Introduction to Statistics
Introduction to Statistics
– A study dealing with the collection, presentation and interpretation and analysis of data is called as statistics.
Data
- Facts /figures numerical or otherwise collected for a definite purpose is called as data.
- data collected first-hand data:- Primary
- Secondary data: Data collected from a source that already had data stored
Frequency
– The number of times a particular instance occurs is called frequency in statistics.
Ungrouped data
Ungrouped data is data in its original or raw form. The observations are not classified in groups.
Grouped data
In grouped data, observations are organized in groups.
Class Interval
- The size of the class into which a particular data is divided.
- E.g divisions on a histogram or bar graph.
- Class width = upper class limit – lower class limit
Regular and Irregular class interval
- Regular class interval: When the class intervals are equal or of the same sizes.
- E.g 0-10, 10-20, 20-30….. 90-100
- Irregular class interval: When the class intervals are of varying sizes.
- E.g 0-35, 35-45, 45-55, 55- 80, 80-90, 90-95, 95-100
Frequency table
– A frequency table or distribution shows the occurrence of a particular variable in a tabular form.
Sorting
- Raw data needs to be sorted in order to carry out operations.-
- Sorting ⇒ ascending order or descending order
Ungrouped frequency table
– When the frequency of each class interval is not arranged or organised in any manner.
Grouped frequency table
– The frequencies of the corresponding class intervals are organised or arranged in a particular manner, either ascending or descending.
Graphical Representation of Data
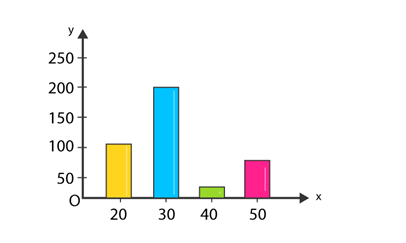
Bar graphs
Graphical representation of data using bars of equal width and equal spacing between them (on one axis). The height
| Savings (in percentage) | Number of Employees (Frequency) |
| 20 | 105 |
| 30 | 199 |
| 40 | 29 |
| 50 | 73 |
| Total | 400 |
The data can be represented as:
Variable being a number
- A variable can be a number such as ‘no. of students’ or ‘no. of months’.
- Can be represented by bar graphs or histograms depending on the type of data.
Discrete → bar graphs
Continuous → Histograms
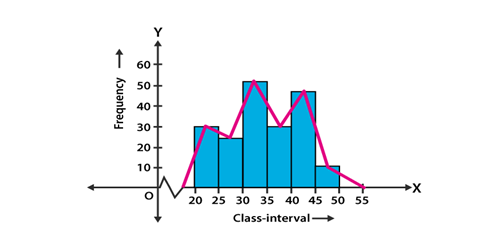
Histograms
- Like bar graphs, but for continuous class intervals.
- Area of each rectangle is ∝ Frequency of a variable and the width is equal to the class interval.
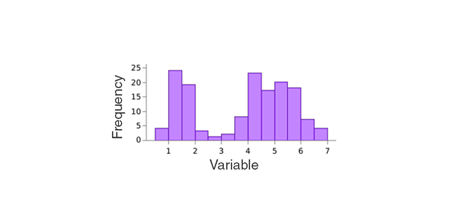
Frequency polygon
- If the midpoints of each rectangle in a histogram are joined by line segments, the figure formed will be a frequency polygon.
- Can be drawn without histogram. Need midpoints of class intervals
Midpoint of class interval
The midpoint of the class interval is called a class mark
Class mark = (Upper limit + Lower limit)/2
Equality of areas
– Addition of two class intervals with zero frequency preceding the lowest class and succeeding the highest class intervals enables to equate the area of the frequency polygon to that of the histogram(Using congruent triangles.)
Measures of Central Tendency
Average
– The average of a number of observations is the sum of the values of all the observations divided by the total number of observations.
Mean

Mode
- The most frequently occurring observation is called the mode.
- The class interval with the highest frequency is the modal class
Median
- Value of the middlemost observation.
- If n(number of observations) is odd, Median =[(n+1)/2]th observation.
- If n is even, the Median is the mean or average of (n/2)th and [(n+1)/2]th observation.