Alkenes
They are the hydrocarbons with C = C (double bond) with one bond and other π bond.
- Their General formula Cn H2n
- They are oil like – called olefins.
- They are reactive due to π bond and common reaction they undergo in addition Reaction.
- The lowest member of alkenes is ethene (C2H4).
- The structure of alkene is:
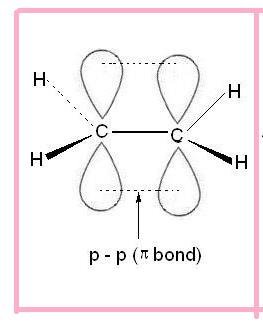
Nomenclature: Primary suffix + ene
CH2 = CH2 CH3 – CH = CH2 CH3 CH = CH – CH3
Ethene Propene But-2-ene
CH2 = CH – CH = CH2
But – 1 , 3 – diene
ISOMERISM: There are two types of isomerism.
- Structural isomerism
- Stereoisomerism
The structural isomerism shown by them are :
- Chain
- Position
Chain: CH3 CH2 CH2 CH = CH2 (pentene)
CH3 – C – CH = CH2 (3-methyl butene)
CH3
- Position: CH3 CH2 – CH2 – CH = CH2
Pentene
CH3 – CH2 – CH – CH – CH3
Stereoisomerism
Geometrical Isomerism – The spatial arrangement of atoms is going to be different in it.
It is caused due to restricted rotation about C = C bond .
Condition Required to show this geometrical isomerism :
- Presence of double
- Both atom attached to C should be different.

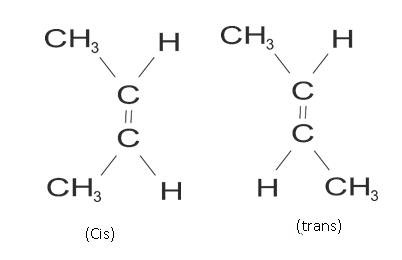
Example: but-2 ene
CH3 CH = CH – CH3
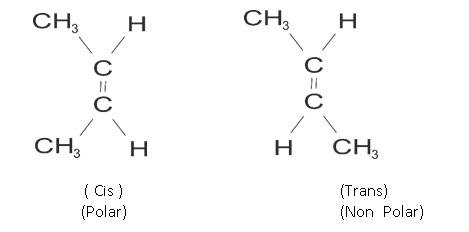
The cis and trans have some chemical properties but different physical properties as arrangement of atoms is different. Like cis is more polar than trans.
(Cis) but 2 ene Trans but-2 ene
Dipole moment = 0.35D Dipole moment is zero
Please note
- Because of different polarites the Cis have higher values of boiling point than Trans.
- Trans will have higher melting point whereas Cis will have lower melting point.
- Trans has symmetrical structure and will fit better in crystal lattice.
- Stability of trans isomer is more than Cis as Cis itself suffer steric hindrence .
If all 4 groups attached are different then we have E and Z system of configuration. In this numbering is done according to masses instead of cis and trans ,we have Z= zussmen form E= entgagen form.

Stability of Alkenes
It is explained on the basis of amount of energy evolved when 1 mole of alkene is hydrogenated
CH2 = CH2 + H2 -> CH3 – CH3 change in energy(H) = -ve
Ethene hydrogen ethane
Example: In cis butene and trans butene, the energy difference is 5kJ/mol, as cis has energy 20kJ/mol and trans has energy 115kJ/mol. Therefore, both on hydrogenation forms butane CH3 CH2CH2CH3.

Trans isomer is more stable as initially it is at lower energy.So, We can say that trans is 5KJ more stable than the Cis isomer.
Please keep in mind :“ More alkylated alkenes are more stable”
Due to hyperconjugation, max conjugated structures are formed and more it is stable as shown below :

Preparation of Alkenes
- From alkyl halides: (RX) by the process of dehydrohalogenation, it is also called Beta elimination .
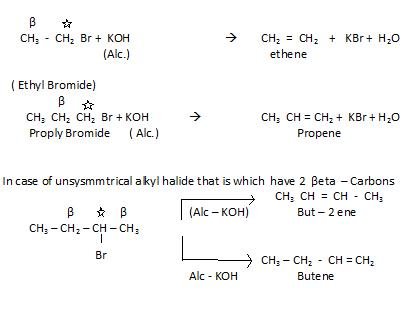
In this case it has two beta carbons so, we make use of special rule that is Saytzeff’s rule.
Saytzeff’s rule: In case of reacting alcoholic KOH with unsymmtrical halide , that
alkene is preffered which is maximum alkylated. So , in above example But – 2 – ene is preferred .
If we see ease of elemination the order is :
I > Br > Cl > F
The better the leaving group more easily the reaction occurs .The reactivity of alkanes towards this reaction is : tertiary > secondary > primary
2.From dihalogen derivatives
Let us take an example of Vicinal dihalide that is :
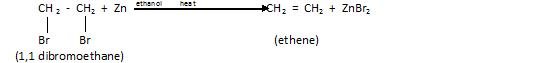
In this renewal of halogen is taking place therefore the process is called dehalogenation .
3. From alkynes : by the process hydrogenation.The reaction involved is given below:

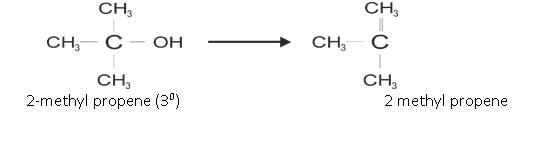
- From Alcohols :
It is prepared by Dehyration Reaction of alcohols.

The ease of Reaction is: 30> 20> 10
Another example is:
- Kolbe’s electrolytic reduction
In this electric current is passed through potassium salt of carboxylic acid and we get alkene as shown below.
Physical Properties Of alkenes
- Existence: Lower members are colourless (Ethene is with sweet smell and other alkenes are odourless).
- C5 to C18 are
- > C18 are
- Melting Point: – Alkenes have higher melting point than alkanes because π e– cloud will be more polarized. If we compare melting point of Cis and Trans then, Trans possess high melting point then Cis because Trans have symmetrical structure so, they fit better in lattice.
- Boiling Point: They show regular graduation.
- With increase in Carbon atoms, Vander wall force increases so, boiling point also increases.
- Boiling point decreases with increase in branching. As surface area reduces vander wall force decreases, therefore boiling point also decrease.
- Out of cis and trans, trans has low boiling point and cis possess high boiling point due to polarity.
- Dipole moment: Cis have certain dipole moment, but Trans have zero dipole moment as both the dipoles are in opposite direction therefore, they cancel each other effect.

In unsymmetrical Trans µ ≠ O it will have certain value due to difference in the type of groups attached.
- Solubility: – Alkenes have greater solubility then alkanes.
- Solubility increase with increase in C atoms.
- Lower members are sparingly soluble but soluble in organic solvents like Benzene, ether, Carbon tetra chloride etc.