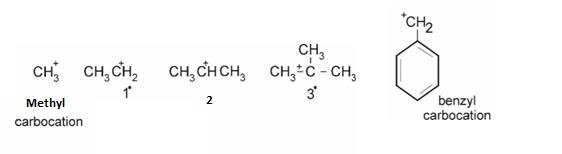
Types of Carbocations :

Stability can be explained on the basis of +I effect –More the alkyl groups , more they release electrons and more the positive charge gets neutralized .Hence, more is the stability.

Carboanion
- They are Carbon with 8 e-.
- They are Electron rich.
- They act as Lewis base.
- They are Formed as a result of heterolytic fission.

Types of Carboanions:

- More the alkyl group,more they release electrons and more intense the charge becomes.Hence, least will be the stability.
Attacking agents
When the reaction occurs, attacking agent attacks and the product is formed.
Type of attacking agents: They can be
- Free radical : With unpaired electron
- Nucleophile: With extra electrons. They also act as Lewis base and does Nucleus love. They are either:
Neutral with Lone pair: H2O , NH3 , NH2 , R – O – H , R – O – R
Negatively Charged: CN– , X– , OH–
- Electrophile: With Positive charge has less electrons and act as Lewis acids. They are either :
Neutral: BF3 , BCl3 , AlCl3 etc .
Positively charged: NH4+ , NO2+ , H3 O+ etc .

Attacking agents
When the reaction occurs, attacking agent attacks and the product is formed.
Type of attacking agents: They can be
- Free radical : With unpaired electron
- Nucleophile: With extra electrons. They also act as Lewis base and does Nucleus love. They are either:
Neutral with Lone pair: H2O , NH3 , NH2 , R – O – H , R – O – R
Negatively Charged: CN– , X– , OH–
- Electrophile: With Positive charge has less electrons and act as Lewis acids. They are either :
Neutral: BF3 , BCl3 , AlCl3 etc .
Positively charged: NH4+ , NO2+ , H3 O+ etc .