Basics ( Force And Laws Of Motion )
Introduction to Force
A force is an effort that changes the state of an object at rest or at motion. It can change an object’s direction and velocity. Force can also change the shape of an object.
Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
When balanced forces are applied to an object, there will be no net effective force acting on the object. Balanced forces do not cause a change in motion.
Unbalanced forces acting on an object change its speed and/or direction of motion. It moves in the direction of the force with the highest magnitude.

Net force
When multiple forces act on a body, they can be resolved into one component known as the net force acting on the object. For Example:

First Law of Motion
Frictional force
The force that opposes relative motion is called friction. It arises between the surfaces in contact.
Example: When we try to push a table and it does not move is because it is balanced by the frictional force.

First Law of Motion
A body continues to be in the state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force. The First Law is also called the Law of Inertia.

Inertia
Basically, all objects have a tendency to resist the change in the state of motion or rest. This tendency is called inertia. All bodies do not have the same inertia. Inertia depends on the mass of a body. Mass of an object is the measure of its inertia.
More the mass → more inertia and vice versa.

Second Law of Motion
Momentum
Impacts produced by objects depend on their mass and velocity. The momentum of an object is defined as the product of its mass and velocity. p = mv. Vector quantity, has direction and magnitude.
Second Law of Motion
The rate of change of momentum of an object is directly proportional to the applied unbalanced force in the direction of the force.

Conservation of Momentum
Concept of system
- The part of the universe chosen for analysis is called a system.
- Everything outside the system is called an environment.
- For example, a car moving with constant velocity can be considered a system. All the forces within the car are internal forces and all forces acting on the car from the environment are external forces like friction.
Conservation of momentum
- The total momentum of an isolated system is conserved.
- Isolated system → net external force on the system is zero.
- Example: Collision of 2 balls A and B.
From Newtons 3rd law F_{AB} = -F_{BA}
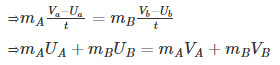
Third Law of Motion
Newton’s 3rd law states that every action has an equal and opposite reaction. Action and reaction forces are equal, opposite and acting on different bodies.

Inertial and Non-inertial frames
- A non-inertial frame of reference is a frame of reference in which Newton’s laws of motion do not hold. A non-inertial reference frame is a frame of reference that is undergoing acceleration with respect to an inertial frame. An accelerometer at rest in a non-inertial frame will, in general, detect a non-zero acceleration.
- A frame of reference where Newton’s Laws hold is known as an inertial frame of reference.
