Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife NCERT Solutions for Class 9 SST Geography
Question-1
Define an Ecosystem.
Solution:
An ecosystem is a community of plants, animals and smaller organisms that live,feed, reproduce and interact in the same area or environment. Some ecosystems are very large. For example, many bird species nest in one place and feed in a completely different area. On the other hand, some ecosystems may be physically small, such as you would find in a meadow at he edge of a forest, or in a coral reef in the ocean.How does everything fit together in a forest ecosystem versus a meadow ecosystem?
While some species may be found naturally in both areas, the species that live in the forest ecosystem are usually very different from those that inhabit the meadow, even though the two environments are right next to each other. In other words, if we protect existing natural habitats, we will help to maintain biodiversity (biodiversity is the variety of life in all its forms, levels and combinations). Unfortunately, natural habitats and their ecosystems are more and more endangered because of the damaging environmental effects of growing human populations everywhere.
Question-2
What factors are responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India?
Solution:
Distribution of plants and animals on the earth is determined mainly by climate. However the other factors are soil, relief and drainage, though most of them are also interrelated.
Question-3
What is a bio-reserve? Give two examples.
Solution:
A protected area reserved for the conservation of endangered species of flora (plants) and fauna (animals) in their natural habitat. The Sunderbans in the West Bengal and Nanda Devi in Uttaranchal are the two examples.
Uses of Biosphere Reserve
- In a biosphere reserve, endangered species of animals and plants are protected.
- This important heritage (of plants and animals) is transmitted to the future generations in all its natural vigour and glory.
- The surrounding areas are reserved for research work for the betterment of flora and fauna.
Question-4
Name two animals having habitat in tropical and montane type of vegetation.
Solution:
The common animals found in the tropical forests are elephants and monkeys and the common animals found in the montane forests are Kashmir stag and spotted dear.
Question-5
Distinguish Between Flora and Fauna.
Solution:
Flora
The flora of a country consists of plant kingdom of that country. It covers trees in the forests, other flowering and non-flowering frees grown by man, grassland, scrubs, fens, etc. India possesses about 47,000 different species of plants and 5,000 of them are exclusively found in India.
Fauna
The fauna of a country consists of birds, fish and animals. It also includes amphibians, reptiles, mammals, small insects and worms. The fauna of India is quite rich and varied. There are about 89,000 species in India.
Question-6
Distinguish Between Tropical Evergreen and Deciduous Forests
Solution:
Tropical Evergreen Forests:
Evergreen forests (or Tropical Rain Forests) are found on the rainy parts of the Western Ghats and the island groups of Lakshadweep and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Ebony, mahogany and rosewood are the most important trees of the Evergreen Forests.Teak is the most dominant species of the deciduous forests. Other trees found here are bamboos, sal, shisham, sandalwood and khair.
Deciduous Forests:
Deciduous forests are found mostly in the eastern parts of the country – northeastern states along the foothills of the Himalayas, Jharkhand, West Orissa and Chhattisgarh and the eastern slopes of the Western Ghats.
Trees of the Evergreen Forests don’t shed their leaves at one and the same time, so these forests remain evergreen.The trees of the deciduous Forests shed their leaves for about six to eight weeks in summer.
Question-7
Name different types of Vegetation found in India and describe the vegetation of high altitudes.
Solution:
The following major types of vegetation may be identified in our country:
- Tropical Rain Forests
- Tropical Deciduous Forests
- Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs
- Montane Forests
- Mangrove Forests
The vegetation of high altitudes are Montane Forests. In mountainous areas, the decrease in temperature with increasing altitude leads to the corresponding change in natural vegetation. As such, there is a succession of natural vegetation belts in the same order as we see from the tropical to the tundra region. The wet temperate type of forests are found between a height of 1000 and 2000 metres. Evergreen broad-leaf trees such as oaks and chestnuts predominate. Between 1500 and 3000 metres, temperate forests containing coniferous trees like pine, deodar, silver fir, spruce and cedar, are found. These forests cover mostly the southern slopes of the Himalayas and places having high altitude in southern and northeast India.
At higher elevations, temperate grasslands are common. At high altitudes, generally more than 3,600 meters above sea level, temperate forests and grasslands give way to the Alpine vegetation. Silver fir, junipers, pines and birches are the common trees of these forests. However, they get progressively stunted as they approach the snow-line. Ultimately through shrubs and scrubs, they merge into the Alpine grasslands. These are used extensively for grazing by nomadic tribes like the Gujjars and the Bakarwals. At higher altitudes, mosses and lichens form part of tundra vegetation. The common animals found in these forests are Kashmir stag, spotted dear, wild sheep, jack rabbit, Tibetan antelope, yak, snow leopard, squirrels, Shaggy horn wild ibex, bear and rare red panda, sheep and goats with thick hair.
Question-8
Quite a few species of plants and animals are endangered in India. Why?
Solution:
Quite a few animal species are endangered and some have become extinct. The main causes for this major threat to nature are hunting by greedy hunters for commercial purposes, pollution due to chemical and industrial waste, acid deposits, introduction of alien species and reckless cutting of the forests to bring land under cultivation and inhabitation, which are also responsible for the imbalance.
Question-9
Why has India a rich heritage of flora and fauna?
Solution:
Our country India is one of the twelve-mega bio-diversity countries of the world. With about 47,000 plant species India occupies tenth place in the world and fourth in Asia in plant diversity. There are about 15,000 flowering plants in India, which account for 6 percent in the world’s total number of flowering plants. The country has many non-flowering plants such as ferns, algae and fungi. India also as 89,000 species of animals as well as a rich variety of fish in its fresh and marine waters.
Natural Vegetation and Wild Life Class 9 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is natural vegetation or virgin vegetation?
Answer:
It refers to a plant community which has grown naturally without human aid, and has been left undisturbed by human beings for a long time.
Question 2.
What is flora and fauna?
Answer:
Flora – Plants of a particular region or period.
Fauna – The species of animals.
Question 3.
“Land and soil affects the natural vegetation directly and indirectly.” Justify by giving two examples.
Answer:
- The sandy soil of the desert support cactus and thorny bushes.
- Wet,marshy,deltaic soil supports mangroves.
Question 4.
What is an ecosystem?[CBSE 1997]
Answer:
The interdependence of species of plants and animals in a given area fdhns a single ecosystem.
Question 5.
Name two non-flowering plants.
Answer:
Ferns, algae and fungi.
Question 6.
Name, any two factors that form the flora and the fauna?
Answer:
Soil, relief, climate and drainage.
Question 7.
What is a biome? [CBSE 2014]
Answer:
A very large ecosystem on land having distinct types of vegetation and animal life is called a biome.
Question 8.
Mention any two regions having tropical evergreen forests.
Answer:
The Western Ghats, plains of West Bengal and Odisha, and the north-eastern India.
Question 9.
Name two commercially useful trees of the Tropical Rain Forests.
Answer:
Ebony, mahogany and rosewood.
Question 10.
Mention any two factors responsible for deforestation.
Answer:
- Overgrazing by animals
- Careless management of forests
Question 11.
Where are the rhinoceros found?[CBSE 1995F]
Answer:
In swampy and marshy lands of Assam and North-West Bengal. .
Question 12.
The ‘Tropical Rain forests appear green all the year round.’ Give reason. [CBSE2014]
Answer:
There is no definite time for trees to shed their leaves.
Question 13.
Which are the most widespread forests of India?
Answer:
Tropical Deciduous Forests.
Question 14.
On the basis of the availability of water, tropical deciduous forests are divided into two parts. What are these two Categories?
Answer:
Dry deciduous and Moist deciduous.
Question 15.
Name one important trees each of the Moist Deciduous and Dry deciduous Forests.
Answer:
Moist Deciduous – Teak.
Dry Deciduous – Sal.
Question 16.
Name any two useful trees of the Thorn Forests.
Answer:
Kikar, babul, khair and date palm.
Question 17.
Name any two trees of the Alpine Forests.
Answer:
Silver fir, pine and junipers.
Question 18.
How many species of birds and fish are known?
Answer:
Fish- About 2500 and Birds-Around 1200
Question 19.
Where are the wild asses found in India? [CBSE 2000]
Answer:
In Rann of Kachchh (Gujarat) and Rajasthan.
Question 20.
Which is the natural habitatof
(i) Indian lion
(ii) Tigers
Answer:
(i) India lions -Gir forests of Gujarat,
(ii) Tigers – Forests of Madhya Pradesh.
Question 21.
Explain with example how temperature can affect the type of . vegetation?
Answer:
On the slopes of the Himalayas, and hills of the Peninsula above, the height of 915m, the fall in the temperature affects the types of vegetation, and its growth and changes it from tropical to subtropical temperature in the alpine vegetation.
Question 22.
Name two areas where the thorn and the scrub forests are formed.
Answer:
Punjab plains, Northern Madhya Pradesh, South-West Uttar Pradesh, (Bundelkhand plateau).
Question 23.
Name any two biosphere reserves.[CBSE 1999]
Answer:
Nilgiri (Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Karnataka), Nanda Devi (Uttarakhand).
Question 24.
Name two endangered species of wildlife. [CBSE 1998]
Answer:
Tiger and rhinoceros.
Question 25.
How are the habitats of camels and those of one Horned rhinoceros diametrically opposite to each other? [CBSE 2000(C)]
Answer:
Camels are found in Rajasthan where as the one-homed rhinoceros are found in Assam and North-West Bengal.
Question 26.
Name any two states of India where elephants are found.
Answer:
Assam, Kerala and Karnataka.
Question 27.
Name any two biosphere reserves of India and their location.
Answer:
- Manas – Assam
- Sundarbans – West Bengal
Question 28.
What is India’s rank in the world and in Asia in plant diversity?
Answer:
In the world – Tenth In Asia – Fourth.
Question 29.
Name any one medicinal plant.
Answer:
Neem
Question 30.
Why are the leaves of the Thorn forests small and stems succulent?
Answer:
Leaves of the Thom Forests are mostly small to minimise evaporation, and the stems are succulent to conserve water.
Question 31.
Where is the Alpine Vegetation found?
Answer:
At high altitudes, generally more than 3,600 metres above the sea-level.
Question 32.
How many species of animals does India possess?
Answer:
More than 90,000 species of animals.
Question 33.
What are endangered species?
Answer:
The plant and animal species which are in danger of getting extinct are called the endangered species.
Question 34.
How many plant species are endangered?
Answer:
About 1300 plant species are endangered.
Question 35.
Carefully study the given picture, and identify the type of vegetation. Mention one feature of that vegetation.
Answer.
Thom forests and scrubs The vegetation is found in regions with less than 70 cm of rainfall.
Question 36.
Name any two states where tigers are found.
Answer:
Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal.
Natural Vegetation and Wild Life Class 9 Important Questions Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why does India possess a great variety of flora and fauna?[CBSE 2o15]
Answer:
- Different types of soil: India has almost all major types of soils. It has alluvial soil which is very fertile, black soil, laterite soil, desert and mountain soil. The sandy soils of the desert support cactus and thorny bushes while wet, marshy deltic soils support mangroves and deltic vegetation.
- Different climatic conditions: Different climatic conditions prevail in India. At some places, the temperature is at 55°C and at other,
it is about – 45°C. So it supports all types of plants. Some places receive a rainfall of more than 1000 cm, and some receive only 50 cm. This also helps in growing different type of plants. - Sunlight: Sunlight is one of the important factors responsible for the growth of vegetation. Due to the longer duration of sunlight, trees grow faster in most parts of India.
- Precipitation: Precipitation also plays a vital role in the growth of different types of vegetation. Tropical rainforests are found in the Western Ghats due to heavy rainfall.
Question 2.
Distinguish between Tropical Evergreen and Deciduous forests JCBSE 2013,14]
Answer: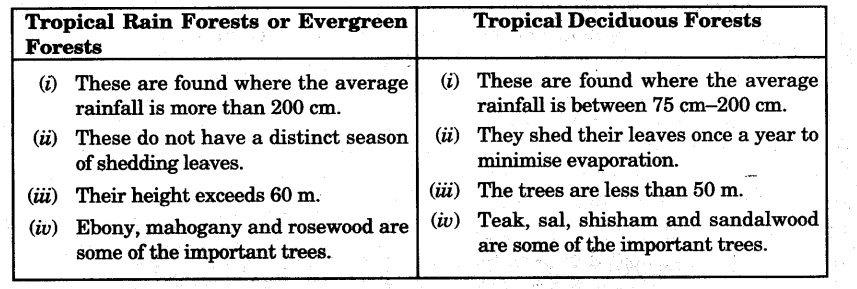
Question 3.
Write any two points of difference between
(i) Dry deciduous
(ii) Moist deciduous.
Answer:
Question 4.
Mention any four characteristics of the thorny forests water.
Answer:
- This type of vegetation is found in regions with less than 70 cm of rainfall.
- This type of vegetation is found in the north-western part of the country including the semi-arid areas of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh and Haryana.
- Acacias, palms, euphorbias and cacti are the main plant species.
- Trees are scattered, and have long roots penetrating deep into the soil in order to get moisture.
- The stems are succulent to conserve
- Leaves are mostly thick, and small to minimise evaporation. .
Question 5.
Mention any four characteristics of the mangrove tidal forests.[CBSE2015]
Answer:
- The mangrove tidal forests are found in the areas of coasts influenced by tides. Mud and silt get accumulated on such coasts.
- Dense mangroves are the common varieties with roots of the plants submerged under water.
- The deltas of the Ganga, the , Mahanadi, the Krishna, the Godavari and the Kaveri are covered by such vegetation.
- In the Ganga-Brahamputra delta, the sundari trees are found, which provide a durable hard timber. Palm, coconut, keora, agar also grow in some parts of the delta.
Question 6.
Write three steps taken by the government for the protection and conservation of great biological diversity of India. [CBSE 2013,14]
Answer:
- Various biosphere reserves have been set up in various parts of India. For example the Nilgiri at Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Kerala, Nanda Devi in Uttarakhand, etc.
- About 99 national parks, 513 wildlife sanctuaries, and 35 zoological gardens have been set up.
Financial and technical assistance is provided to many Botanical Gardens set up by the government.
Natural Vegetation and Wild Life Class 9 Important Questions Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the altitude zones of vegetation in the mountainous regions. .
Or
“The mountainous region of India exhibits a succession of natural vegetation belts from tropical to tundra types, all compressed into an altitude of six kilometres or so”. Elaborate the above statement with four examples from different altitudinal belts.
Or
Describe the major vegetation zones of the Himalayan region.
Or
In mountainous area, there is change in natural vegetation due to decrease in temperature. Justify giving examples from different zones. [CBSE March 2011 ]
Answer:
In the Himalayan region of our country, the vegetation differs according to the height.
- In the foothill, (the Shiwalik) are tropical deciduous forests. ‘Sal’ is the most important species of economic significance.
- The zone with altitude 1000 m – 2000 m consists of evergreen forests. Beech, chestnut, oak, ash, etc., are the main trees. These at a higher altitude are replaced by ‘chir’ and ‘chil’.
- The zone between 1500m – 3000 m includes pine, cedar, silver fir and spruce. They are the famous coniferous trees, typical of the dry temperate region found in the inner Himalayan region.
- At the height of 3600 m or more, shrubs, scrubs, and grasses of alpine variety are found.
Question 2.
Write three steps taken by the government for the protection and conservation of great biological diversity of India. [C.B.S.E 1999]
Or
Give any three steps taken by the government of India to protect the flora and fauna. [CBSE March 2011, 2012]
Answer:
- Various biosphere reserves have been set up in various parts of India. For example, the Nilgiri at Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala, Nanda Devi in Uttarakhand, etc.
- About 100 national parks, 515 wildlife sanctuaries, and 35 zoological gardens have been set up.
- The endangered species are being identified and special efforts are being made to preserve them. For example: Tiger Project’.
- Killing of wildlife has been banned and special forest officers have been appointed.
Natural Vegetation and Wild Life Class 9 Important Questions Higher Order Thinking Skills (Hots) Questions
Question 1.
Carefully study the given table and answer the following questions:
(i) Is there any relationship between temperature and type of vegetation?
Answer:
Yes, thie fall in temperature affects the type of vegetation and its growth and changes it from tropical to subtropical.
(ii) Identify the type of vegetation you can expect in zone D.
Answer:
Alpine.
(iii) Is temperature the only criteria for all types of vegetation?
Answer:
No, vegetation also depends on rainfall, humidity, and altitude.
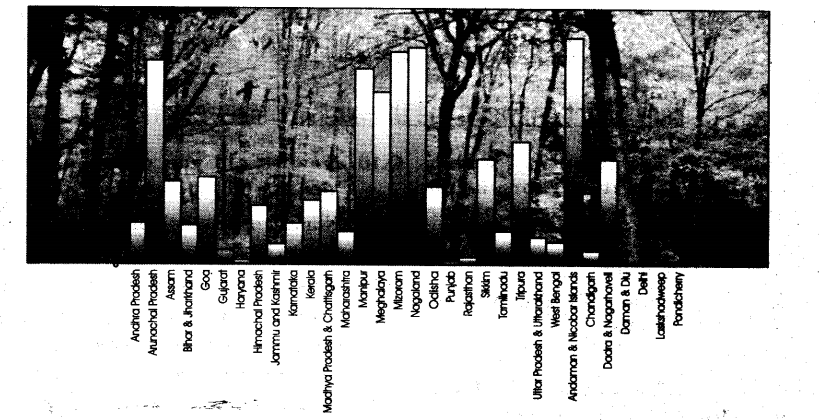
Question 2.
Study the given bar graph carefully, and answer the following questions to which state has the highest area under forests?
(i) Which state has the highest area under forests?
(ii) Name any two states which have more than 80% of the area under forests?
(iii) Which Union territory has the highest area under forests?
(iv) Name any two states having very low area under forests.
Answer:
(i) Nagaland
(ii) Nagaland and Mizoram
(iii) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
(iv) Punjab and Haryana
Natural Vegetation and Wild Life Class 9 Important Questions Value Based Questions
Question 1.
Mention any two values which are reflected by the ecosystem?
Answer:
Importance of interdependent and interrelationship.
Question 2.
How do the human beings influence the ecology of a region?
Answer:
The greed of human beings leads to over utilisation of these resources. They cut the trees and kill the animals creating ecological imbalance.
Question 3.
What are the major factors responsible for the threat to the nature? Mention any two.
Answer:
- Destruction of habit
- Human predation.
Question 4.
What is the importance of awlwmlg for us?
Answer:
- Animals provide us meat,eggs etc.
- Fish provide us nutritive food.
- Many insects helps in pollination of crops.
- Animals are important part of our ecosystem.
- Animals skin is used to prepare leather