Chapter 12 – Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles & Techniques Part- 1 | Class 11th Chemistry
Chapter 12 – Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles & Techniques Part- 2 | Class 11th Chemistry
Chapter 12 – Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles & Techniques Part- 3 | Class 11th Chemistry
Introduction ( Organic Chemistry )
As we know, we come across different types of compounds in nature. Some are man-made. Out of them, organic compounds also form one of the categories.
COMPOUNDS
They are of mainly two types
- Inorganic: Obtained from Mineral.
(b) Organic: Obtained from plants and animal.
Organic compounds
- They play a vital role in our life.
- They constitute our body, our diet, our medicine etc.
- Earlier, it was thought the has made organic compounds are not possible.
- Later, it was seen that preparation of these compounds are possible. Almost 95% of organic compound are manmade (prepared in laboratory).
Friedrich Wohler: -He gave a blow to vital force theory, as he accidently prepared organic compound in laboratory: –

Unique properties of carbon
- TETRAVALENCY
It is a characteristic property of Carbon atom by virtue of which it can form four covalent bonds.
Atomic Number =6
1s2, 2s2,2px1,2py2,2pz0
Valency =+4 or -4
It mainly forms covalent compounds.
- CATENATION
“The property of forming bonds with atoms of same element and give rise to long chains, branched or un-branched chains.”
In 14th group the Carbon –Carbon bond requires bond dissociation energy equal to 335 KJ. The Sulphur –Sulphur bond requires energy in order of 220kJ.But, the maximum catenation is shown by carbon as it forms strong bond with atom of its own kind.
IMPORTANT FEATURE OF π BONDS
- In C2H4 , the two un-hybridized orbital forming bond are parallel to each other. So, they restrict the molecule in planar shape.
- Because of sidewise overlapping, rotation of one CH2 group with respect to other is hindered, as rotation will break bond. Therefore, only 2 forms are possible.
- For example: C2H2Cl2

(pi) bonds are more reactive sites, as they are placed above and below the plane of bonding atoms. So, more exposed to attacking agent.
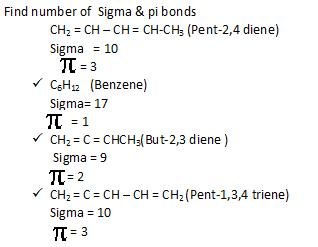
Find

Problem 1:-
Q: Rewrite as bond line :
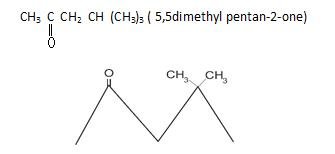
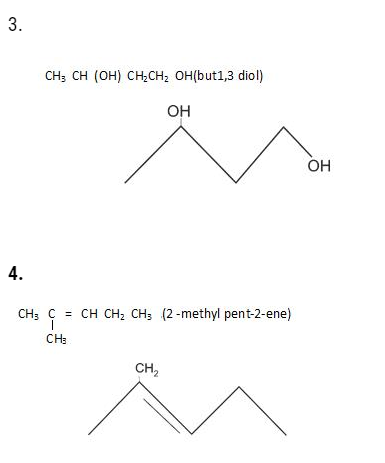
1.
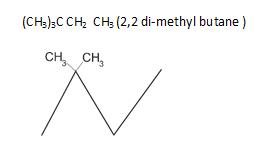
2.