NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is meant by electrochemical series? What are characteristics of electrochemical series?
Answer: Electrochemical series is the series of elements in which elements are arranged in decreasing order of their reduction potential.
Reducing power goes on increasing whereas oxidising power goes on dcreasing down the series.
Question 2. What is standard hydrogen electrode? For what purpose it is used? What are signs of oxidation potential and reduction potential decided by using SHE (Standard hydrogen electrode)?
Answer: Standard hydrogen electrode is used as reference electrode. Its electrode potential is taken as 0.000 volt. Hydrogen electrode can be made. If we use a piece of platinum coated with finely divided black containing hydrogen gas absorbed in it. Platinum black catalyses the reaction and equilibrium is attained faster. When the given electrode acts as anode SHE, we give -ve sign to its reduction potential and +ve sign to its oxidation potential.

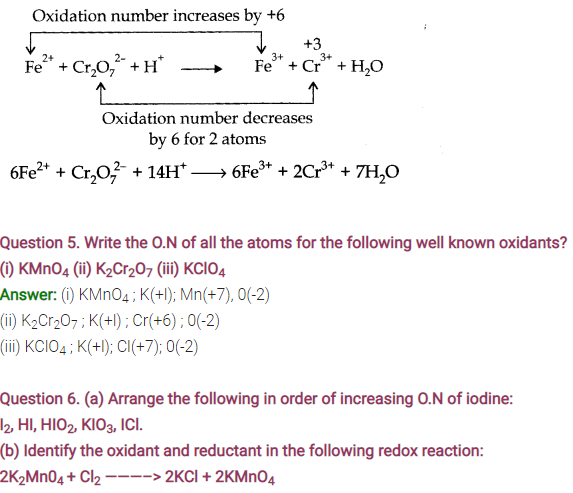



Answer: (a) Ag+ is reduced, C6H6O2 is oxidised.Ag+ is oxidising agent whereas C6H6O2 is reducing agent.
(b) HCHO is oxidised, Ag+ is reduced.Ag+ is oxidising agent whereas HCHO is reducing agent.
(c) N2H4is getting oxidised it is reducing agent. H2O2 is getting reduced it acts as an oxidising agent.
Question 10. (a) Calculate the oxidation number of
(i) C in CH3COOH (ii) S in S2O8-2
(b) Give one example of disproportionation reaction.
Answer:
