Understanding Motion (motion class 9)
Reference point and reference frame
- To describe the position of an object we need a reference point or origin. An object may seem to be moving to one observer and stationary to another.
- Example: A passenger inside a bus sees the other passengers be at rest, whereas an observer outside the bus sees the passengers are in motion.
- In order to make observations easy, a convention or a common reference point or frame is needed. All objects must be in the same reference frame.
Distance and Displacement (motion class 9)
- The magnitude of the length covered by a moving object is called distance. It has no direction.
- Displacement is the shortest distance between two points or the distance between the starting and final positions with respect to time. It has magnitude as well direction.
- Displacement can be zero, but distance cannot.

Distance VS Displacement
Magnitude (motion class 9)
Magnitude is the size or extent of a physical quantity. In physics, we have scalar and vector quantities.
Scalar quantities are only expressed as magnitude. E.g. time, distance, mass, temperature, area, volume
Vector quantities are expressed in magnitude as well as the direction of the object. E.g. Velocity, displacement, weight, momentum, force, acceleration, etc.
Time, Average Speed and Velocity
Time and speed (motion class 9)
Time is the duration of an event that is expressed in seconds. Most physical phenomena occur with respect to time. It is a scalar quantity.
Speed is the rate of change of distance. If a body covers a certain distance in a certain amount of time, its speed is given by
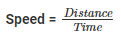
Average speed = Total distance travelled / Total time taken
Uniform motion and non-uniform motion
When an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time it is in uniform motion.
When an object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time it is said to be in non-uniform motion.
Velocity (motion class 9)
The Rate of change of displacement is velocity. It is a vector quantity. Here the direction of motion is specified.

Acceleration (motion class 9)
The rate of change of velocity is called acceleration. It is a vector quantity. In non-uniform motion, velocity varies with time, i.e., change in velocity is not 0. It is denoted by “a”
Acceleration = Change in Velocity / Time
(OR)

Where, t (time taken), v (final velocity) and u (initial velocity).
Motion Visualised (motion class 9)
Distance-Time graph (motion class 9)
- Distance-Time graphs show the change in position of an object with respect to time.
- Linear variation = uniform motion and non-linear variations imply non- uniform motion
- The slope gives us speed
Distance – Time Graph
- OA implies uniform motion with constant speed as the slope is constant
- AB implies the body is at rest as the slope is zero
- B to C is non-uniform motion
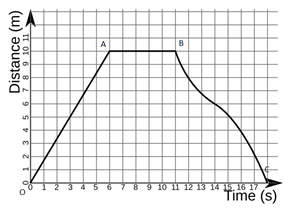
Velocity-Time Graph (motion class 9)
- Velocity-Time graphs show the change in velocity with respect to time.
- Slope gives acceleration
- The area under the curve gives displacement
- Line parallel to x-axis implies constant velocity-

Velocity – Time Graph
OA = constant acceleration, AB = constant velocity, BC = constant retardation
Equations of Motion (motion class 9)
The motion of an object moving at uniform acceleration can be described with the help of three equations, namely
(i) v = u + at
(ii) v2 – u2 = 2as
(iii) s = ut + (1/2)at2
Derivation of velocity-time relation by graphical method

Velocity – Time Graph

Derivation of position-time relation by graphical method
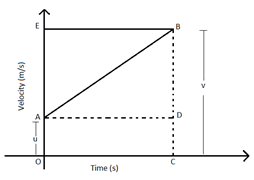
Velocity – Time Graph

Derivation of position-velocity relation by graphical method

Velocity – Time Graph

Uniform circular motion (motion class 9)
- If an object moves in a circular path with uniform speed, its motion is called uniform circular motion.
- Velocity is changing as direction keeps changing.
- Acceleration is constant