Question 1.
Classify the following as motion along a straight line, circular or oscillatory motion:
- Motion of your hands while running.
- Motion of a horse pulling a cart on a straight road.
- Motion of a child in a merry-go-round.
- Motion of a child on a see-saw.
- Motion of the hammer of an electric bell.
- Motion of a train on a straight bridge.
Solution:
- oscillatory
- straight line
- circular
- oscillatory
- oscillatory
- straight line
Question 2.
Which of the following are not correct?
(i) The basic unit of time is second.
(ii) Every object moves at a constant speed.
(iii) Distances between two cities are measured in kilometers.
(iv) The time period of a given pendulum is not constant.
(v) The speed of a train is expressed in m/h.
Solution:
(ii), (v)
Question 3.
A simple pendulum takes 32 s to complete 20 oscillations. What is the time period of the pendulum?
Solution:
Given here,
No. of oscillations = 20
Total time taken = 32 sec.
We know that the time period of a pendulum is the time taken by it to complete one oscillation. Thus,
Time period = TotaltimetakenNo.ofoscillations=32sec/20=1.6seconds
Therefore, the time period of this pendulum will be 1.6 s.
Question 4.
The distance between the two stations is 240 km. A train takes 4 hours to cover this distance. Calculate the speed of the train.
Solution:
Here, it is given that,
The distance between two stations = 240 km
Time is taken to cover this distance = 4 hr.
Now, Speed = DistanceTime=240Km/4hr=60Km/h
Therefore, the speed of the train will be 60 km/h.
Question 6.
Salma takes 15 minutes from her house to reach her school on a bicycle. If the bicycle has a speed of 2 m/s, calculate the distance between her house and the school.
Solution:
According to the question,
Speed of the bicycle = 2 m/s
Total time taken = 15 min = 900 sec.
We know that,
The distance covered = Speed x Time
= 2 m/s x 900 sec.
= 1800 m
Therefore, the distance between her house and the school will be 1800 m or 1.8 km.
Question 7.
Show the shape of the distance-time graph for the motion in the following cases :
(i) A car moving at a constant speed.
(ii) A car parked on a side road.
Solution:
(i) A car moving with a constant speed covers equal distance in equal intervals of time
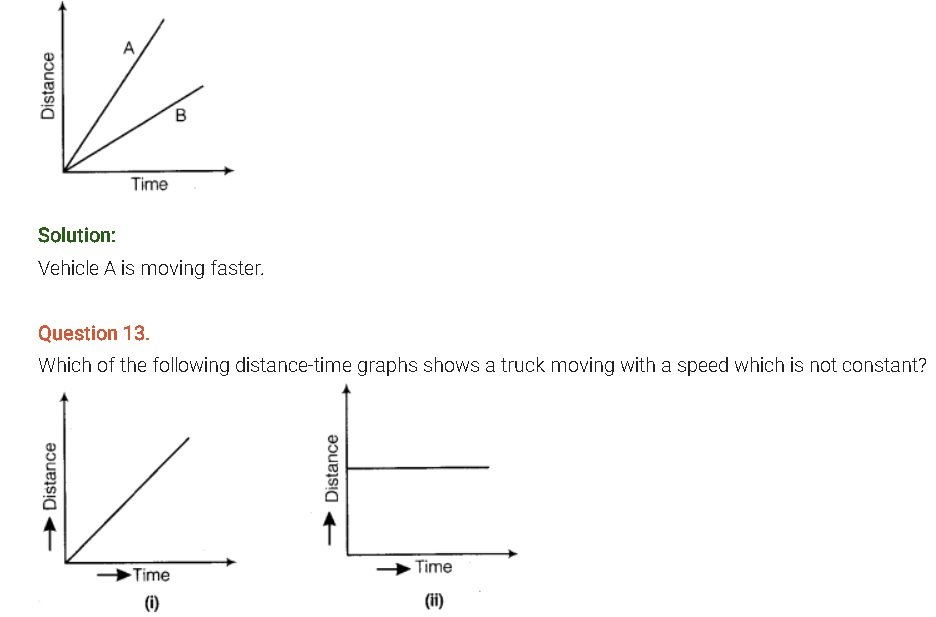
Question 10.
A car moves with a speed of 40 km/h for 15 minutes and then with a speed of 60 km/h for the next 15 minutes. The total distance covered by the car is:
(i) 100 km
(ii) 25 km
(iii) 15 km
(iv) 10 km
Solution:
Distance travelled in first 15 min
= speed x time
= 40 km/h x 15 min
= 40 km/h x 15/60 h = 10 km
Distance travelled in last 15 min
= speed x time
= 60 km/h x 15 min
= 60 km/h x 15/60 h = 15 km
Total distance = (10 +15) km = 25 km
Hence, option (ii) is correct.
Question 11.
Suppose the two photographs, shown in Fig. 13.1 and Fig. 13.2, had been taken at an interval of 10 seconds. If a distance of 100 meters is shown by 1 cm. in these photographs, calculate the speed of the blue car.
Solution:
Speed = 100 m/10 s = 10 m/s
Question 12.
shows the distance-time graph for the motion of two vehicles A and B. Which one of them is moving faster?