Projectile Motion
An object that becomes airborne after it is thrown or projected is called projectile. Example, football, javelin throw, etc.
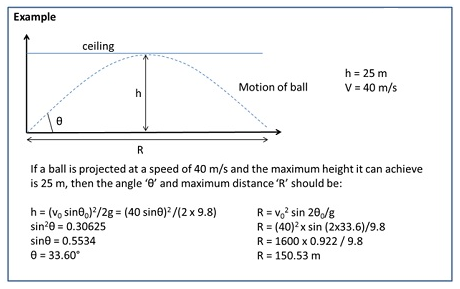
| Quantity | Value |
| Components of velocity at time t | vx = v0 cosθ0vy = v0 sinθ0–gt |
| Position at time t | x = (v0 cosθ0)ty = (v0 sinθ0)t – ½ gt2 |
| Equation of path of projectile motion | y = (tan θ0)x – gx2/2(v0 cosθ0)2 |
| Time of maximum height | tm = v0 sinθ0 /g |
| Time of flight | 2 tm = 2 (v0 sinθ0 /g) |
| Maximum height of projectile | hm = (v0 sinθ0)2/2g |
| Horizontal range of projectile | R = v02 sin 2θ0/g |
| Maximum horizontal range (θ0=45°) | Rm = v02/g |