Suggestion Firstly watch the Video Part 1, Part 2. Then go through the notes for the better understanding.
Part 1: Solution
Part 2: The Solution
Introduction
During summer after returning home from outside it feels refreshing to drink a glass lemon water. What is it actually?? It is nothing just a mixture of salt, sugar, lemon juice in water. This a rehydrating solution. Solution can be defined as a liquid mixture with minor component (salt, sugar, lemon juice) uniformly distributed within the major component (water).
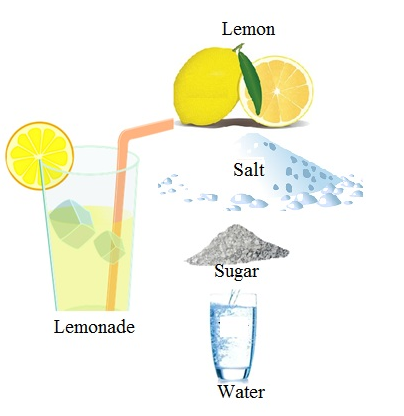
The component of a solution present in the huge quantity is referred to as solvent which determines the physical state of the solution whereas the components of a solution present in the lesser amount is referred to as solute.
In the case of lemonade Water is the solvent whereas salt/sugar are the solute.
Types of solutions
Solutions can be broadly categorized into two types:
Homogeneous solutions: Solutions with uniform composition and properties throughout the solution are known as homogenous solution. E.g. solution of salt or sugar in water, cough syrup, cup of coffee, Mouthwash, perfume are homogeneous mixture of chemicals and dyes, etc.


| Type of solution | Solute | Solvent | Example |
| Gaseous | Gas | Gas | Oxygen and nitrogen mixture |
| Liquid | Gas | Chloroform with nitrogen gas | |
| Solid | Gas | Camphor in nitrogen gas | |
| Liquid | Gas | Liquid | Oxygen in water |
| Liquid | Liquid | Ethanol in water | |
| Solid | Liquid | Glucose in water | |
| Solid | Gas | Solid | Hydrogen solution in palladium |
| Liquid | Solid | Amalgam of mercury with sodium | |
| Solid | Solid | Dissolved copper in gold |
2.1. Define the term solution. How many types of solutions are formed? Write briefly about each type with an example. (NCERT Book)
Sol: A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more chemically non-reacting substances. Types of solutions: There are nine types of solutions.
Types of Solution Examples
Gaseous solutions
(a) Gas in gas Air, mixture of 02 and N2, etc.
(b) Liquid in gas Water vapour
(c) Solid in gas Camphor vapours in N2 gas, smoke etc.
Liquid solutions
(a) Gas in liquid C02 dissolved in water (aerated water), and 02 dissolved in water, etc.
(b) Liquid in liquid Ethanol dissolved in water, etc.
(c) Solid in liquid Sugar dissolved in water, saline water, etc.
Solid solutions
(a) Gas in solid Solution of hydrogen in palladium
(b) Liquid in solid Amalgams, e.g., Na-Hg
(c) Solid in solid Gold ornaments (Cu/Ag with Au)
2.2. Suppose a solid solution is formed between two substances, one whose particles are very large and the other whose particles are very small. What type of solid solution is this likely to be ? (NCERT Book)
Sol: The solution likely to be formed is interstitial solid solution.
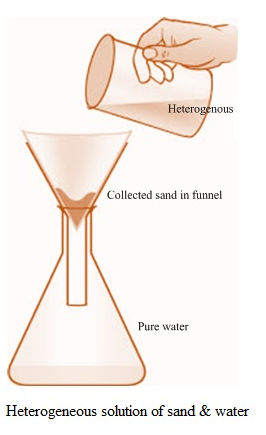
Q. What is The Difference Between Homogenous and Hetrogenous Solution?