Polarity & Dipole moment
In homo-atomic molecules having same type of atoms are present .In them sharing of electrons occur the shared pair remain in the middle that is equal attraction by atoms towards shared pair.
- The hetro-atomic molecules (having different types of atoms in them) when sharing of electrons occur the shared pair do not lie in middle, it gets displaced towards more electronegative atom.
- So, it will acquire partial negative charge and other atom will acquire partial positive charge. Due to this the poles are developed and the bond formed is polar covalent bond.
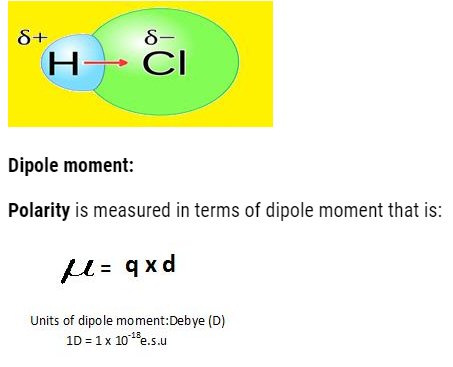
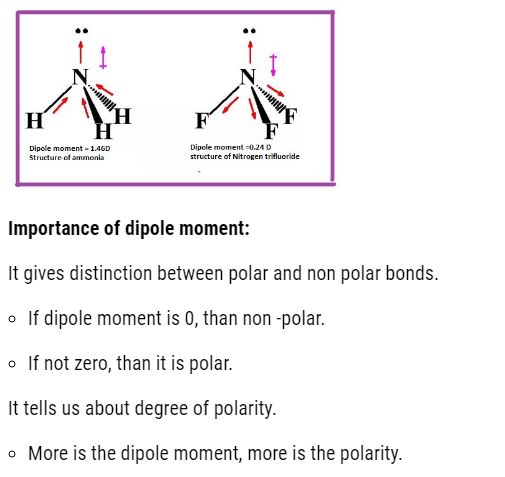
Let us calculate the dipole moment of different molecules with different atomicity. Dipole moment tells us about the structure of molecule.
- If dipole moment is zero, than the molecule is non polar.
- If dipole moment is not zero, than the polar molecule.
Dipole moment and molecular structure
Let us consider:
- Diatomic molecule: Its structure is generally linear.
Example:- In HCl, dipole moment is : 1.07 D
In HBr, dipole moment is : 1.78 D
In Hl, dipole moment is : 0.79 D



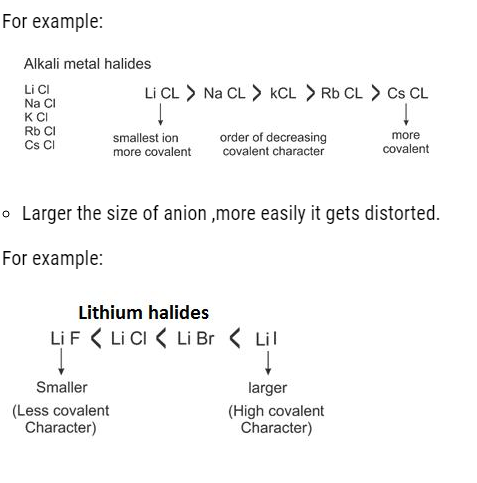
- More is the magnitude of charge: More is the covalent character.
For Example:- NaCl< CaCl2 < AlCl3
(Maximum covalent character in aluminium chloride)
- Electronic configuration of cation: Cation with 18 electrons in its outermost shell can cause more distortion.
For Example:- Na+ = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6
Cu+ = 1s2,2s2,2p6,3s2,3p6,4s1,3d10
Out of NaCl and CuCl, the latter has more covalent character.