INTRODUCTION ( Law of Motion )
External force is needed to make a stationary body move as well as to stop a moving body.

To understand this chapter i.e. Laws of Motion, lets have a quick recap on what we already know about Motion.
- Motion in simple is tendency to move. An object is said to be in motion when it changes its position with time
- A body is said to be at Rest if it is not moving
- An external force is always involved in motion. This force helps body to perform required actions and these actions are according to rules or laws i.e. Laws of Motion.
Contact & Non-contact forces
- External force comes into picture when the body starts moving or comes to rest either by coming in contact with the body or without being in contact.
- Contact force– force applied by coming in contact with the body
Example: hitting of cricket ball with bat in game
- Non-contact force– force applied without coming in contact with body
Example: coin attracted towards magnet(magnetic force) ball dropped at height attracted towards the earth (gravitational force)


Aristotle’s fallacy:
Aristotle, the Greek Scientist held the view that an external force is required to keep a body in uniform motion.
His concept is obsolete now, because he considered only one side of motion and fails to explain the other i.e. if body is in motion then how does it come to rest? There came the concept of the opposing external force of Friction.
For example, a ball rolled on the floor comes to rest after some time due to opposing force of friction.
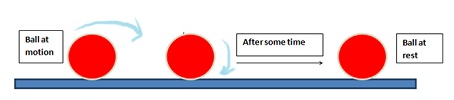
Conclusion:
An external force is required to keep a body in motion, only if resistive forces ( like frictional & viscous forces) are present.