About Lesson
Calorimetry
Calorimetry is made up of 2 words:-
- Calorie which means heat andmetry means measurement.Therefore Calorimetry means measurement of heat.
- Calorimetry is defined as heat transfers from a body at a higher temperature to a body at a lower temperature provided there is no loss of heat to the atmosphere.
- Principle of Calorimetry is heat lost by one body is equal to the heat gained by another body.
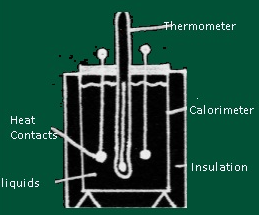
- The Device which measures Calorimetry is known as Calorimeter.
- Description of Calorimeter
- A calorimeter consists of metallic vessel and a stirrer both are made of same material (copper or aluminium) and the vessel is kept in a wooden jacket so that there is no heat loss .A mercury thermometer can be inserted through a small opening in the outer jacket.
Change of State
The transition from either solid to liquid or gas and gas to either liquid or solid is termed as change of state.
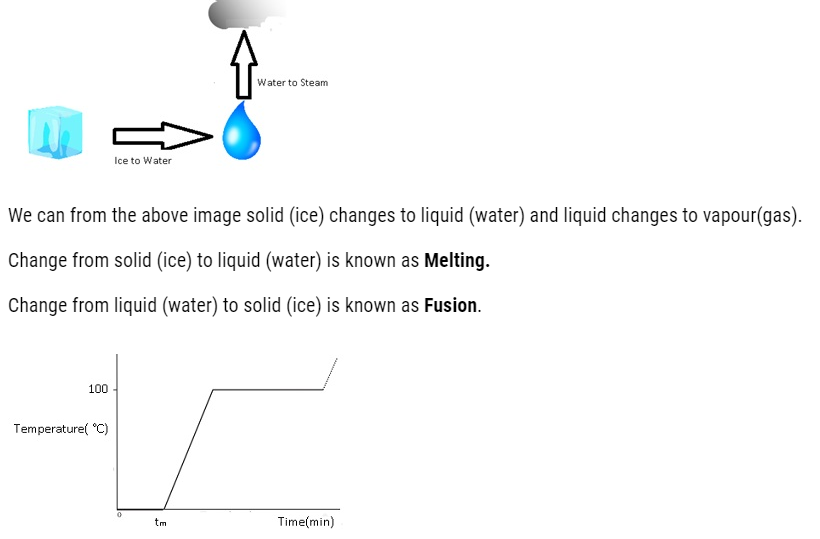
Thermal Equilibrium: – At this state there is no loss or gain of heat takes place.
The temperature at which the solid and the liquid states of the substance are in thermal equilibrium with each other is called its melting point.

Regelation:-
- Regelation can be defined as phenomenon in which the freezing point of water is lowered by the application of pressure.
Example:-

Cause of regelation:-
- If we have a block of ice and a copper wire pulled by two masses if we will observe that copper wire can pass through ice block this is because copper is good conductor of heat so as it passes through the ice it gets refreeze as the copper will generate heat and this heat will pass quickly to the ice below and it starts melting because there is increase in pressure which lowers temperature as a result the wire will move through the ice. This happens because of regelation.
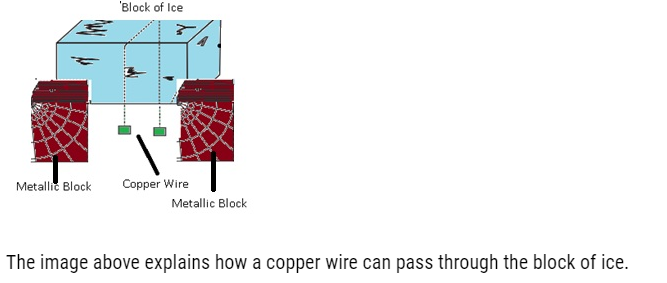
The image above explains how a copper wire can pass through the block of ice.
Vaporisation: – Transition from liquid to vapour.
- The change of state from liquid to vapour (or gas) is called vaporisation.

