Entropy: is “measure if degree of randomness.”It is denoted by S, it is a state function and extensive property.
∆S = ∆Sp – ∆Sr
In term of energy it is given as:
∆S = (qrev/t)
How s & q related?
When q increases, kinetic energy increase, randomness increases, entropy also increase.
How S&T related?
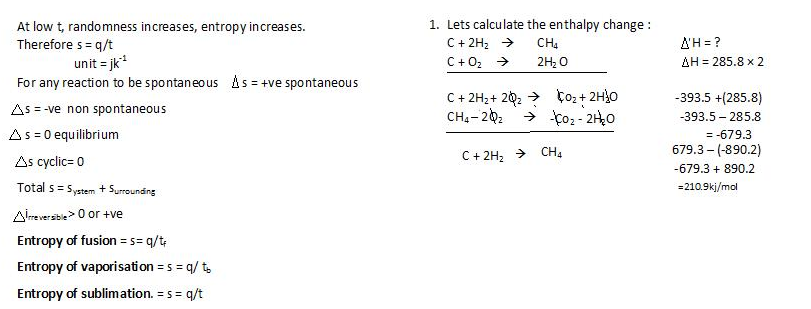
Second law of thermodynamics
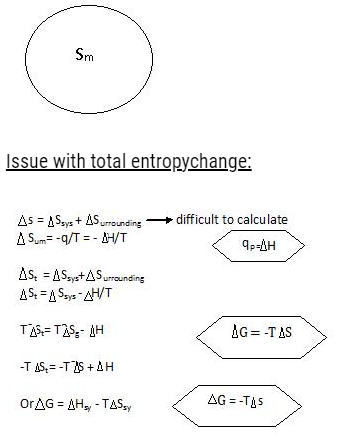
To determine spontaneous, total entropy is needed.
∆S >0 = spontaneous
∆S = 0 Equilibrium
∆S < 0 Non-Spontaneous
Stotal = Ssystem + SSurroundings
∆Ssys depends on the following:-
Absolute entropy depends upon
- Mass
- Molecular structure
- Temperature &pressure
Standard molar entropy:
It is the entropy for 1 mole of substance at 298k & 1 atm.
It is represented as:
Gibbs free energy
- It is denoted by G
- It is given by G = H – TS
- It is state function
- Extensive property
- ∆G = ∆H – T∆S ( at constant t)
It is defined as the amount of energy for a system that can be converted into useful work.
∆G = (-ve) spontaneous
∆G = 0 Equilibrium
∆G = (+ve) Non-Spontaneous
Spontaneity in terms of free energy change:
We know
∆G = ∆H – T∆S
This equation takes into account both the concepts (a) energy factor and other (b) entropy factor
Depending upon the signs of h and t.s. and their relative magnitudes the following possibilities arise:
- When both H and T.S are negative: Energy factor favours and randomness oppose then: if H <T.S(non-spontaneous), G=negative
- When both H = T.S the process is in equilibrium and G =0
- when both H and T.S are positive: Energy factor opposes and randomness favours then:
- If H >T. S process is non spontaneous, G =+ve
- If H<T.S process is spontaneous, G= -ve
- If H=T.S the process is in equilibrium, G=0
- When H = -ve and T.S =+ve, process is spontaneous and G= -ve
- When H = +ve and T.S =-ve, process is non spontaneous and G= +ve
Effect of temperature on spontaneity of process
Endothermic process à high t-> spontaneous
Exothermic process à low t-> spontaneous
Third law of thermodynamics:
- At absolute zero, the entropy of perfect crystalline is o.
- Please note there are certain substances which possess certain entropy even at absolute zero. This entropy is also known as residual entropy.
- The origin of residual entropy can be explained on the basis of the disorder which remains at absolute zero in certain crystals composed of ab types of molecules where a and b are similar atoms .
- There is little energy difference between ab—ab—ab and ab –ba—ba –ab and other arrangements so that the molecules adopt the orientation ab and ba at random in solid .this give rise to residual entropy .