Centre of Gravity
- The centre of gravity of a body is that point where the total gravitational torque on the body is zero.
- The centre of gravity of the body coincides with the centre of mass in uniform gravity or gravity-free space.
- If g varies from part to part of the body, then the centre of gravity and centre of mass will not coincide.

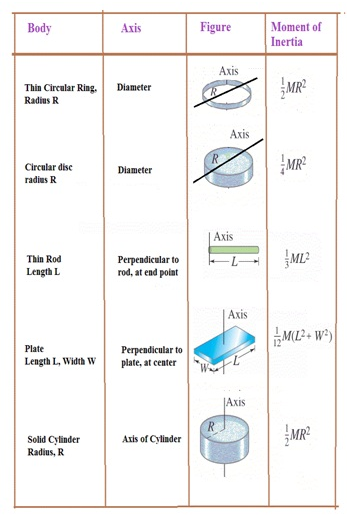
Moment of Inertia
- Moment of inertia (I) is analogue of mass in rotational motion.


Theorem of perpendicular axis
- Perpendicular Axis Theorem: The moment of inertia of a planar body (lamina) about an axis perpendicular to its plane is equal to the sum of its moments of inertia about two perpendicular axes concurrent with perpendicular axis and lying in the plane of the body.

Theorem of parallel axis
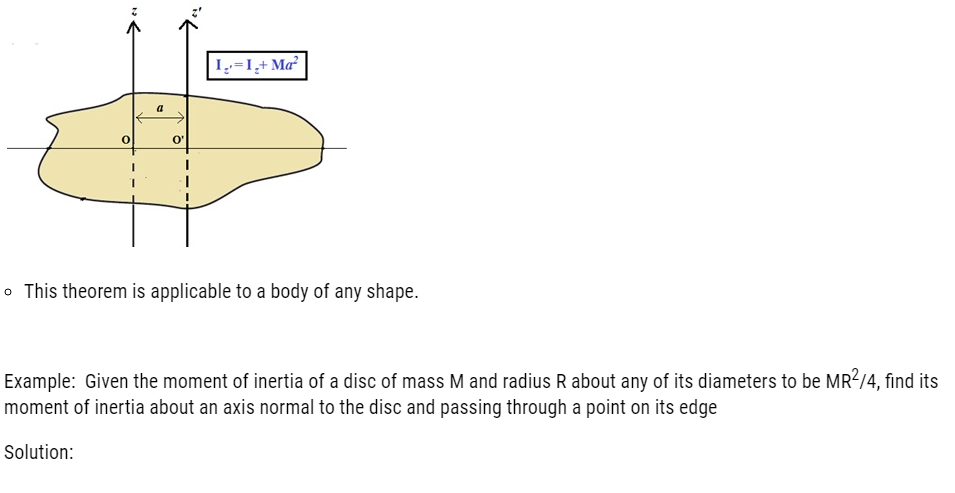
- Parallel Axis Theorem: The moment of inertia of a body about any axis is equal to the sum of the moment of inertia of the body about a parallel axis passing through its centre of mass and the product of its mass and the square of the distance between the two parallel axes.

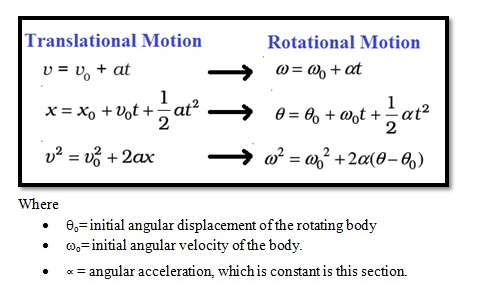
Kinematics of Rotational Motion about a Fixed Axis
- We can derive equation of motion similar to translational motion