Transportation in Plants Class 7 Science
Transportation in Animals Class 7 Science
CBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants
Transport means ‘to carry things from one place to another’. The body of an organism requires nutrients and oxygen to carry out various life processes. Waste products, produced due to the various functions inside the body also need to be transported and removed. Therefore, the term transport may be defined as a life process in which a material is absorbed in one part or organ of an organism and is carried to other parts in its body.
In animal body, these functions are carried out by an internal transport system called as circulatory system.
Circulatory System
Circulatory system or blood circulatory system is the main transport system in human beings and animals. It makes food, water and oxygen available to every parts of the body and helps in removing waste material (urea, CO2, etc).
The circulatory system consists of blood, blood vessels and heart.
Blood
It is a fluid tissue that flows in blood vessels. It is red in colour and it flows through a network of tubes in whole body called blood vessels. Blood is pumped to every part of the animal by heart. Blood consist of four components, i.e. plasma, Red Blood Cells (RBCs), White Blood Cells (WBCs) and platelets. Plasma is a liquid while RBCs, WBCs and platelets that float in it.
1. Plasma
It is the sticky liquid part of the blood which is pale yellow in colour. It is 90% water and 3.5% common salt. It contains dissolved substance such as digested food and waste products and carry them from one part to another part in the body.
2. Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
RBCs are red in colour due to the presence of pigment called haemoglobin. This pigment carries oxygen by binding with it. Haemoglobin is a red protein that binds with oxygen and transports oxygen to all the parts of the body and ultimately to all the cells. It is the presence of haemoglobin which makes the blood appear red. When haemoglobin binds with oxygen, it forms oxyhaemoglobin which is transported to various body parts. The carbon dioixde from the various body parts is transported back by binding again with haemoglobin. It forms carboxyhaemoglobin with C02, this C02 is expelled out from the body.
3. White Blood Cells (WBCs)
The WBCs fight against infection and protect us from diseases. WBCs eats up the germs (like bacteria) that cause disease. WBC also makes antibodies that fight against infection. The number of WBC is quite less than RBC. WBC can change their shape and move on their own. They can squeeze out of the blood vessels to reach any part of the body.
4. Platelets
Blood platelets are small, irregular, tiny fragments of special cells formed in the bone marrow. These are colourless and help in the clotting of blood in a cut or wound. If a cut or wound is made the blood starts flowing from it, after some time the platelets plug the cut and the bleeding stops due to the formation of a dark red clot.
If the platelets are not present in the blood, the blood flow from the cut or wound will not stop causing excess loss of blood which may be fatal to a person leading to death.
Functions of Blood
Various functions of blood are
- It transports substances like digested food from the small intestine to the other parts of the body.
- It carries water to all the parts of the body.
- It carries oxygen and C02 during circulation.
- It carries waste products like urea from liver to kidney for excretion in urine.
- It protects the body from disease.
Blood Vessels
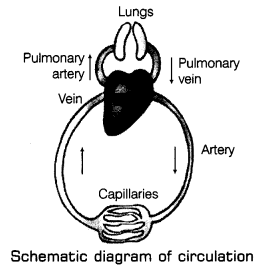
These are tubes or pipes that carry blood throughout the body. It runs between the heart and the rest of the body. There are three major types of blood vessels in the body, i.e. arteries, veins and capillaries.
1. Arteries
These carry blood from the heart to all the parts of the body. These lie quite deep under our skin and cannot be seen easily. Arteries have thick elastic walls as the blood flows at high pressure due to pumping action from the heart through arteries. No valves are present in the arteries. The main artery, i.e. aorta is connected to the left ventricle of the heart. It carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to all the parts of the body except the lungs. Another artery called the pulmonary artery is connected to the right ventricle of the heart and carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
Note: The arteries normally carry oxygenated blood from the heart but one artery called pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to lungs.
2. Veins
These are the blood vessels that carry blood from all the parts of the body back to the heart. These tube-like blood vessels are situated just under the skin and can easily be seen as greenish-blue tubes or lines below the skin. These carry deoxygenated blood from the body parts to the heart. Veins have thin walls and blood flows at low pressure through the veins. Therefore, veins have valves in them which allow the blood to flow in one direction and prevent the backflow of blood in veins.
Usually, veins carry deoxygenated blood but pulmonary vein that is connected to the left atrium of the heart carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
Differences between artery and vein
| Artery | Vein |
| It is thick walled tube present deep under the skin. | It is thin walled tubes lying just below the skin. |
| It cannot be seen easily. | It appears as a greenish blue line under the skin. |
| It does not possess valves. | It has valves which prevent the backflow of blood. |
| It carries oxygenated blood (except pulmonary artery). | It carries deoxygenated blood (except pulmonary vein). |
| Blood flows at high pressure. | Blood flows at low pressure. |
Pulse Rate
To know your pulse rate, place the middle and index finger of your right hand on the inner side of your left wrist. You will feel the throbbing movement at this place. This throbbing is called the pulse the pulse is produced due to the blood flowing in the arteries.
Now count the number of beats or pulse in one minute. The number of beats per minute is called the pulse rate.
At the resting phase, a normal person has a pulse rate between 72-80 beats per minutes. Run for about 5 minutes and again measure the pulse rate, you will notice that the pulse rate per minute will be increased after running.
3. Capillaries
These are extremely thin blood vessels that connect the arteries to veins. These allow substances to pass from blood into the body cells and also from body cells into the blood. The exchange of substances like food, 02, C02, etc., between the blood and the body cells take place through the capillaries.
Oxygenated and Deoxygenated Blood
The blood that carry oxygen in it is called oxygenated blood, i.e. it is rich in oxygen. The oxygenated blood comes from the lungs, where oxygen from the fresh air gets mixed into blood and is carried towards the heart.
The blood that is rich is carbon dioxide, i.e. all oxygen has been used by tissues and organs is called deoxygenated blood. It is formed in alt the organs of the body except lungs. Oxygenated blood is bright red in colour while deoxygenated blood is darher in colour.
Blood Groups
The blood group of an individual human being always remains unchanged throughout their life. Karl Landsteiner described that human blood can be divided into four groups, i.e. A, B, AB and O. These are named on the basis of substance present in the blood (RBC). Every man has one of these four groups of blood which is inherited from parents to offspring and is never changed.
If a person gets injured and heavy blood loss occurs, there is a need to give blood of other people to the patient. The person who gives the blood is called a donor while the person who receives the blood is called the recipient.
| Blood Group | Can donate blood to | Can receive blood from |
| A | A and AB | A and O |
| B | B and AB | B and O |
| AB | AB | All the group i.e., A, B, AB and O |
| O | All the group i.e., A, B, AB and O |
O |
The process of donation of blood from one person to another is called blood transfusion. Before donation, the blood group must be matched because transfusion of different groups can be dangerous. The RBCs of the patient receiving blood will stick together and may cause the death of the patient. This matching of blood group is called blood group compatibility. It can be shown as follows :
Heart
The heart is an organ which beats continuously as a pump for the transport of blood carrying other substances with it, through a network of tubes or blood vessels. The heart pumps blood throughout our life without stopping or relaxing.
Location of Heart
The heart is located in the chest cavity slightly towards the left side. It lies between the two lungs and above the diaphragm. The heart is made up of special muscles called cardiac muscles that do not fatigue and are not the solid muscle. The size of our heart is roughly equal to our left closed and is enclosed in a protective cover called pericardium fist. The heart is hollow inside.
Structure of Heart
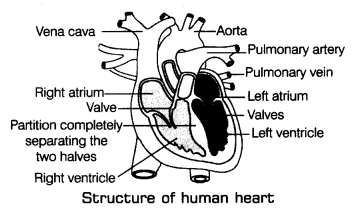
The heart has four compartments called as chambers. The upper two chambers of heart are called atria (sing, atrium) and the lower two chambers of heart are called ventricles. On the left side of heart are left atrium and left ventricle and on the right side of the heart are right atrium and right ventricle.
The atria and ventricles are separated by valves. These are the muscular flaps that allow the blood to flow in only one direction. The right side of the heart carries deoxygenated blood while the left side of the heart carries oxygenated blood. The heart is separated by a partition called septum (from right side of the heart to the left side). This prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood inside the heart.
Left and Right Side of the Heart
The left and right side of the heart act as two separate pumps.
The left side of heart pumps the oxygenated blood into the whole body, while the right side of heart pumps the deoxygenated blood to the lungs. The oxygenated blood must be kept separated from deoxygenated blood to supply good amount of oxygen to the body cells for respiration and release of energy.
If the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood will mix with each other, the body cells will not be able to get enough oxygen for respiration due to which less energy will be released in the body.
Heartbeat
The rhythmic contraction and relaxation of heart muscles that produce a specific sound of lubb-dubb is called heartbeat. The average heartbeat of an adult person is 72-80 beats per minute at resting but the number increases during and after a physical exercise or when a person is excited. During fast beating of heart, the blood is pumped more rapidly to the organs to supply more oxygen to the body cells. It helps in rapid respiration and to produce more energy. The heartbeat is equal to the number of pulse in a minute.
Stethoscope
The heartbeat can be heard by an instrument called as stethoscope. It is used by doctor to amplify the sound of heart. It consists of
- a chest piece that carries a sensitive diaphragm
- two earpieces
- a tube joining both the parts
Doctors get to know about the condition of heart by listening to the sound through a stethoscope.

You can prepare a model of the stethoscope by yourself. Take a small funnel of 6-7cm in diameter and fix a rubber tube tightly on the stem of the funnel. Stretch a rubber sheet on the mouth of the funnel. Fix it tightly with the help of rubber band. Put the open end of the tube on one of your ear. Now place the mouth of the funnel on your chest near the heart.
Listen the thumping sound carefully. These sounds are the heartbeat. Count the number of beats in a minute.
Mechanism of Circulation
The contraction of two atria is immediately followed by the contraction of two ventricles which leads to the continuous flow of blood in the human body. The mechanism of circulation can be summarised as follows:
- The blood passes through the capillaries of the lungs and is mix with oxygen. This oxygenated blood is then carried from the lungs to the left auricle by four pulmonary veins.
- The left atrium contracts and the oxygenated blood is pushed into left ventricles.
- The left ventricle pumps the blood into the biggest blood vessels of the body called aorta. It distributes oxygen-rich blood to the different parts of the body.
- The oxygenated blood is distributed to all the organs of the body through capillaries.
- The deoxygenated blood from various organs of the body enters from the capillaries to veins and then to the right atrium.
- The right atrium contracts and pushes the deoxygenated blood into right ventricles through the opened valve.
- Right ventricles pump the impure blood into pulmonary arteries that carry it to the right and left lungs for purification.
- The CO2 is released as a waste product from the lungs and again the blood absorbs oxygen and becomes oxygenated. The valves present on both sides of heart regulate the blood flow from one chamber to another.
This cycle keeps on circulating continuously day and night, even when we sleep.
The English physician, William Harvey (AD 7578-1657), discovered the circulation of blood. The current opinion in those days was that blood oscillates in the vessels of the body. For his views, Harvey was ridiculed and was called circulator. He lost most of his patients. However, before he died, Harvey’s idea about circulation was generally accepted as a biological fact.
Circulation in Sponges and Hydra
Sponges and Hydra are simple animals that do not possess any circulatory system. They live in water and therefore, the food and oxygen enter into their body along with water. The water also carries the C02 and other waste material away from the body as it moves out of their bodies.
Excretion
The process of removal of waste materials produced in the cells of the living organism is called excretion. When our body uses food, water and air, it produces some by-products or unwanted substances. These are called waste materials. These waste material are toxic or poisonous and causes harm to the body. These poisonous substances if get mixed with blood may become fatal and may cause the death of an organism. Therefore, the waste material must be removed from the body so that a person may stay healthy.
These waste material produced after the various functions of body cells include CO2, urea, sweat, etc. These waste materials are removed from the body different organs of the body like lungs (CO2), kidney (urea) and sweat glands (sweat). These parts or organs of the body that are involved in the process of excretion are called excretory system.
Excretory System in Humans
Urea is the major waste product released in our body. It is produced as a waste product of the decomposition of unused food proteins in the liver. It is a poisonous substance which must be removed from the body. Urea from blood is removed by the kidney. Therefore, the kidney is the main excretory organ in our body. The urea and other unwanted salts when dissolving in water form a yellowish liquid waste called urine.
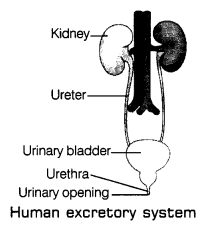
It consists of 2.5% urea, 2.5% other waste salts and 95% water. An adult human being normally passes out 1-1.8 L of urine per day. The excretory system collects the urine and remove it. The excretory system of human being consists of two kidneys, two ureters, a bladder and a urethra.
Kidneys
These are called the magic filters. Kidney are bean-shaped organs present at the back of our body, just above the waist. It is brick red coloured about 4 inches long. It is richly supplied with blood vessels. Kidney can filter the unwanted substances from the blood. Each kidney consists of thousands of tiny filters called nephrons. When the blood containing urea and other waste salts pass through these nephrons, it filters the blood and removes urea and salts and urine are left in the kidney.
The urine thus formed by each of the kidney is then passed through the ureter (a tube-like structure which connects the kidney to the bladder) to urinary bladder. The urine is stored in the urinary bladder for some times and at regular intervals it, is removed through the opening at the end of the tube called urethra. The process of ejection of urine is called micturition.
The opening of urinary bladder is controlled by the ring of muscle called as bladder sphincter. When the bladder becomes full with urine this bladder sphincter opens and allows the urine to flow out.
Carbon Dioxide
It is produced as a waste product in our body cells during the process of respiration. The food is broken down during respiration to release energy and releases CO2 as a by-product. This CO2 is removed from our body by the lungs during exhalation. Therefore, lungs also act as the excretory organs for removing the waste product, CO2from the body.
Sweat
It is the liquid waste of the body that is produced by the sweat glands present in our skin. Sweat contains water, some unwanted salts and urea in a very small amount. During hot summer, we sweat a lot. This gets evaporated from our body. This helps to provide the cooling effect to the body. The two major functions of sweat are as follows :
- It helps to remove excess water, salt and urea from the body.
- It helps to keep our body cool during hot summer days.
Dialysis
The normal functioning of the kidney is necessary for good health of a person. But sometime s the kidney may stop working due to infection or injury. This condition of kidney is called kidney failure which may lead to the accumulation of urea in the blood of a person. Since, urea is a toxic substance which must be removed from the blood. Such person having kidney failure cannot survive unless his blood is filtered periodically through the artificial kidney machine to remove urea. The process used for cleaning the blood of a person by separating the waste product urea from it is called dialysis.This machine removes urea and other waste the product periodically.
The long term solution for the patient suffering from kidney failure is kidney transplantation. In this method, the diseased or damaged kidney is removed and the matching kidney is donated by a healthy person. The donated kidney is transplanted in its place by performing ^surgery.
Excretion in Animals
Like humans, animals also excrete waste products from their body. The way in which waste materials are removed from the body of the animal depends upon the availability of water. Fishes are the aquatic animals that excrete ammonia as their waste product. This ammonia is excreted in the gaseous form which directly gets dissolved in water. The land animals like lizards, birds, snakes, etc, have less water availability. These animals excrete this waste material in the form of uric acid pellets. These are white coloured semi-solid excretory products of several land animals. Urea is the excretory product of animals like human, cow, goat, etc. and is eliminated as urine.
Amoeba, Paramecium, etc., are the unicellular organisms and their excretory products are removed by diffusion from the body of the organism into the surrounding water.
Transport of Substances in Plants
Plants take up water and dissolved minerals from the soil through their roots and transport it to their leaves. The leaves use this water and mineral for synthesising their food by the process called photosynthesis.The food produced by green plants in transported back to all the parts of plant body.
Therefore, it is clear that plants also need a transport system for carrying water, minerals and food through various parts of their body.
Transport of Water and Minerals
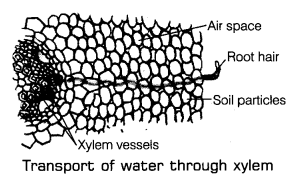
Plant root absorbs the water and mineral from the soil. The roots possess root hair which increase the surface area of the root for absorption of water and minerals nutrient that is dissolved in the water. It is moved from roots up to the stem and leaves through the tube-like tissue called as xylem.
Absorption and flow of water is a continuous process through the xylem tissue. Xylem tissues are the continuous network of channels which connect roots to the leaves through the stem and branches. It thus transports water and minerals to the leaves of the entire plant.
Transport of Food Material
The food manufactured in the leaf is transported to different parts of plants. This transportation of food material from leaves to the other parts of plants is carried out by the tissue called phloem and the process of transport of food material is called translocation. The phloem consists of vessels that are known as sieve tubes.
The xylem and phloem tissues together form the vascular bundles or conducting tissues.
Transpiration
The process of evaporation of water through the stomata present on the surface of leaves is called transpiration. The continuous evaporation of water from the leaves produces an upward pull, called a suction force. This force pulls the water from roots upward through the stem, branches and finally to the leaves. Though transpiration causes loss of water from the plants, still it is a necessary process for plants due to the following reasons:
- Suction pull caused due to the evaporation of water helps to draw water to a great height in tall trees.
- It produces a cooling effect on the plant and therefore, prevents the plants from the damage caused by heat of sunlight.
- It also helps in the transport of water and minerals to the leaves for performing photosynthesis in them.
The rate of transpiration increases in a hot sunny day or in moving air. This happens because the heat from sun or moving air causes evaporation of water at a faster rate from the stomata.
Increases in the rate of transpiration cause an increased rate of absorption of water through the roots. Therefore, when a potted plant is kept under the moving fan, the absorption of water through root will be increased along with the increased rate of evaporation.