Question 1. What is meant by equilibrium?
Answer: Equilibrium is a state at which rate of forwarding reaction is equal to the rate of backward reaction.
Question 2. State the law of mass action?
Answer: It states that the rate at which a substance reacts is directly proportional to its molar concentration.
Question 3. What is meant by reaction quotient?
Answer: It is defined as the ratio of the product of molar concentration of products to the product of molar concentration of reactants at any stage of the reaction.
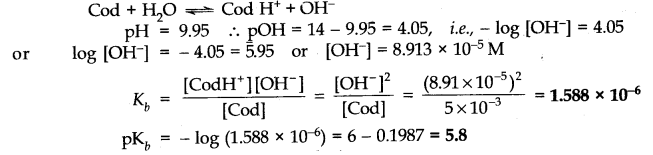
Question 4. Define ionic equilibrium.
Answer: The equilibrium between ions and unionised molecules is called ionic equilibrium.
Question 5. What is meant by ionic product of water (kw)?
Answer: It is the product of concentration of [ H3O+] and [OH–] at a specific temperature.
Kw = [H3O+] [OH–]
= 1.0 x 10-14 at 298 K
Question 6. Define solubility product.
Answer: It is product of molar concentration of ion raised to the power of number of ions produced per compound in saturated solution.
Question 7. How does common ion affect the solubility of electrolyte?
Answer: Solubility of electrolyte decreases due to common ion effect.
Question 8. Write conjugate add and conjugate base of H2O?
Answer: Conjugate acid is H3O+ and conjugate base is OH–.
Question 9. Give two characteristics of a buffer solution.
Answer:
- Its pH does not change on the addition of small amount of acid or base.
- Its pH does not change on dilution or standing.




Question 4. In the reaction A + B———> C + D, what will happen to the equilibrium if concentration of A is increased?
(b) The equilibrium constant for a reaction is 2 x 10-23 at 25°C and 2 x 10-2 at 50°C. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic?
(c) Mention at least three ways by which the concentration of S03 can be increased in the following reaction in a state of equilibrium.
Answer: (a) The reaction will shift in the forward direction.
(b) Endothermic
(c) (i) lowering the temperature (ii) increasing pressure.
(iii) increasing concentration of oxygen.
Question 5. (i) Define Le Chatelier’s principle.
(ii) Following reactions occur in a Blast furnace.
Fe203(s) + 3CO(g) ———–>2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g)
use Le chatelier’s principle to predict the direction of reaction when equilibrium mixture is disturbed by
(a) adding Fe203 (b) removing CO2 .
(c) removing CO.
Answer: (a) When a system under equilibrium is subjected to a change in temperature, pressure or concentration, then the equilibrium shifts in such a direction so as to undo the effect of the change.
(ii) (a) On adding Fe203(s), the equilibrium will remain unaffected.
(b) By removing CO2 (g), the equilibrium will be shifted in the forward direction.
(c) By removing CO(g), the equilibrium will be shifted in the backward direction.