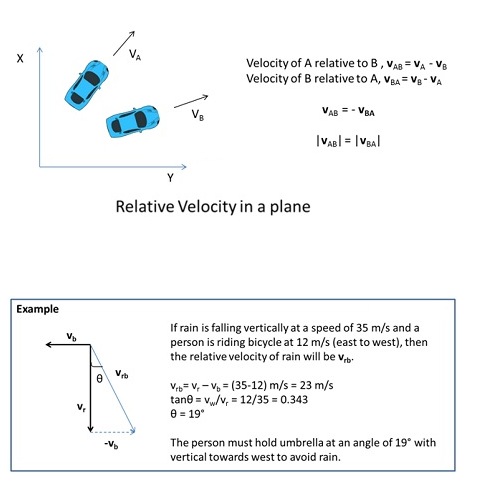
Motion in a plane with constant acceleration
Motion in a plane (two dimensions) can be treated as two separate simultaneous one-dimensional motions with constant acceleration along two perpendicular directions. X and Y directions are hence independent of each other.
If v0 being the velocity at time 0, the displacement can be written as:
x = x0 + v0xt+ ½ axt2 and y = y0 + v0yt+ ½ ayt2
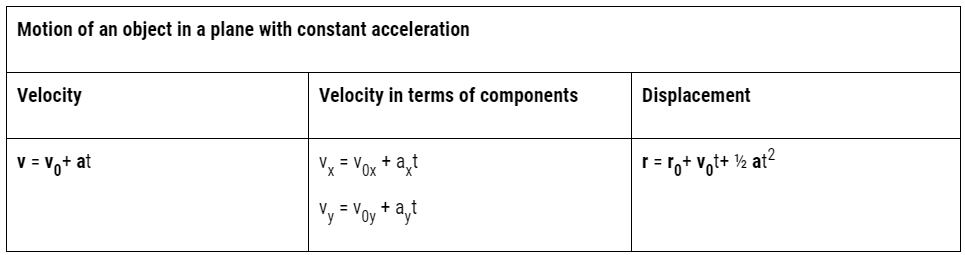
Relative velocity in two dimensions
The concept of relative velocity in a plane is similar to the concept of relative velocity in a straight line.