ISOMERISM
It is existence of compounds in two or more forms, having same molecular formula but different physical and chemical properties.
It is basically of two types:
- Structural
- Stereoisomerism
Structural isomerism: Differ in arrangement of atoms within molecule.
Stereoisomerism: Differ in arrangement of atom in space.
The structural isomerism type:
- Chain
- Position
- Functional
- Meta-merism
- Tauto-merism
The different types of stereoisomerism are:
- Geometrical
- Optical
- conformational
Let us study first structural isomerism types :
- Chain isomerism– The compounds that have same molecular formula ,but different arrangement of atoms within the chain.

Position isomerism: The compounds with same molecular formula, but differ in position of substituent, side chain or functional groups.
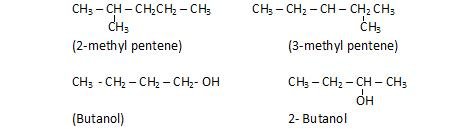
Functional isomerism: The compounds with same molecular formula but differ in type of functional group and also in physical and chemical properties.
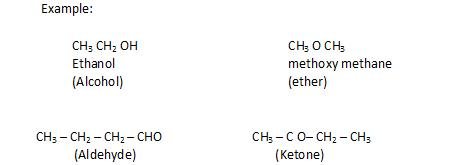
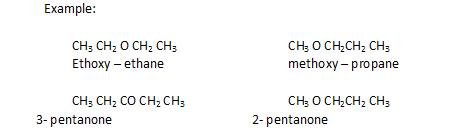
- Metamerism: The compounds that have same molecular formula ,but differ in number of carbon atoms around functional group.
It is shown by functional groups like ether, esters, ketones.
- Tautomerism: In this simultaneous movement of π electron cloud and Hydrogen take place. Most common tautomerism is keto – enol tautomerism.
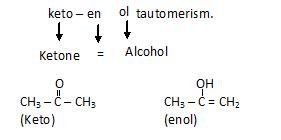
let us study stereo isomerism now
In it the compounds have same molecular formula , but different arrangement of atoms in three-dimensional space.
It is of three types:
- Geometrical : It arises due to restricted rotation around C=C bond.
Conditions required are :
- Presence of C=C bond.
- The two groups attached to carbon atoms must be different.

Examples:
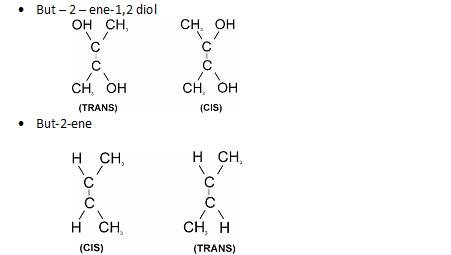

- As far as stability is concerned, more bulky is the group, more is the Stearic hindrance.
- Stearic hindrance which creates obstruction in rotation therefore, less is the stability.
But-2-ene> Pent-2-ene-Hex>3-ene
CONFORMATIONAL ISOMERISM: It exists in Alkanes (C-C). It is due to full rotation around C-C single bond.