Exercise 2.3 Page: 36
1. Divide the polynomial p(x) by the polynomial g(x) and find the quotient and remainder in each of the following:
(i) p(x) = x3-3x2+5x–3 , g(x) = x2–2
Solution:
Given,
Dividend = p(x) = x3-3x2+5x–3
Divisor = g(x) = x2– 2
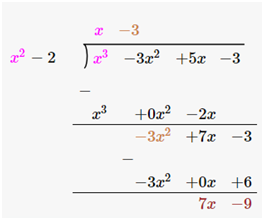
Therefore, upon division we get,
Quotient = x–3
Remainder = 7x–9
(ii) p(x) = x4-3x2+4x+5 , g(x) = x2+1-x
Solution:
Given,
Dividend = p(x) = x4 – 3x2 + 4x +5
Divisor = g(x) = x2 +1-x
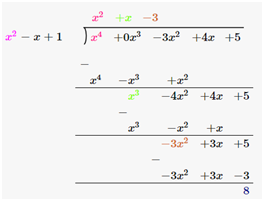
Therefore, upon division we get,
Quotient = x2 + x–3
Remainder = 8
(iii) p(x) =x4–5x+6, g(x) = 2–x2
Solution:
Given,
Dividend = p(x) =x4 – 5x + 6 = x4 +0x2–5x+6
Divisor = g(x) = 2–x2 = –x2+2
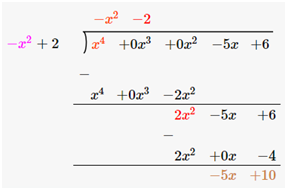
Therefore, upon division we get,
Quotient = -x2-2
Remainder = -5x + 10
2. Check whether the first polynomial is a factor of the second polynomial by dividing the second polynomial by the first polynomial:
(i) t2-3, 2t4 +3t3-2t2-9t-12
Solutions:
Given,
First polynomial = t2-3
Second polynomial = 2t4 +3t3-2t2 -9t-12
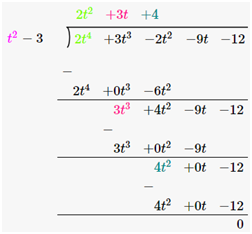
As we can see, the remainder is left as 0. Therefore, we say that, t2-3 is a factor of 2t2+3t+4.
(ii)x2+3x+1 , 3x4+5x3-7x2+2x+2
Solutions:
Given,
First polynomial = x2+3x+1
Second polynomial = 3x4+5x3-7x2+2x+2
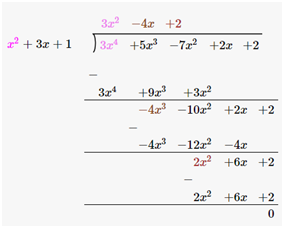
As we can see, the remainder is left as 0. Therefore, we say that, x2 + 3x + 1 is a factor of 3x4+5x3-7x2+2x+2.
(iii) x3-3x+1, x5-4x3+x2+3x+1
Solutions:
Given,
First polynomial = x3-3x+1
Second polynomial = x5-4x3+x2+3x+1

As we can see, the remainder is not equal to 0. Therefore, we say that, x3-3x+1 is not a factor of x5-4x3+x2+3x+1 .
3. Obtain all other zeroes of 3x4+6x3-2x2-10x-5, if two of its zeroes are √(5/3) and – √(5/3).
Solutions:
Since this is a polynomial equation of degree 4, hence there will be total 4 roots.
√(5/3) and – √(5/3) are zeroes of polynomial f(x).
∴ (x –√(5/3)) (x+√(5/3) = x2-(5/3) = 0
(3x2−5)=0, is a factor of given polynomial f(x).
Now, when we will divide f(x) by (3x2−5) the quotient obtained will also be a factor of f(x) and the remainder will be 0.
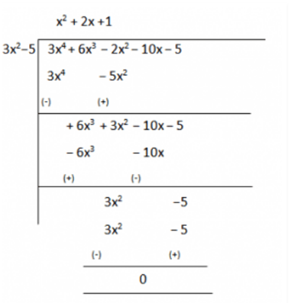
Therefore, 3x4 +6x3 −2x2 −10x–5 = (3x2 –5)(x2+2x+1)
Now, on further factorizing (x2+2x+1) we get,
x2+2x+1 = x2+x+x+1 = 0
x(x+1)+1(x+1) = 0
(x+1)(x+1) = 0
So, its zeroes are given by: x= −1 and x = −1.
Therefore, all four zeroes of given polynomial equation are:
√(5/3),- √(5/3) , −1 and −1.
Hence, is the answer.
4. On dividing x3-3x2+x+2 by a polynomial g(x), the quotient and remainder were x–2 and –2x+4, respectively. Find g(x).
Solution:
Given,
Dividend, p(x) = x3-3x2+x+2
Quotient = x-2
Remainder = –2x+4
We have to find the value of Divisor, g(x) =?
As we know,
Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
∴ x3-3x2+x+2 = g(x)×(x-2) + (-2x+4)
x3-3x2+x+2-(-2x+4) = g(x)×(x-2)
Therefore, g(x) × (x-2) = x3-3x2+x+2
Now, for finding g(x) we will divide x3-3x2+x+2 with (x-2)
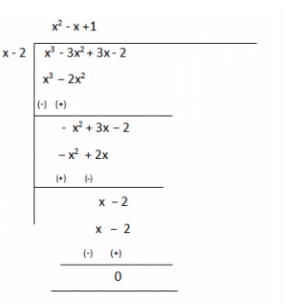
Therefore, g(x) = (x2–x+1)
5. Give examples of polynomials p(x), g(x), q(x) and r(x), which satisfy the division algorithm and
(i) deg p(x) = deg q(x)
(ii) deg q(x) = deg r(x)
(iii) deg r(x) = 0
Solutions:
According to the division algorithm, dividend p(x) and divisor g(x) are two polynomials, where g(x)≠0. Then we can find the value of quotient q(x) and remainder r(x), with the help of below given formula;
Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
∴ p(x) = g(x)×q(x)+r(x)
Where r(x) = 0 or degree of r(x)< degree of g(x).
Now let us proof the three given cases as per division algorithm by taking examples for each.
(i) deg p(x) = deg q(x)
Degree of dividend is equal to degree of quotient, only when the divisor is a constant term.
Let us take an example, 3x2+3x+3 is a polynomial to be divided by 3.
So, (3x2+3x+3)/3 = x2+x+1 = q(x)
Thus, you can see, the degree of quotient is equal to the degree of dividend.
Hence, division algorithm is satisfied here.
(ii) deg q(x) = deg r(x)
Let us take an example , p(x)=x2+x is a polynomial to be divided by g(x)=x.
So, (x2+x)/x = x+1 = q(x)
Also, remainder, r(x) = 0
Thus, you can see, the degree of quotient is equal to the degree of remainder.
Hence, division algorithm is satisfied here.
(iii) deg r(x) = 0
The degree of remainder is 0 only when the remainder left after division algorithm is constant.
Let us take an example, p(x) = x2+1 is a polynomial to be divided by g(x)=x.
So,( x2+1)/x= x=q(x)
And r(x)=1
Clearly, the degree of remainder here is 0.
Hence, division algorithm is satisfied here.