System and Surroundings
System: – System is defined as any part of universe enclosed by some boundary through which exchange of heat or energy takes place.
Surroundings: – Any part of the universe which is not a system.
- For example: – If we consider a hot coffee in a kettle then the kettle is the system and everything else is the surroundings.
- System and surroundings constitute Universe.


Types of Systems
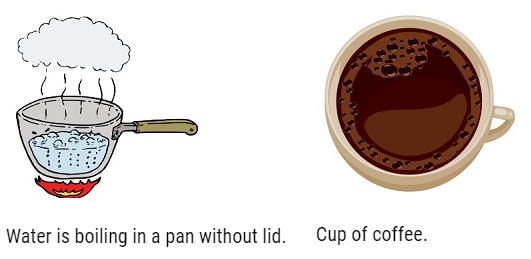
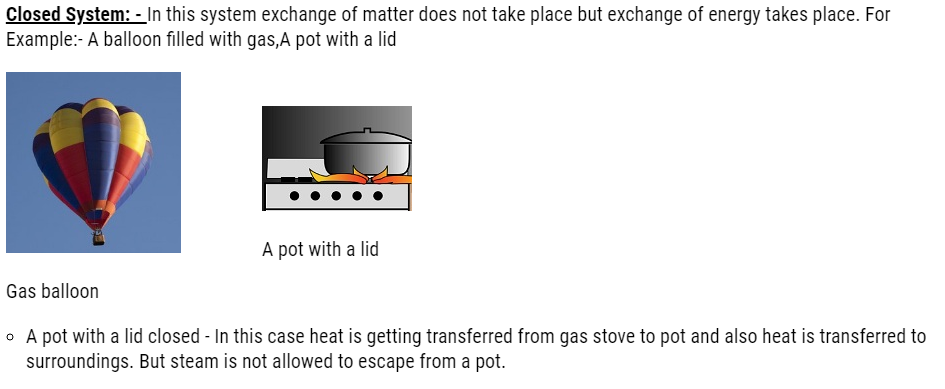
- Open System: – In this system there is exchange of energy and matter. For Example: – Water boils in a pan without lid, a cup of coffee.

Types of Walls
- Adiabatic wall: – It is an insulating wall which doesn’t allow heat to flow from one system to another. This means temperature of both the systems won’t change with time.
- Consider 2 systems A and B as shown in the figure, which are separated by adiabatic wall. Let pressure and volume of A be(P1,V1) and B be(P2,V2)
- Both are at the same temperature as there is no change in temperature with time.
- There is no heat flow between A and B as they are separated by an adiabatic wall.
- Both these systems are also separated from the surroundings by adiabatic wall which means there is no flow of heat between A and surroundings and also B and surroundings.

- Diathermic Wall: – It is a conducting wall which allows the flow of heat between any 2 systems.
- Consider two systems A and B which are separated by a conducting wall. System A is at higher temperature T1 , pressure P1 and volume V1 and System B is at lower temperature T2 , pressure P2 and volume V2.
- There is flow of heat from a system at a higher temperature to the system at a lower temperature till the systems reach thermal equilibrium.
- For Example: – A vessel made up of metals like copper or aluminium has diathermic walls.

