Introduction
In this chapter we will see the importance of waves in our life.
We will also study about the different properties of waves, some terms related to waves and also about different types of waves.We will also learn how waves propagate.
For example: –
- Medium required by the waves to travel from one point to another:-
- Consider a boy holding a thread and one end of thread is tied to the wall.
- When a boy moves the thread, the thread moves in the form of a wave.

- Similarly a boat sailing over the sea,the boat is able to move because of waves.
- The ripples formed in a lake when we drop a stone in the lake.They are also waves.
- Earthquakes are caused due to the waves under the surface of the earth.
- The strings of the guitar when we play them are also waves again.
- Music system which we use to hear songs.This is due to sound waves.
- When 2 people talk they are able to hear each other because of the sound waves.
In the below Picture we can see waves need a medium to propagate.

Some type of waves can propagate from one point to another without any medium.
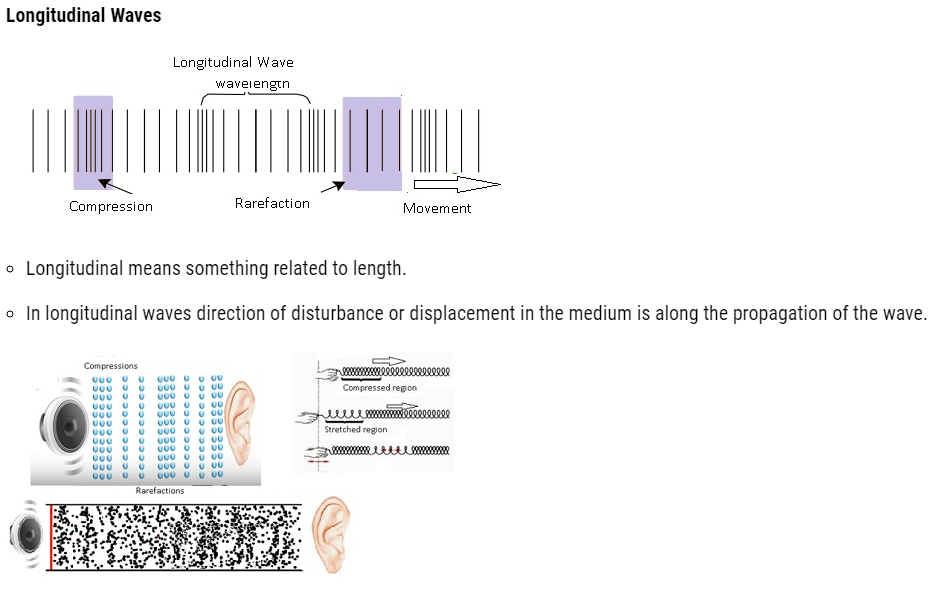
- Waves which are related to matter:-
- There are some set of waves which are inside the matter.
- For example: – whole of universe.

What is a wave?
A wave is s disturbance that propagates through spaceand time,usually with transference of energy.
For example: –
- Consider the sound of the horn; this sound reaches our ear because of sound waves.
- There is transfer of energy from one point to another with the help of particles in the medium.
- These particles don’t move they just move around their mean position,but the energy is getting transferred from one particle to another and it keeps on transferring till it reaches the destination.
- The movement of a particle is initiated by the disturbance.And this disturbance is transferred from one point to another through space and time.
Note:-Energy and not the matter is transferred from one point to another.
- When a source of energy causes vibration to travel through the medium a wave is created.

Types of Waves
- Mechanical waves
- Electromagnetic waves
- Matter waves
Mechanical waves: –
- The mechanical waves are governed by all the Newton’s laws of motion.
- Medium is needed for propagation of the wave.
For Example: – Water Waves, Sound Waves
Water waves: They are mechanical waves for which a medium is required to propagate.

Electromagnetic waves:-
- Electromagnetic waves are related to electric and magnetic fields.
- An electromagnetic wave, does not need a medium to propagate, it carries no mass,does carry energy.
Examples: – Satellite system, mobile phones,radio, music player, x-rays and microwave.

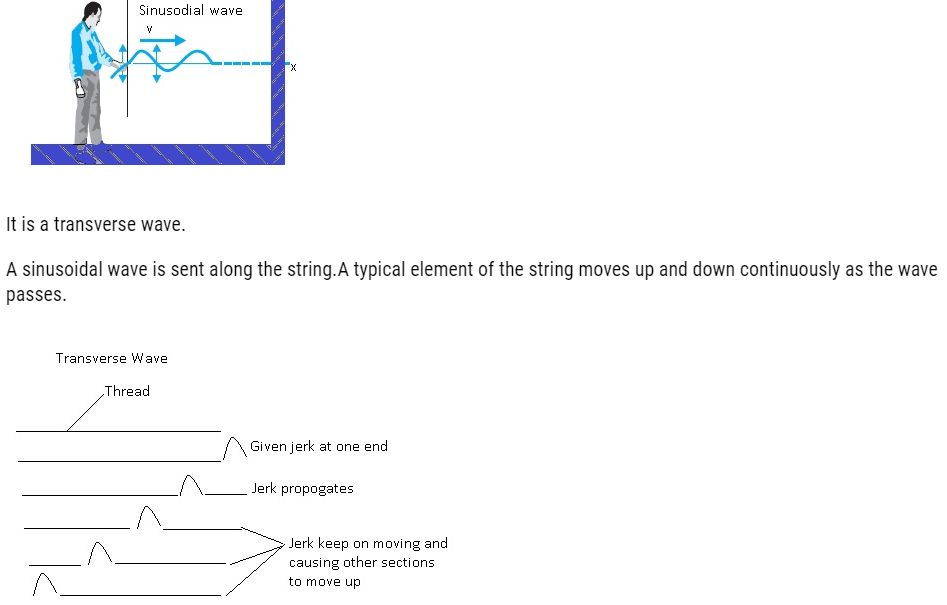
Transverse Waves
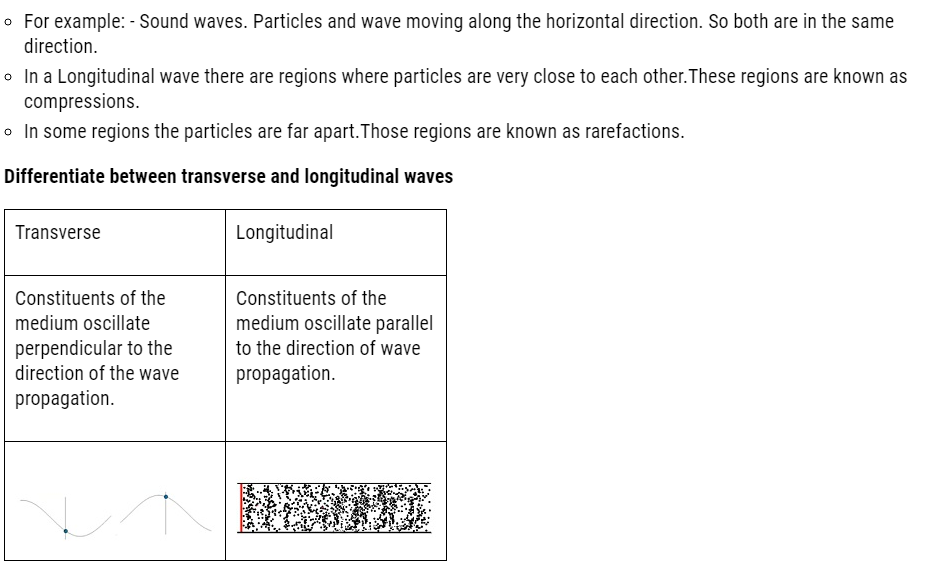
- The transverse waves are those in which direction of disturbance or displacement in the medium is perpendicular to that of the propagation of wave.
- The direction in which a wave propagates is perpendicular to the direction of disturbance.