Crystal Lattice
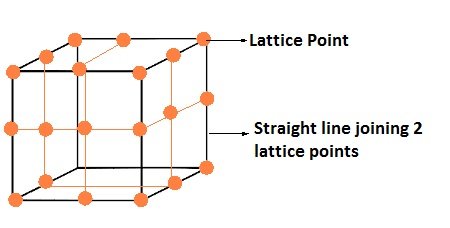
A regular 3D arrangement of points [constituent particles] in space is called a crystal lattice.
Characteristics of Crystal Lattice:-
- Each point in a crystal lattice represents one constituent particle which may be an atom, a molecule or an ion.
- Each point in a lattice is called lattice point/lattice site.
- Lattice points are joined by straight lines to bring out the geometry of lattice.
Unit Cells
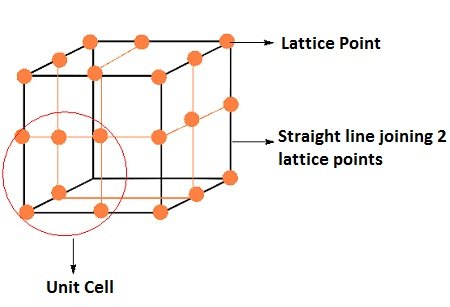
It is the smallest portion of a crystal lattice. when it repeated in different directions generates the entire lattice. [Delhi 2011/CBSE 2011]
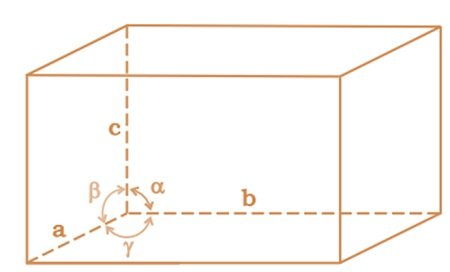
A unit cell is characterized by:
(i) Its dimensions along the three edges, a, b and c which may or may not be mutually perpendicular.
(ii) Angles between the edges, α (between b and c) β (between and c) and γ (between a and b). Thus, a unit cell is characterized by six parameters a, b, c, α, β and γ.

Types of Unit Cell
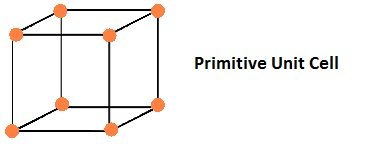
Primitive Unit Cells
If the constituent particles of a crystal lattice are present only on the corner positions of a unit cell, it is known as primitive unit cell.
Centered Unit Cells
- If the constituent particles of a crystal lattice are present at positions other than corners in addition to those at corners, it is known as centered unit cell.
- Centered unit cells are of three types:
- Body-Centred Unit Cells:
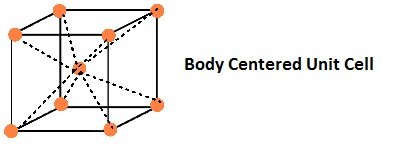
If the constituent particles of a unit cell are present at its body-centre besides the ones that are at its corners.
- Face-Centred Unit Cells:
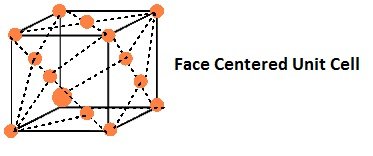
If the constituent particles of a unit cell are present at the center of each face, besides the ones that are at its corners.
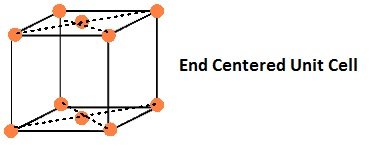
If the constituent particles of a unit cell are present the center of any two opposite faces besides the ones present at its corners.

There are 7 primitive unit cells and 14 possible 3D lattices [Bravais Lattice]

Q. Define Primitive Unit Cells? (CBSE 2015/2011/Delhi 2009)
Q 1.10. Give the significance of a lattice point. (NCERT Book)
Ans: The lattice point denotes the position of a particular constituent in the crystal lattice. It may be atom, ion or a molecule. The arrangement of the lattice points in space is responsible for the shape of a particular crystalline solid.
Q. 1.11. Name the parameters that characterise a unit cell. (NCERT Book)
Ans: A unit cell is characterised by the following parameters:
(i)the dimensions of unit cell along three edges: a, b and c.
(ii)the angles between the edges: α (between b and c); β (between a and c) and γ (between a and b)
1.12. Distinguish between :
(i) Hexagonal and monoclinic unit cells
(ii) Face-centred and end-centred unit cells.
Ans:
(i) In a hexagonal unit cell :
a = b # c; α = β = 90° and γ = 120°
In a monoclinic unit cell :
a # b # c and α = γ = 90° and β # 90°
(ii) In a face-centered unit cell, constituent particles are located at all the corners as well as at the centres of all the faces.
In end-centered unit cell, constituent particles are located at all the corners as well as at the centres of two opposite faces. (C.B.S.E Foreign 2015)
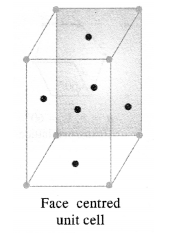

Q. Distinguish between Unit Cell & Crystal Lattice?
