Friction
- Friction is a contact force that opposes relative motion.
- No friction exists till an external force is applied.
There are 3 types of Friction:
- Static friction
- Force that resists initiation of motion of one body over another with which it is in contact
- Opposes Impending motion
- Denoted by fs
Let the ball be at rest initially
Applied force, Fa = 0; Static friction, fs = 0

fs acts when a body is at rest. Hence called Static friction
- Limiting value of fs depends on Normal reaction, and is independent of the area of contact
fs max ∝ N
fs max = constant * N
fs max = μs N
where μs is the coefficient of static friction
This coefficient depends on the nature of surfaces in contact.
- According to the Law of Static friction, Static friction is always less than or equal to the limiting value of fs
fs =< fs max
fs max = μs N
fs =< μs N
Kinetic friction
- Force that resists motion of one body over another with which it is in contact.
- Denoted by fk
- As motion starts, fs vanishes and fk appears

(Fa – fk) = ma
a = (Fa – fk)/m
- When applied force = fk
Fa = fk
Therefore, a = 0 i.e. the body moves with uniform velocity
- When applied force = 0
Fa = 0
A = -fk/m
No motion occurs, the body stops
Relation between Coefficient of Static & Kinetic friction
fk = μk N
fs =< μs N
fs > fk (to keep the body moving)
μs N > μk N
Or, μk < μs
Coefficient of kinetic friction is smaller than the coefficient of static friction.

Problem: Calculate the force required for pushing a 30 kg wooden bar over a wooden floor at a constant speed. Coefficient of friction of wood over wood = 0.25
Solution.
M = 30 kg
μ = 0.25
(Fa – f) = ma
For constant speed, a = 0
So, Fa = f= μN

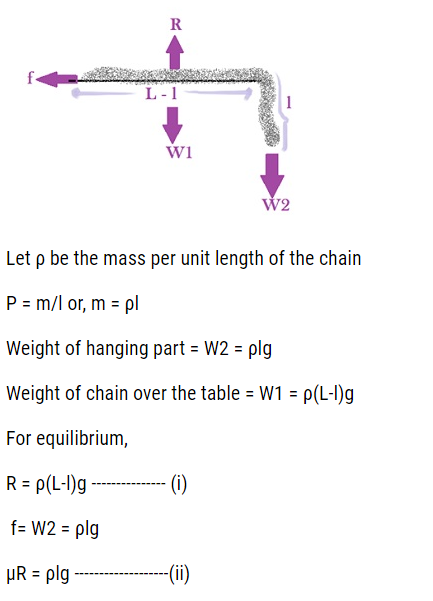
(i)Divided by (ii) gives
1/μ = (L-l)/l
l = μL – μl
l + μl = μL
Therefore, l = μL/( μ + 1)