Water
It covers 71% of earth surface but its distribution is not uniform.
That is:- 97.33% Oceans, 2% Polar ice caps and 1% remaining H2O
Physical properties
- It is tasteless and odourless liquid.
- It freezes to ice at 273K.
- Its boiling point is 373K.
- Its density is — 1g / cc.
It has Hydrogen bonding due to this it exist as associated molecules. Thereforeit has high freezing Point , high boiling point and high Heat of vaporisation.That is why, the order for decrease of these properties is such :
H2O(water) > H2S(hydrogen sulpide) >H2Se(selenium hydride).
- It has high thermal conductivity , dipole moment , dilectric constant and high specific heat value.
- It is an excellent solvent.
- The structure of water is given below :

Chemical properties
- Reaction with metal : It reacts with metal to form hydroxides and hydrogen gas is released.
Na + H2O –> NaOH + H2
Sodium Water Sodium Hydroxide Hydrogen Gas
- Water is amphoteric in nature ,so reacts with acid as well as with base as shown below :


Hardness of water
Types of water :We have two types of water:
- Hard : Forms No lather with soap .
Example : : River water ,sea water etc .
- Soft : Forms lather with soap .
Example : Rain water
Hardness of water
It is due to the presence of Calcium and Magnessium ( Ca2+ and Mg2+ )salts in water . The water with these salts is called as hard water.
The salts basicaly are Magnessium bicarbonates ,sulphates and chlorides or Calcium bicarbonates ,sulphates and chlorides.
Hard water actually contain Calcium and magnessium salts that react with soap to form insoluble precipitate called scum. It sticks to the cloth .
Therefore ,it cant be used for laundry purpose .
In Laundry: The Soap used is sodium sterate.
Sodium sterate + M2+ à (C17H35 – COO)2 M + 2Na+
Scum
Due to formation of scum lather is not produced with soap.
There are two types of hardness :
- Temporary: It is due to soluble Ca(HCO3)2 and Mg (HCO3)2 (calcium and magnessium bicarbonates) .
- Permanent: It is due to soluble Mg and Ca chlorides and sulphides .
Methods to remove hardness
Temporary hardness : It can be removed by following methods :
- Boiling
- Clarks method
- Boiling : In this when we boil hard water, bicarbonates are convereted into hydroxides and calcium bicarbonate is converted into carbonates. These precipitates are filtered and thus, hardness is removed .
- Clark’s method: In this method calculated amount of lime is added that precipitates Calcium and Magnessium carbonates .

- Ion – exchange method
In this a substance called zeolite or permutit is added. This zeolite exchange Sodium with Calcium and Magnessium ions of hard water .
Example of permutit are many like :hydrated Sodium Aluminium Silicates (Na2Al2Si2O8.xH2O)commonly can be indicated as NaZ .
The apparatus is set as shown :

Procedure :
- The zeolite is loosely packed over layers of gravel and sand in big tank .
- Hard water is introduced from top into the base of tank.
- From the bottom water rises up through gravel and sand layers.
- Finally it percolates through the bed of permutit.
- During this the ions are exchanged .
- So ,the water above the permutit layer is generally soft water .
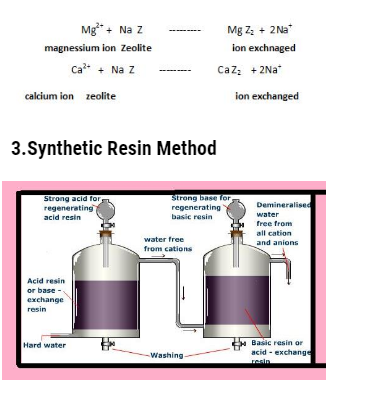
Synthetic resin methods are more superior then the ion exchange method as they remove all types of cations and anions and the resultant water is distilled water .
These resins are generally of two types :
- Cation exchange resin
- Anion exchnage resin
Cation exchange resin : It consist of giant hydrocarbon framework attached to basic groups . They are represented by general formula R-COOH or R-SO3H .In this R is giant hydrocarbon .These resins can exchange H+ ions with cations present in hard water .
Anion exchange resin : It consist of giant hydrocarbon frmaework attached to basic groups like OH– ions, usually in the form of subsituted ammonium hydroxides. They are represented as R-NH3OH– where R denotes giant hydrocarbon framework .These resins can exchange hydroxide ion with anions like chloride ions and sulfate ions present in hard water
