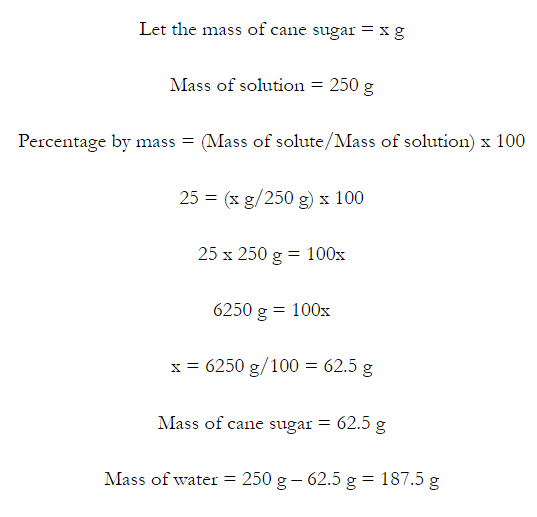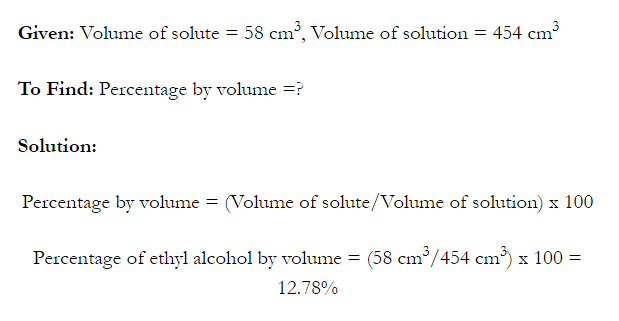- Concentration of a solution is the measure of the composition of a solution.
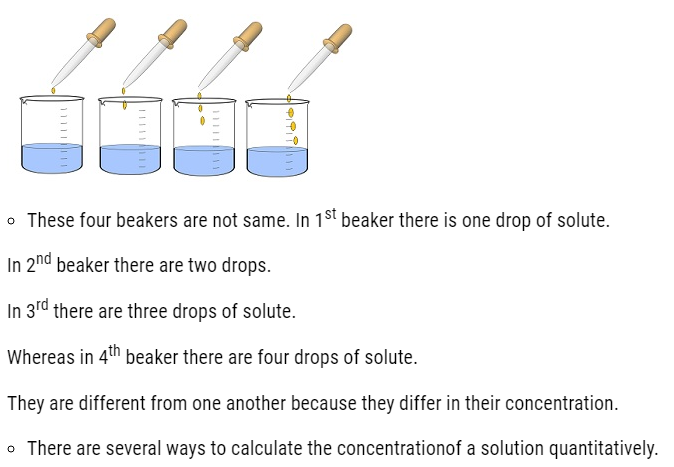
- A solution with relatively very large quantity of solute is called concentrated solution.
- A solution with relatively very small quantity of solute is called a dilute solution.




Problem:
Ami took a 20 cm3 mixture of CO, CH4 and He gases and exploded it by an electric discharge at room temperature with excess of oxygen. The volume initially contracted to 13.0 cm3. Then it further contracted to 14.0 cm3 when the residual gas is treated with KOH solution. Find out the consumption of gaseous mixture in terms of volume percentage.
Solution:
Take V1= Partial volumes of CO
V2= Partial volumes of CH4
V3 = Partial volumes of He
V1+V2+V3 = 20.0 cm3
The equation for combustion is as follows:
CO + ½ O2 –> CO2
CH4 + 2O2 –> CO2 + 2H2O
V1 volume of CO = ½ V1 volume of O2 = V1 volume of CO2
V2 volume of CH4 = 2V2 volume O2 = V2 volume of CO2
V1/2 + 2V2 = 13.0 cm3
Treating of residual gases with KOH solution would cause the absorption of CO2
V1+ V2 = 14.0 cm3
V1 = 10 cm3
V2 = 4.0 cm3
V3 = 6.0 cm3
Volume % of CO = 10/20 x 100 = 50
Volume % of CH4 = 4/20 X 100 = 20
Volume % of He = 100 – (50 + 20) = 30

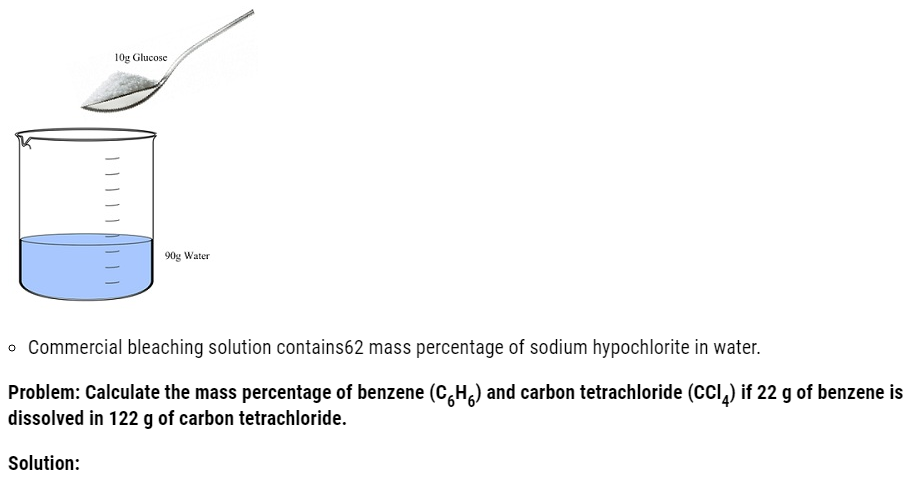
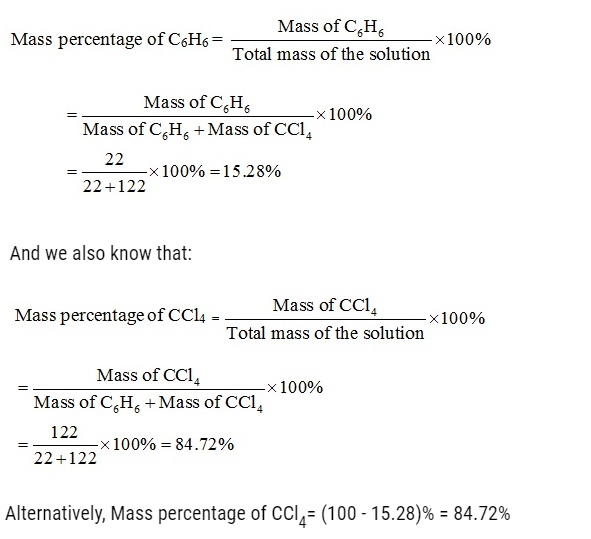
2.1. Calculate the mass percentage of benzene (C6H6) and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) if 22 g of benzene is dissolved in 122 g of carbon tetrachloride. (NCERT Book)
Ans: Mass of solution = Mass of C6H6 + Mass of CCl4
= 22 g+122 g= 144 g
Mass % of benzene = 22/144 x 100 =15.28 %
Mass % of CCl4 = 122/144 x 100 = 84.72 %
2.28. Calculate the mass percentage of aspirin (C9H8O4 in acetonitrile (CH3CN) when 6.5g of CHO is dissolved in 450 g of CH3CN. (NCERT Book)


Q.