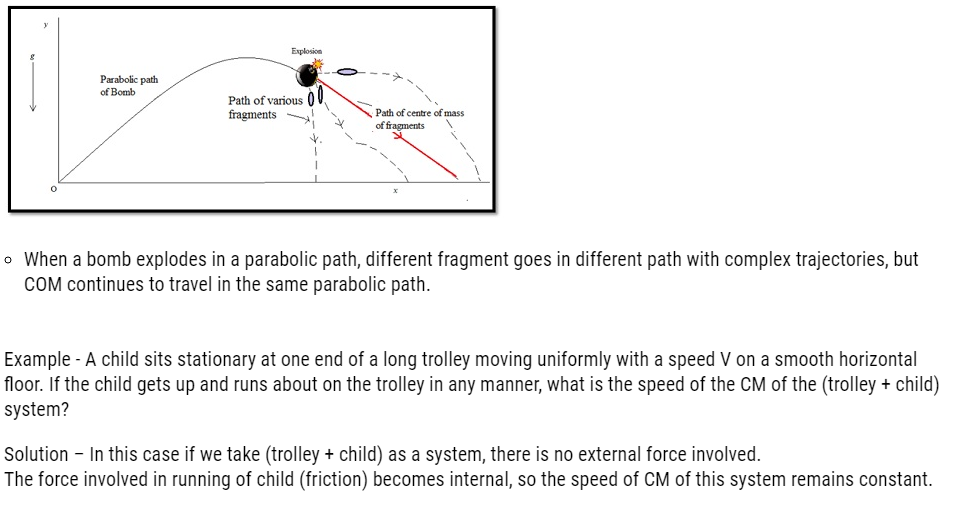
Introduction
Rigid body is a body with a perfectly definite and unchanging shape. The distances between all pairs of particles of such a body do not change.

In pure translational motion at any instant of time all particles of the body have the same velocity.
In rotation of a rigid body about a fixed axis, every particle of the body moves in a circle, which lies in a plane perpendicular to the axis and has its centre on the axis.


Centre of mass
- Imaginary point where the whole mass of system can be assumed to be concentrated
- The centre of mass of two bodies lies in a straight line.
(Here m1 & m2 are two bodies such that m1 is at a distance x1 from O, & m2 at a distance x2 from O. )
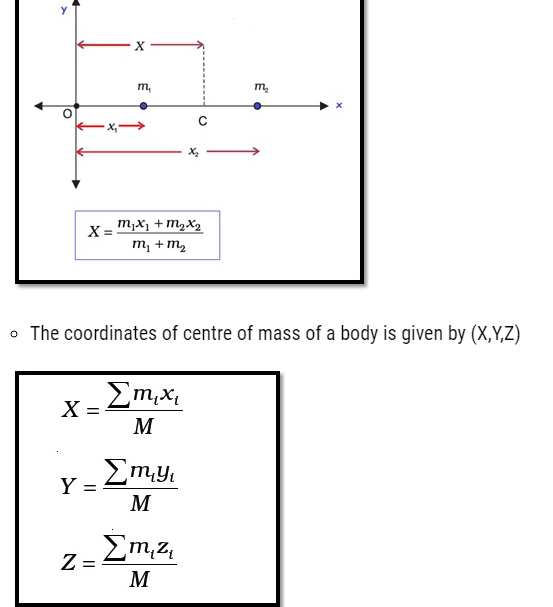
Here,
- M = S mi, the index i runs from 1 to n
- mi is the mass of the ith particle
- the position of the ith particle is given by (xi, yi, zi).
- If we increase the number of elements n , the element size Dmi decreases , and coordinates of COM is given by:
, ,
Where x,y,z = coordinates of COM of small element dm
- The vector expression equivalent to these three scalar expressions is
Where
- R = position of COM of body
- r = position of COM of small element of mass dm
Consider a thin rod of length l, taking the origin to be at the geometric centre of the rod and x-axis to be along the length of the rod, we can say that on account of reflection symmetry, for every element dm of the rod at x, there is an element of the same mass dm located at –x.

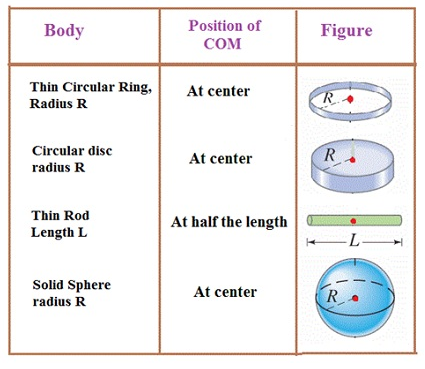
Example – Find COM of semicircular ring.

Motion of COM
- The centre of mass of a system of particles moves as if all the mass of the system was concentrated at the centre of mass and all the external forces were applied at that point.
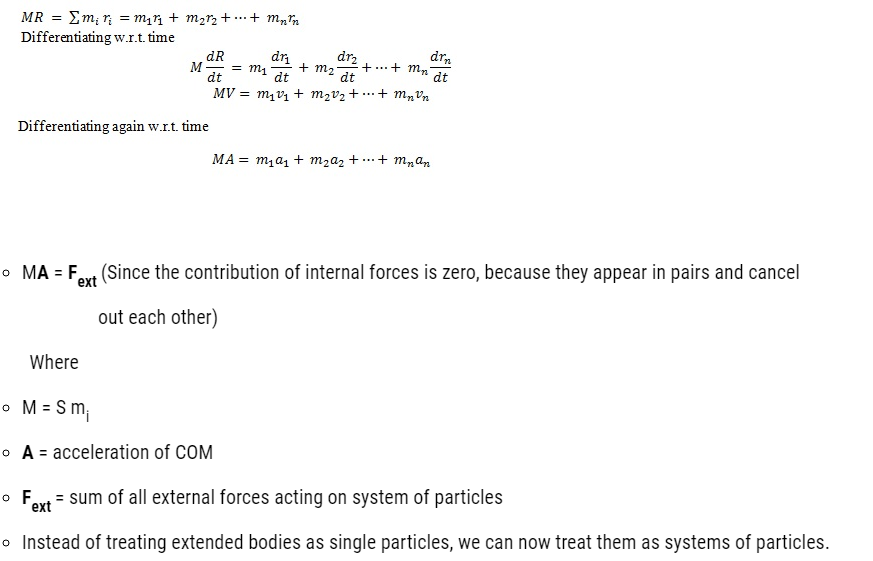
We can obtain the translational component of their motion, i.e. the motion COM of the system, by taking the mass of the whole system to be concentrated at the COM and all the external forces on the system to be acting at the centre of mass.