Introduction
You might have noticed that youfeel hotter on a sunny afternoon as compared to a windy night. This is because of the difference in temperatures. Temperature is very high in the afternoon as compared to night. This chapter basically gives us the
Examples: information about thermal properties of matter where we will study about the properties of different substances by virtue of heat / heat transfer.
In simple terms, we can say that when temperature is more heat is more and when temperature is less heat is less.
Hot Sunny day (Temperature is more)and ice cold water (Temperature is less).
Temperature and Heat
Temperature is defined as the measure of degree of hotness or coldness of a body.
Example:-
- A cup of hotsoup or a scoop of Ice-cream.

After some time we will see this hot cup of coffee will become cold as there will be transfer of heat.
The S.I Unit of Heat is joule (J) and some of the commonly used units are: calorie and kilocalorie
Relation between Joule and Calorie
1calorie=4.18 Joules
1kilocalorie = 1000 calories
The S.I. Unit of Temperature is Kelvin (K) and some of the commonly used unitsare:Fahrenheit (°F) and Celsius (°C)
Measurement of Temperature
Temperature is measured with the help of thermometer. Mercury and Alcohol are commonly used liquids in the liquid-in-glass thermometers.
- To construct a thermometer two fixed points are to be chosen as a reference points. These fixed points are known asfreezing(ice point) and boiling point(steam point). The water freezes and boils at these two points under standard pressure.
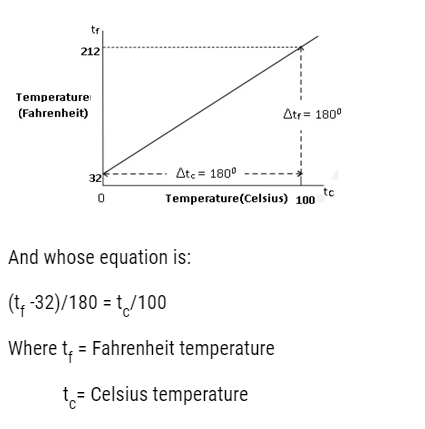
- The ice and steam point in Fahrenheit Temperature scale are 32°F and 212 °F resp.It has 180 equal intervals between two reference points.
- On Celsius Scale values are 0°C and 100°C for ice and steam point resp. It has 100 equal intervals between two reference points.