No. Atoms in Unit Cell:-
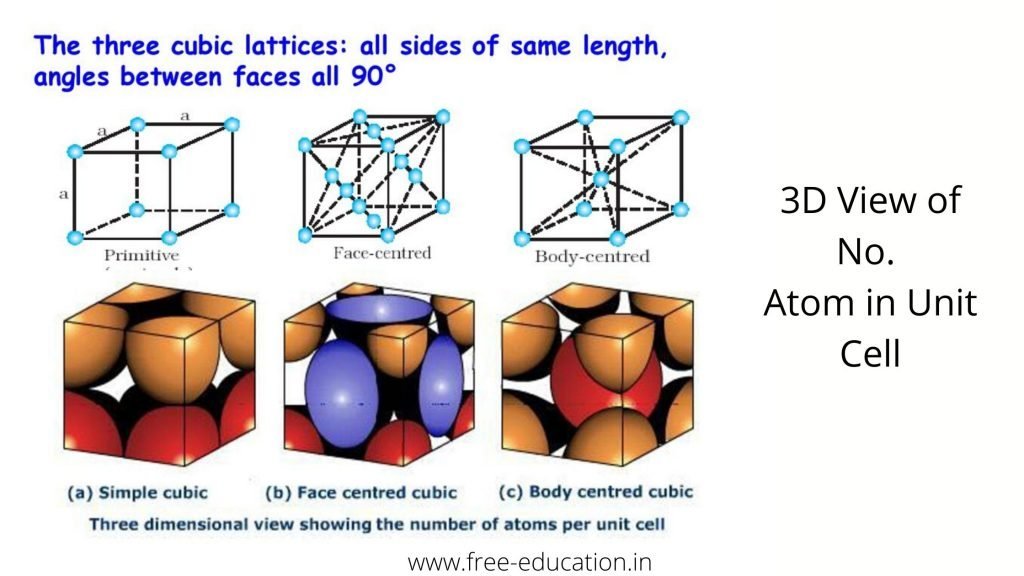
Number of atoms per unit cell : Body Centered Cubic Unit Cell
In a body-centered cubic (bcc) unit cell, the atoms are present in the body-center besides the ones that are at its corners that wholly belongs to the unit cell in which it is present. Thus in a body-centered cubic (bcc) unit cell:
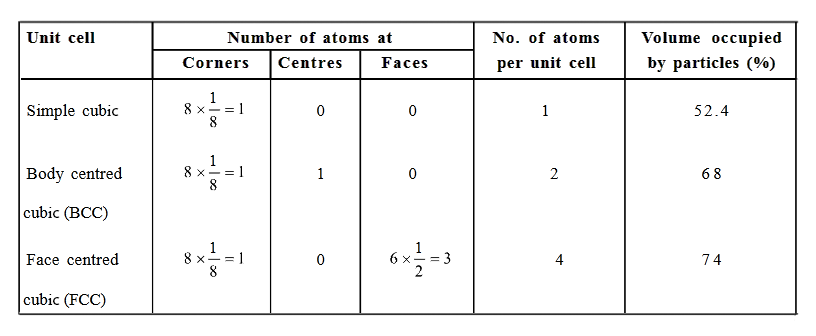
8 corners X 1/8 per corner atom = 8 * 1/8 = 1 atom
1 body center atom = 1 X 1 = 1 atom
Total number of atoms per unit cell = 2 atoms
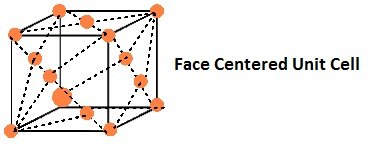
Number of atoms per unit cell : Face Centered Cubic Unit Cell
In a face-centered cubic (fcc) unit cell the atoms are present in the corners and at the center of all the faces of the cube.
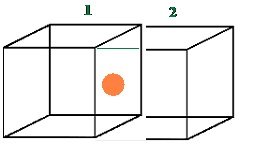
Each atom present at the face-center is shared between two adjacent unit cells and only a ½ of each atom belongs to a unit cell.
Thus, in a face-centered cubic (fcc) unit cell:
8 corners X 1/8 per corner atom = 8 * 1/8 = 1 atom
6 face-centered atoms X 1/2 per unit cell = 6 X 1/2 = 3 atoms
Total number of atoms per unit cell = 4 atoms
In solids, these constituent particles are closely-packed that leaves minimum vacant space.
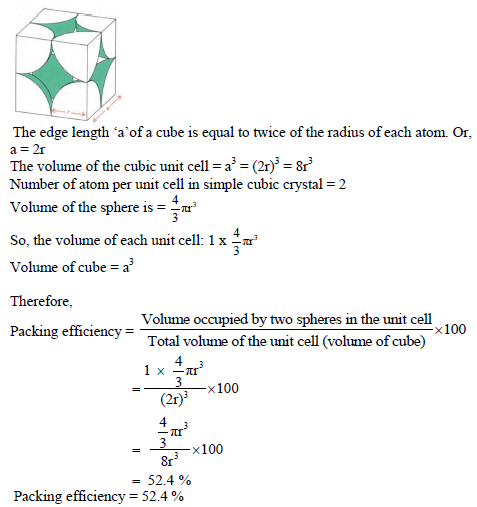
Numerical on Packing efficiency
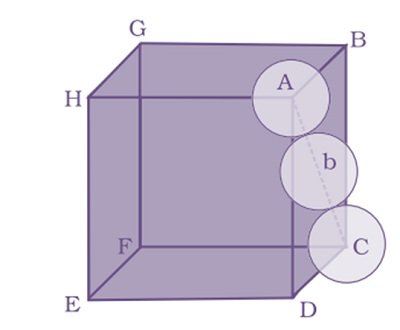
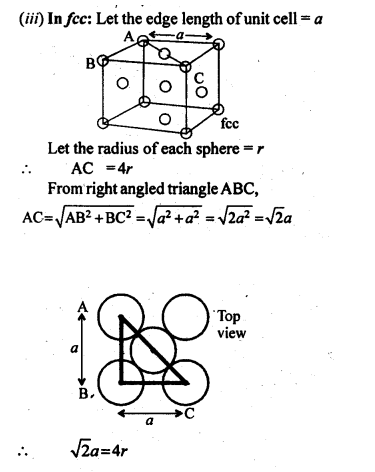
Packing Efficiency in hcp and ccp Structures
let the unit cell edge length be ‘a’ and face diagonal AC = b.
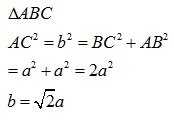

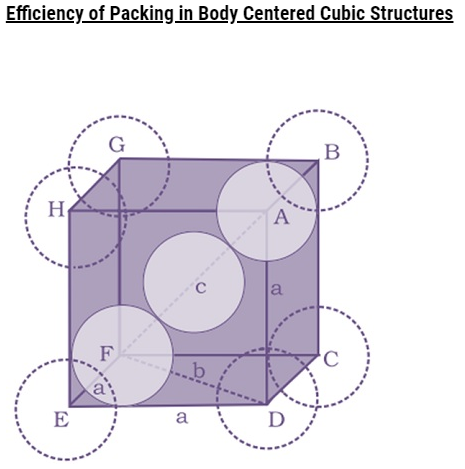

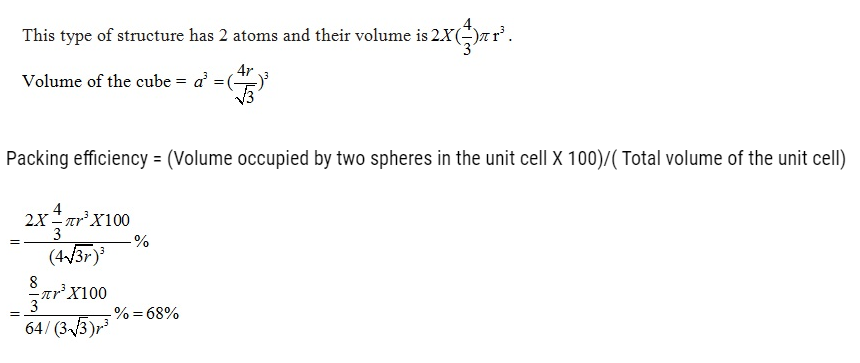


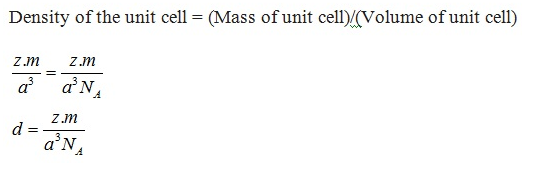
Q.Find out the no. of atoms in BCC (Body Centered Cubic Unit Cell)? [Delhi 2014/2015C]
Q. Find out the no. of atoms in FCC (Face Centered Cubic Unit Cell)? [Delhi 2008/2013/CBSE 2008/2009]
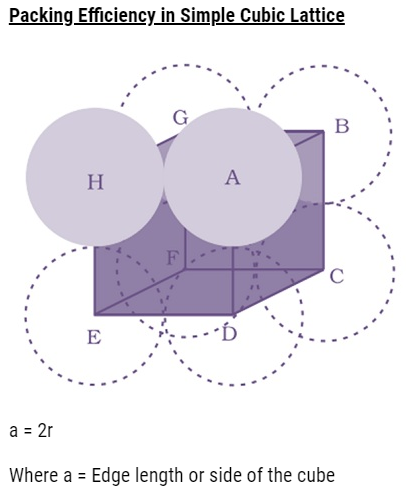
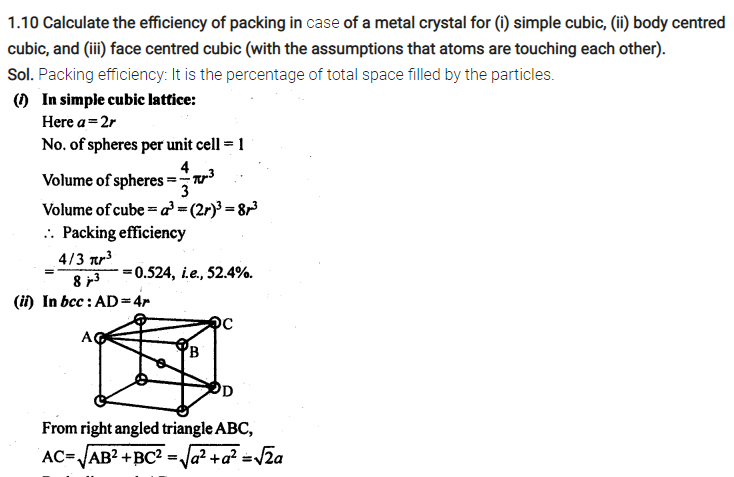
Q. Find out the packing efficiency in simple cubic lattice? [Delhi 2011C/CBSE2011/2009C]
Q. Calculation involving unit cell dimensions? {Relation} [Delhi 2011]
Q. Aluminium crystallises in FCC structure. Atomic radius of metal is 125 pm. what is the lenght of the side of unit cell of the metal? [CBSE 2013]
Ans. length of side (a) = 4r/√2 or [√2a = 4r] for FCC
= (4 x 125 pm)/√2 = 35.3.61 pm
Q. An element with density 11.2 gcm-3 form a fcc lattice with edge length of 4 x 10-8 cm. calculate the atomic mass of elements? [CBSE 2014]
Ans. Given data, d= 11.2 gcm-3 , a = 4 x 10-8 , NA = 6.023 x 1023
For FCC, Z = 4
We know the relation, d = Z M / a3 NA
M = ? , M = d x a3 x NA / Z
Put the values and Answer will be 107.9 gmol-1 or 108 gmol-1


NCERT Book Questions
Q 1.18. An element with molar mass 2:7 x 10-2 kg mol-1 forms a cubic unit cell with edge length 405 pm. If its density is 2:7 x 103 kg m-3, what is the nature of the cubic unit cell ? (C.B.S.E. Delhi 2015) (NCERT Book)
Ans:
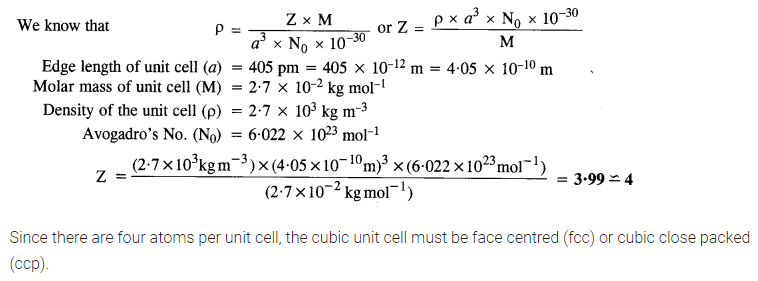








(i) In metals, conductivity strongly depends upon the number of valence electrons available in an atom. The atomic orbitals of metal atoms form molecular orbitals which are so close in energy to each other, as to form a band. If this band is partially filled or it overlaps with the higher energy unoccupied conduction band, then electrons can flow easily under an applied electric field and the metal behaves as a conductor.
If the gap between valence band and next higher unoccupied conduction band is large, electrons cannot jump into it and such a substance behaves as insulator.
(ii) If the gap between the valence band and conduction band is small, some electrons may jump from valence band to the conduction band. Such a substance shows some conductivity and it behaves as a semiconductor. Electrical conductivity of semiconductors increases with increase in temperature, since more electrons can jump to the conduction band. Silicon and germanium show this type of behaviour and are called intrinsic semiconductors. Conductors have no forbidden band.