Exercise 11.4 Page: 226
1. A garden is 90 m long and 75 m broad. A path 5 m wide is to be built outside and around it. Find the area of the path. Also find the area of the garden in hectare.
Solution:-
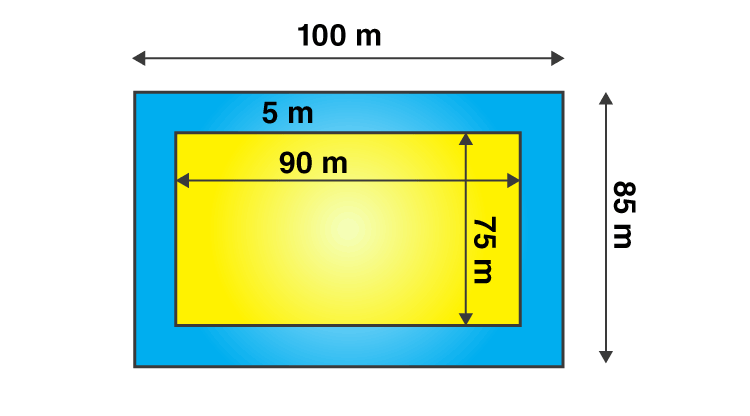
From the question it is given that,
Length of the garden (L) = 90 m
Breadth of the garden (B) = 75 m
Then,
Area of the garden = length × breadth
= 90 × 75
= 6750 m2
From the figure,
The new length and breadth of the garden when path is included is 100 m and 85 m respectively.
New area of the garden = 100 × 85
= 8500 m2
The area of path = New area of the garden including path – Area of garden
= 8500 – 6750
= 1750 m2
For 1 hectare = 10000 m2
Hence, area of garden in hectare = 6750/10000
= 0.675 hectare
2. A 3 m wide path runs outside and around a rectangular park of length 125 m and breadth 65 m. Find the area of the path.
Solution:-

From the question it is given that,
Length of the park (L) = 125 m
Breadth of the park (B) = 65 m
Then,
Area of the park = length × breadth
= 125 × 65
= 8125 m2
From the figure,
The new length and breadth of the park when path is included is 131 m and 71 m respectively.
New area of the park = 131 × 71
= 9301 m2
The area of path = New area of the park including path – Area of park
= 9301 – 8125
= 1176 m2
3. A picture is painted on a cardboard 8 cm long and 5 cm wide such that there is a margin of 1.5 cm along each of its sides. Find the total area of the margin.
Solution:-

From the question it is given that,
Length of the cardboard (L) = 8 cm
Breadth of the cardboard (B) = 5 cm
Then,
Area of the cardboard = length × breadth
= 8 × 5
= 40 cm2
From the figure,
The new length and breadth of the cardboard when margin is not included is 5 cm and 2 cm respectively.
New area of the cardboard = 5 × 2
= 10 cm2
The area of margin = Area of the cardboard when margin is including – Area of the
cardboard when margin is not including
= 40 – 10
= 30 cm2
4. A verandah of width 2.25 m is constructed all along outside a room which is 5.5 m long and 4 m wide. Find:
(i) the area of the verandah.
(ii) the cost of cementing the floor of the verandah at the rate of Rs 200 per m2.
Solution:-
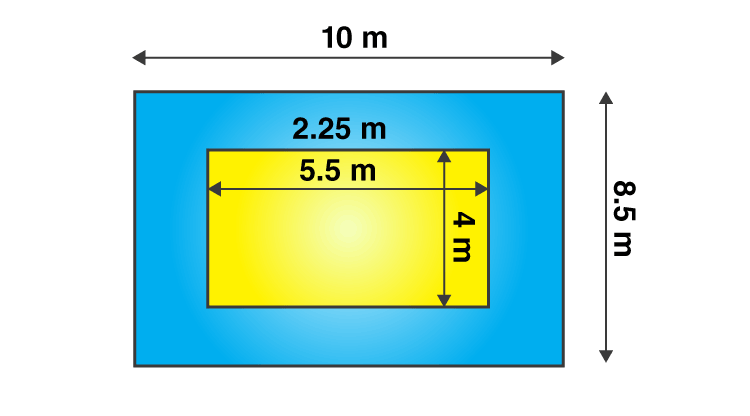
(i)
From the question it is given that,
Length of the room (L) = 5.5 m
Breadth of the room (B) = 4 m
Then,
Area of the room = length × breadth
= 5.5 × 4
= 22 m2
From the figure,
The new length and breadth of the room when verandah is included is 10 m and 8.5 m respectively.
New area of the room when verandah is included = 10 × 8.5
= 85 m2
The area of verandah = Area of the room when verandah is included – Area of the room
= 85 – 22
= 63 m2
(ii)
Given, the cost of cementing the floor of the verandah at the rate of Rs 200 per m2
Then the cost of cementing the 63 m2 area of floor of the verandah = 200 × 63
= Rs 12600
5. A path 1 m wide is built along the border and inside a square garden of side 30 m. Find:
(i) the area of the path
(ii) the cost of planting grass in the remaining portion of the garden at the rate of Rs 40 per m2.
Solution:-

(i)
From the question it is given that,
Side of square garden (s) = 30 m
Then,
Area of the square garden = S2
= 302
= 30 × 30
= 900 m2
From the figure,
The new side of the square garden when path is not included is 28 m.
New area of the room when verandah is included = 282
= 28 × 28
= 784 m2
The area of path = Area of the square garden when path is included – Area of the square
Garden when path is not included
= 900 – 784
= 116 m2
(ii)
Given, the cost of planting the grass in the remaining portion of the garden at the rate of
= Rs 40 per m2
Then the cost of planting the grass in 784 m2 area of the garden = 784 × 40
= Rs 31360
6. Two cross roads, each of width 10 m, cut at right angles through the centre of a rectangular park of length 700 m and breadth 300 m and parallel to its sides. Find the area of the roads. Also find the area of the park excluding cross roads. Give the answer in hectares.
Solution:-

From the question it is given that,
Length of the park (L) = 700 m
Breadth of the park (B) = 300 m
Then,
Area of the park = length × breadth
= 700 × 300
= 210000 m2
Let us assume that ABCD is the one cross road and EFGH is another cross road in the park.
The length of ABCD cross road = 700 m
The length of EFGH cross road = 300 m
Both cross road have the same width = 10 m
Then,
Area of the ABCD cross road = length × breadth
= 700 × 10
= 7000 m2
Area of the EFGH cross road = length × breadth
= 300 × 10
= 3000 m2
Area of the IJKL at center = length × breadth
= 10 × 10
= 100 m2
Area of the roads = Area of ABCD + Area of EFGH – Area of IJKL
= 7000 + 3000 – 100
= 10000 – 100
= 9900 m2
We know that, for 1 hectare = 10000 m2
Hence, area of roads in hectare = 9900/10000
= 0.99 hectare
Finally, Area of the park excluding roads = Area of park – Area of the roads
= 210000 – 9900
= 200100 m2
= 200100/10000
= 20.01 hectare
7. Through a rectangular field of length 90 m and breadth 60 m, two roads are constructed which are parallel to the sides and cut each other at right angles through the centre of the fields. If the width of each road is 3 m, find
(i) the area covered by the roads.
(ii) the cost of constructing the roads at the rate of Rs 110 per m2.
Solution:-

(i)
From the question it is given that,
Length of the field (L) = 90 m
Breadth of the field (B) = 60 m
Then,
Area of the field = length × breadth
= 90 × 60
= 5400 m2
Let us assume that ABCD is the one cross road and EFGH is another cross road in the park.
The length of ABCD cross road = 90 m
The length of EFGH cross road = 60 m
Both cross road have the same width = 3 m
Then,
Area of the ABCD cross road = length × breadth
= 90 × 3
= 270 m2
Area of the EFGH cross road = length × breadth
= 60 × 3
= 180 m2
Area of the IJKL at center = length × breadth
= 3 × 3
= 9 m2
Area of the roads = Area of ABCD + Area of EFGH – Area of IJKL
= 270 + 180 – 9
= 450 – 9
= 441 m2
(ii)
Given, the cost of constructing the roads at the rate of Rs 110 per m2.
Then the cost of constructing the 441 m2 roads = 441 × 110
= Rs 48510
8. Pragya wrapped a cord around a circular pipe of radius 4 cm (adjoining figure) and cut off the length required of the cord. Then she wrapped it around a square box of side 4 cm (also shown). Did she have any cord left? (π = 3.14)
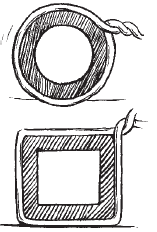
Solution:-
From the question it is given that,
Radius of a circular pipe = 4 cm
Side of a square = 4 cm
Then,
Perimeter of the circular pipe = 2πr
= 2 × 3.14 × 4
= 25.12 cm
Perimeter of the square = 4 × side of the square
= 4 × 4
= 16 cm
So, the length of cord left with Pragya = Perimeter of circular pipe – Perimeter of square
= 25.12 – 16
= 9.12 cm
Yes, 9.12 cm cord is left.
9. The adjoining figure represents a rectangular lawn with a circular flower bed in the middle. Find:
(i) the area of the whole land (ii) the area of the flower bed
(iii) the area of the lawn excluding the area of the flower bed
(iv) the circumference of the flower bed.

Solution:-
(i)
From the figure,
Length of rectangular lawn = 10 m
Breadth of rectangular lawn = 5 m
Area of the rectangular lawn = Length × Breadth
= 10 × 5
= 50 m2
(ii)
From the figure,
Radius of the flower bed = 2 m
Area of the flower bed = πr2
= 3.14 × 22
= 3.14 × 4
= 12.56 m2
(iii)
The area of the lawn excluding the area of the flower bed = Area of rectangular lawn –
Area of flower bed
= 50 – 12.56
= 37.44 m2
(iv)
The circumference of the flower bed = 2πr
= 2 × 3.14 × 2
= 12.56 m
10. In the following figures, find the area of the shaded portions:
(i)
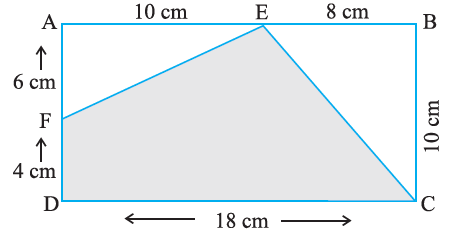
Solution:-
To find the area of EFDC, first we have to find the area of ΔAEF, ΔEBC and rectangle ABCD
Area of ΔAEF = ½ × Base × Height
= ½ × 6 × 10
= 1 × 3 × 10
= 30 cm2
Area of ΔEBC = ½ × Base × Height
= ½ × 8 × 10
= 1 × 4 × 10
= 40 cm2
Area of rectangle ABCD = length × breadth
= 18 × 10
= 180 cm2
Then,
Area of EFDC = ABCD area – (ΔAEF + ΔEBC)
= 180 – (30 + 40)
= 180 – 70
= 110 cm2
(ii)
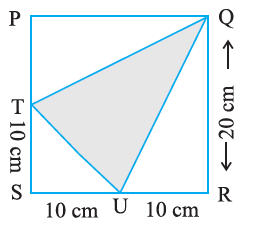
Solution:-
To find the area of ΔQTU, first we have to find the area of ΔSTU, ΔTPQ, ΔQRU and square PQRS
Area of ΔSTU = ½ × Base × Height
= ½ × 10 × 10
= 1 × 5 × 10
= 50 cm2
Area of ΔTPQ = ½ × Base × Height
= ½ × 10 × 20
= 1 × 5 × 20
= 100 cm2
Area of ΔQRU = ½ × Base × Height
= ½ × 10 × 20
= 1 × 5 × 20
= 100 cm2
Area of square PQRS = Side2
= 20 × 20
= 400 cm2
Then,
Area of ΔQTU = PQRS area – (ΔSTU + ΔTPQ + ΔQRU)
= 400 – (50 + 100 + 100)
= 400 – 250
= 150 cm2
11. Find the area of the quadrilateral ABCD.
Here, AC = 22 cm, BM = 3 cm,
DN = 3 cm, and BM ⊥ AC, DN ⊥ AC
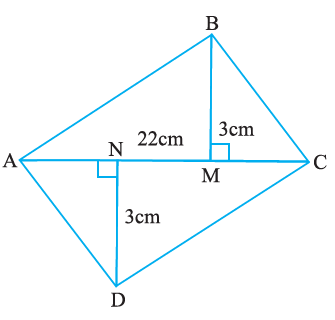
Solution:-
From the it is given that,
AC = 22 cm, BM = 3 cm DN = 3 cm and BM ⊥ AC, DN ⊥ AC
To find the area of quadrilateral ABCD, first we have to find the area of ΔABC, and ΔADC Area of ΔABC = ½ × Base × Height
= ½ × 22 × 3
= 1 × 11 × 3
= 33 cm2
Area of ΔADC = ½ × Base × Height
= ½ × 22 × 3
= 1 × 11 × 3
= 33 cm2
Then,
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = Area of ΔABC + Area of ΔADC
= 33 + 33
= 66 cm2