
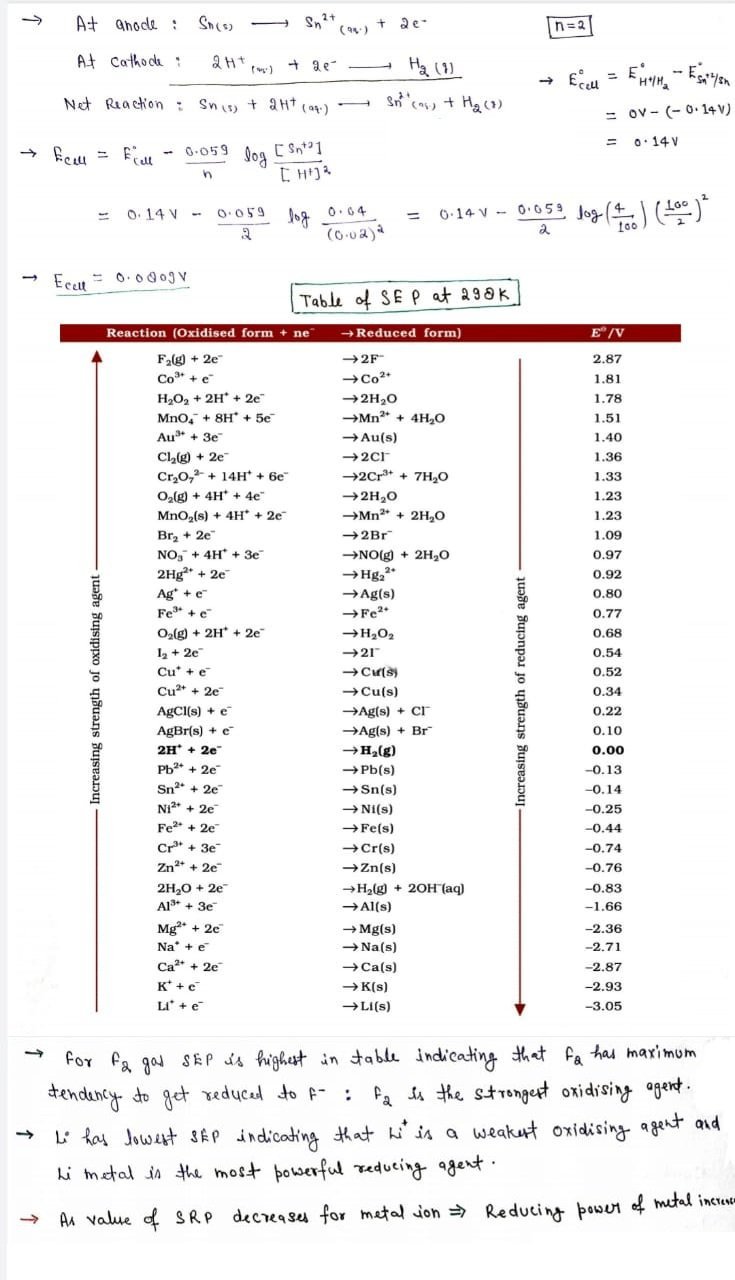
Nernst Equation
- This equation was named after a German physicist Walther Nernst.

- The Nernst Equation empowers the assurance of cell potential under non-standard conditions and relates the measured cell potential to the reaction quotient and permits the exact measurement of equilibrium constants.
- Let us consider an electrochemical reaction of the following type:
aA +bB –> cC + dD
- Nernst equation for this can be written as follows:

- If the circuit in Daniel cell is closed:
Zn(s) + Cu2+ (aq) →Zn2+ (aq) + Cu(s)


Problem:
Calculate the emf of the cell in which the following reaction takes place: Ni(s) + 2Ag+ (0.002 M) → Ni2+ (0.160 M) + 2Ag(s). Given that Eøcell = 1.05 V.




Electrochemical Cell and Gibbs Energy of the Reaction

- Electrical work done (1 second) = Electrical potentialX Total charge passed
- Passing the charges reversibly through the galvanic cell results in maximum work.
- Reversible work done by galvanic cell = Decrease in Gibbs energy
- Let E = Emf of the cell
nF = Amount of charge passed
ΔrG = Gibbs energy of the reaction
ΔrG = -nFEcell
For the reaction,
Zn(s) + Cu2+ (aq) –> Zn2+ (aq) + Cu(s)
[ΔrG = -2FEcell ]
But when the equation becomes
2Zn(s) + 2Cu2+ (aq) –> 2Zn2+ (aq) + 2Cu(s)
[ΔrG = -4FEcell ]
Problem:
The cell in which the following reactions occurs:
