CBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
Physical Properties of Metals:
Metals are:
- hard to touch.
- lustrous i.e., freshly Cut surfaces of metals have characteristic shining.
- malleable; the property of metals by which they can be beaten mW thin sheets is called malleability.
- ductile; the property of metal by which it can be drawn into wires is called ductility.
- sonorous i.e., metals produce ringing sound when struck on a hard surface.
- Good conductors of heat and electricity.
Metals like sodium and potassium are soft and can be cut with a knife.
Mercury is the only metal which is found in the liquid state at room temperature.
Physical Properties of Non-metals:
- Non-metals are soft and dull (e.g., coal and sulphur).
- Non-metals are generally brittle, i.e., they break down into a powdery mass on tapping with a hammer.
- They are not sonorous.
- They are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
Chemical Properties of Metals and Non-metals:
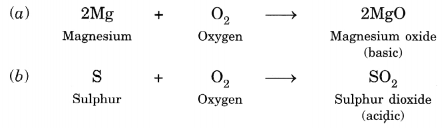
Reaction with Oxygen: Both metals and non-metals when burnt in oxygen from their oxides. Oxides of metals are basic in nature while that of non-metals are generally acidic in nature e.g.,
Reaction with Water: Some metals react with water to produce metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas. Generally, non-metals do not react with water.
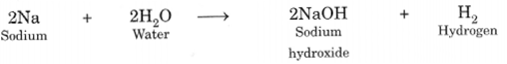
Reaction with Acids: Metals react with dii. acids and produce metal salt and hydrogen gas. Generally, non-metals do not react with dil. acids.
Reaction with Bases: Metals react with bases to produce hydrogen gas.
Displacement Reaction: More reactive metals displace less reactive metals from their metal compounds in aqueous solutions.
Uses of Metals and Non-metals
- Metals are used in making machinery automobiles, aeroplanes. trains, satellites, industrial gadgets, cooking utensils, water boilers etc.
- Non-metals are also used in day-to-day life. Some examples are:
- oxygen is essential for life.
- nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium are used as fertilizers.
- chlorine is used as a water purifier.
Atom: Atom is the smallest particle of matter which cannot be divided further by any physical means. Atoms are the basic units from which molecules and ions are formed.
Conductor: Substances which allow heat/electricity to pass through them are called conductors of heat/electricity
Displacement reaction: More reactive metals displace less reactive metals from their compounds in aqueous solutions.
Ductility: The property of metals by which they can be drawn into wires is called ductility
Elements: Substances whose molecules contain only one type of atoms are known as elements.
Hardness: Metals are hard, on the other hand, non-metals are generally brittle.
Malleability: The property of metals by which they can be beaten into thin sheets is called malleability.
Metals: The materials which are generally hard, lustrous, malleable, ductile, sonorous and good conductors of heat and electricity are called metals
Metalloids: Elements which possess characters of both metals and non-metals are called met.alloids.
Non-metals: Materials which are soft, dull in appearance, brittle, not sonorous and poor conductors of heat and electricity are called non-metals.
Sonorous: Metals are called sonorous because they produce a specific ringing sound.