Arrangement for measurement of Resistance
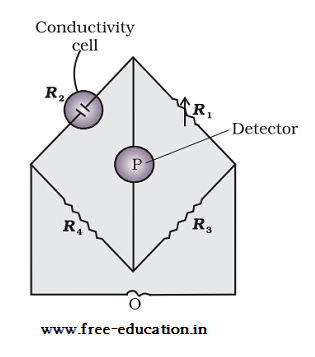
- The arrangement consists of two resistances R3 and R4.
- There is a variable resistance R1 and a conductivity cell with unknown resistance R2.
- The Wheatstone bridge is provided with an oscillator O that acts as source of a.c. power.
- The arrangement has a suitable detector P.
- The Wheatstone bridge is balanced when there is no flow of current through the detector.
Unknown resistance = R2 = R1R4 /R3
- After calculating the resistance the conductiviry can be easily calculated using the formula:
- κ = G’ /R
Molar conductivity
- It is denoted by the symbol. It is related to the conductivity of the solution by the following equation:
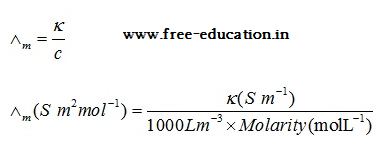
- The units of is S m2 mol-1.
Problem:
THE CONDUCTIVITY OF 0.20 M SOLUTION OF KCL AT 298 K IS 0.0248 SCM-1. CALCULATE ITS MOLAR CONDUCTIVITY.
Solution:
k = 0.0248 S cm – 1
c = 0.20 M
Molar conductivity,Λm = (k x 1000) / c
= 0.0248 x1000 / 0.20
= 124 Scm2 mol – 1
Variation of Conductivity and Molar Conductivity with Concentration
- They depend on the concentration of the electrolyte. The Conductivity and Molar Conductivity of both weak and strong electrolytes decreases withdecrease in concentration as the number of ions per unitvolume carrying the current in a solution decreases on dilution.
- Conductivity of a solution at a specific concentration = Conductance of solution placed in between the two platinum electrodes where
- Volume of solution = 1 unit
Cross sectional area of electrodes = 1unit
