual reproduction.
- There is no mixing of genetic information.
- Eg: buds in Hydra
Sexual reproduction
The type of reproduction, which involves two parents to give rise to an offspring is called as sexual reproduction.
- The males and females have different reproductive parts or organs.
- These organs produce the male and female gametes, which fuse together to form the offspring.
- Genetic information from both parents is inherited.
- Eg: humans
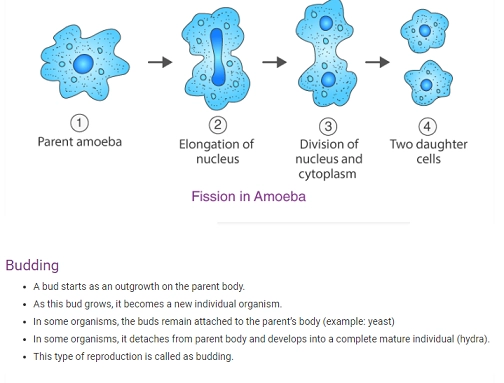
Fission
It is a type of asexual reproduction in which a single-celled organism divides into two.
- Division of nucleus is followed by division of other cell organelles in the cytoplasm and finally the cytoplasm.
- Thus two cells are produced from one parent cell.
- Example: Amoeba.
- Amoeba reproduces by binary fission, which is dividing into two cells.
If one parent cell gives rise to many daughter cells, this type of fission is called as multiple fission.
Cell division provides more cells:
- For growth
- Regeneration
- Repair and damage control
- Gamete formation
There are two types of cell division:
- Mitosis
- Meiosis
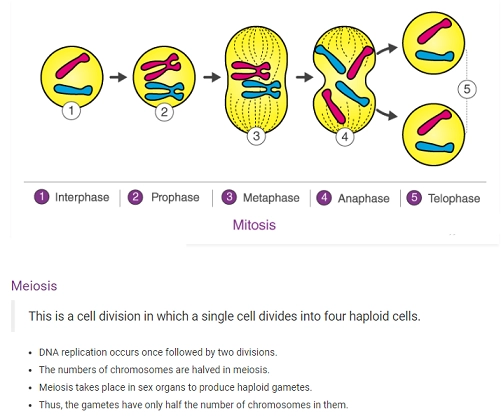
Mitosis
Mitosis is a process where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
- DNA replication occurs once followed by a single division.
- The number of chromosomes is maintained in this type of division.
- This type of division happens in asexual reproduction.
- It is also used for growth, repair and regeneration of tissues.

Sexual Reproduction in Humans
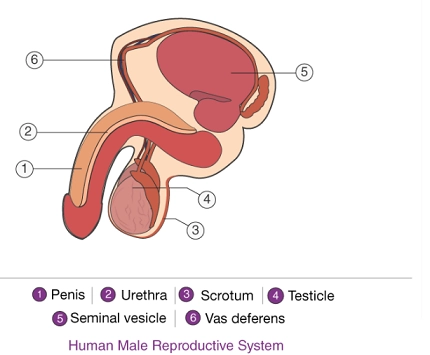
Male reproductive system
- The male reproductive system consists of a pair of testes, a pair of sperm ducts and a penis.
- The testes are located outside the male body.
- Sperms are produced in testes.
- Sperms are the male gametes.
Testosterone
- Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and is produced by the testes.
- Testosterone is responsible for the development of sex organs, production of sperms and also the development of secondary sexual characteristics.
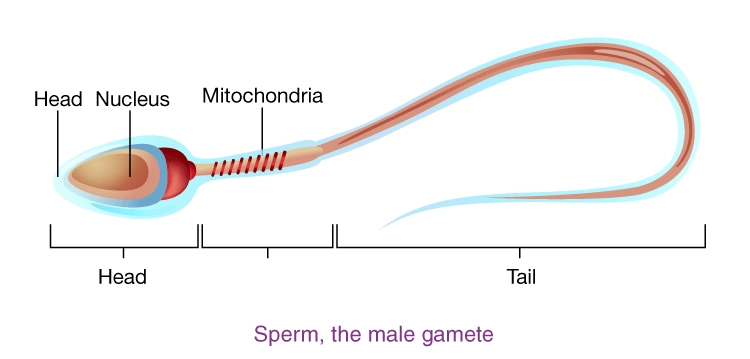
Sperms
- Sperms are the male gametes produced by testes in humans.
- Millions of sperms are produced by the testes in a day.
- Each sperm is a single, microscopic cell having a head, a middle piece and a tail as its parts.
- Head contains a nucleus with a single set of chromosomes.
- The middle piece contains a large number of mitochondria that provide energy during active movement.
- Sperm is a motile gamete, which moves through the female reproductive tract with the help of the tail.
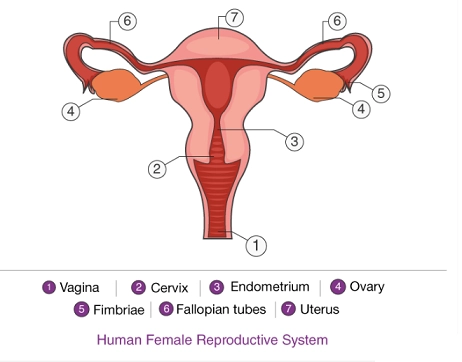
Female reproductive system
- The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of fallopian tubes (oviducts) and a single uterus.
- Ova are produced by ovaries.
- Fallopian tubes (oviducts) carry the ova from ovaries to the uterus.
- Uterus holds the growing embryo/foetus and thus helps in holding the pregnancy.
Oestrogen
- Estrogen or oestrogen is the primary female sex hormone secreted by ovaries.
- It is responsible for the development of female reproductive organs, secondary sexual characteristics, development of female gamete i.e. Ovum and maintenance of menstrual cycle.
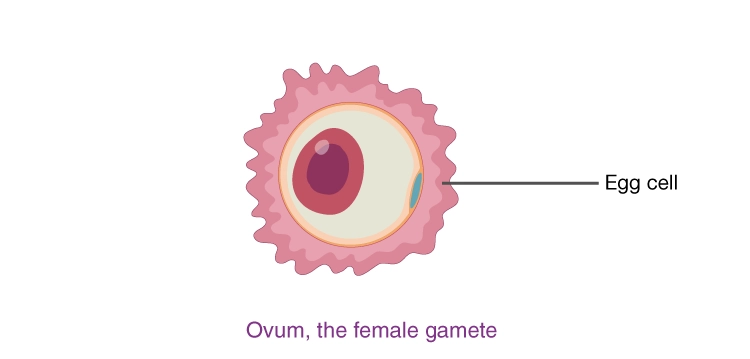
Ovum
- The ovary produces the female gametes known as ovum or ova (plural).
- In human beings, a single mature egg or ovum is released into the oviduct/fallopian tube by the respective side ovary every month.
- The ovum is a single cell and is much larger than the sperm.
- It is non-motile and is carried to the uterus by the oviduct.
Fertilization
Fertilization is the process of fusion of the male gamete with the female gamete.
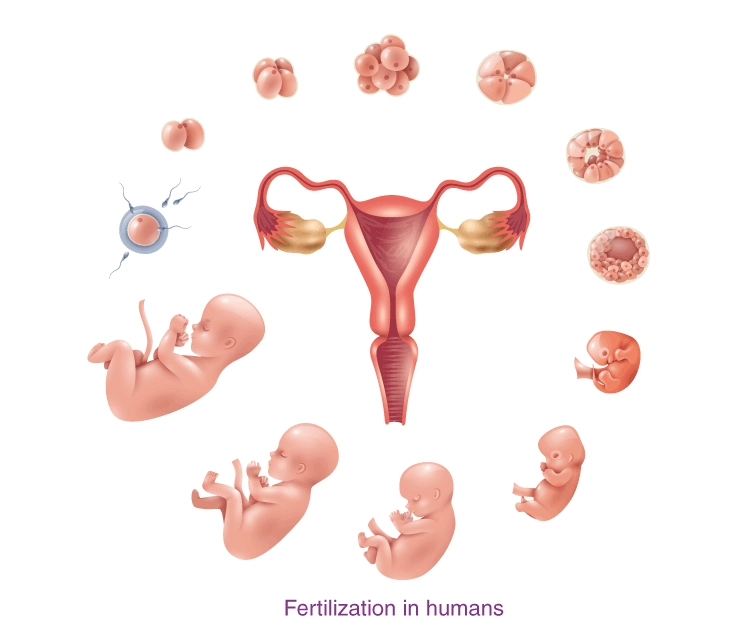
- Both the gametes containing haploid (single) set of chromosomes fuse and thus maintain the diploid (double) number of chromosomes.
- The fertilized ovum is now called a zygote.
- In human fertilization takes place in the fallopian tube and then the zygote is carried to the uterus.
- Inside the uterus, it undergoes repeated divisions and grows and becomes an embryo.
Join the conversation