About Lesson
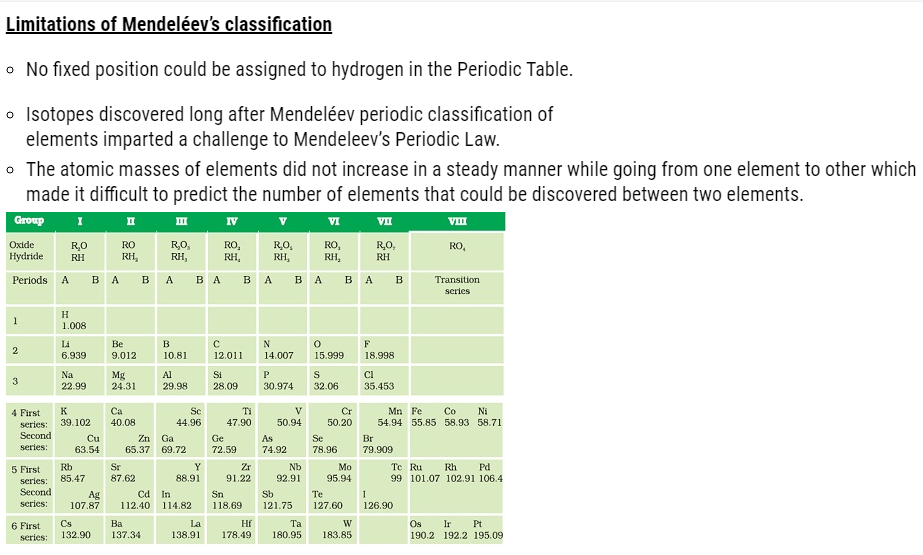
Mendeléev’s periodic table ( Classification of Elements )
- In Mendeléev’s periodic table only 63 elements were arranged that were examined on the basis of the relationship between the atomic masses of elements
and their physical and chemical properties. - Hydrogen and oxygen were selected due to their high reactivity and formation of compounds with most elements giving rise to hydrides and oxides that were treated as one of the basic properties of an element.
- Properties of 63 elements were written on 63 cards and then the elements with similar properties were sorted.
- Most of the elements were arranged in the order of their increasing atomic masses in the Periodic Table with the occurrence of periodic recurrence of elements with similar physical and chemical properties.
- As per the arrangement of elements Mendeléev formulated a Periodic Law stated as ‘the properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic masses’.
- The Periodic Table consists of vertical columns termed as ‘groups’ and horizontal rows termed as ‘periods’.
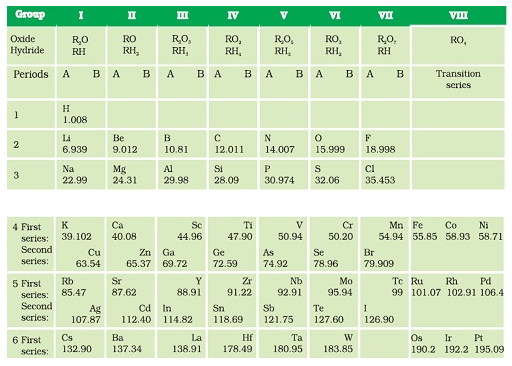
Achievements of Mendeléev’s periodic table ( Classification of Elements )
- element with a slightly greater atomic mass were placed
before an element with a slightly lower atomic mass with an inverted sequence so as to group the elements with similar properties. For example, cobalt with atomic mass 58.9 was placed before nickel with atomic mass 58.7. - He left some gaps in the Periodic Table with the prediction of
existence of some elements that were not discovered at that time. - He named the future elements by prefixing a Sanskrit numeral, Eka (one) to the name of preceding element in the same group.
- For instance, scandium, gallium and germanium, discovered later, have properties
similar to Eka–boron, Eka–aluminium and Eka–silicon, respectively. - Noble gases like helium (He), neon (Ne) and argon (Ar) were discovered
later as they are present in exceptionally low concentrations in the atmosphere due to their inertness.